rec07
... • < 43% C+G : 62% of genome, 34% of genes • >57% C+G : 3-5% of genome, 28% of genes • Gene density in C+G rich regions is 5 times higher than moderate C+G regions and 10 times ...
... • < 43% C+G : 62% of genome, 34% of genes • >57% C+G : 3-5% of genome, 28% of genes • Gene density in C+G rich regions is 5 times higher than moderate C+G regions and 10 times ...
Arabidopsis thaliana
... 13. In addition to the usual several hundred genes of mitochondrial origin, Arabidopsis has about 800 with best protein matches to proteins of the photosynthetic cyanobacterium Synchocystis, presumably resulting from transfer from the chloroplast to the nuclear genome. So this is another component ...
... 13. In addition to the usual several hundred genes of mitochondrial origin, Arabidopsis has about 800 with best protein matches to proteins of the photosynthetic cyanobacterium Synchocystis, presumably resulting from transfer from the chloroplast to the nuclear genome. So this is another component ...
Genes and Variation
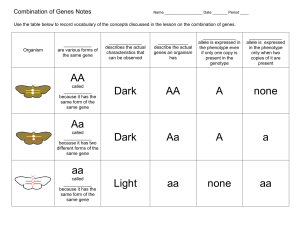
... Many genes have more than one form or alleles - Examples? There is also additional variation that is “invisible” because it involves small variations in biochemical processes ...
... Many genes have more than one form or alleles - Examples? There is also additional variation that is “invisible” because it involves small variations in biochemical processes ...
Epistasis is not dominance.
... The heterozygote expresses both traits at the same time. In this example, the heterozygous chickens are speckled. They express both feather colors at the same time. ...
... The heterozygote expresses both traits at the same time. In this example, the heterozygous chickens are speckled. They express both feather colors at the same time. ...
gene therapy - Thalassemia.com
... Chemotherapy is given to make room for the modified stem cells. The modified stem cells are then transplanted back into the body. ...
... Chemotherapy is given to make room for the modified stem cells. The modified stem cells are then transplanted back into the body. ...
Chromosome vs. Gene Mutations
... • Are due to a change in a single gene. • Can involve changes in several nucleotides ...
... • Are due to a change in a single gene. • Can involve changes in several nucleotides ...
Lab 11: Simple genomic data analysis using R 1. UCSC genome
... Select “Table Browser” under the “Tool” menu. In the table browser page, select: “Mammal” under clade, “Human” under genome, “Mar. 2006 (NCBI36/hg18)” assembly, “Genes and Gene Prediction” under group, “RefSeq Genes” under track, “refGene” under table. Then select “genome” under region, which means: ...
... Select “Table Browser” under the “Tool” menu. In the table browser page, select: “Mammal” under clade, “Human” under genome, “Mar. 2006 (NCBI36/hg18)” assembly, “Genes and Gene Prediction” under group, “RefSeq Genes” under track, “refGene” under table. Then select “genome” under region, which means: ...
What Is Gene cloning and How Is It Used? 1. Explain what is meant
... Define the term "restriction enzymes" and explain how they are used to insert genes into a vector. ...
... Define the term "restriction enzymes" and explain how they are used to insert genes into a vector. ...
What Is Gene cloning and How Is It Used? 1. Explain what is meant
... Define the term "restriction enzymes" and explain how they are used to insert genes into a vector. ...
... Define the term "restriction enzymes" and explain how they are used to insert genes into a vector. ...
Introduction to databases
... pattern results in terms of predicted function. Explain why these small motifs are so evolutionarily conserved that they can be used to predict what a protein’s function is? ...
... pattern results in terms of predicted function. Explain why these small motifs are so evolutionarily conserved that they can be used to predict what a protein’s function is? ...
Red Line - iPlant Pods
... – 19 students used Red Line to visualize next-gen RNA-Seq data to investigate presence/absence variation (PAV) in maize – 12 hours effort, each student group annotated 100 kb and then imported next-gen RNA-Seq data from 5 different tissues in 30 maize inbred lines for a gene that they had previously ...
... – 19 students used Red Line to visualize next-gen RNA-Seq data to investigate presence/absence variation (PAV) in maize – 12 hours effort, each student group annotated 100 kb and then imported next-gen RNA-Seq data from 5 different tissues in 30 maize inbred lines for a gene that they had previously ...
families and function.pptx
... – Create a model of evolu0on of func0on for every gene family • Annota0on of a tree node means “this func0on evolved on the branch prior to this node” • A NOT annota0on of a tree node means ...
... – Create a model of evolu0on of func0on for every gene family • Annota0on of a tree node means “this func0on evolved on the branch prior to this node” • A NOT annota0on of a tree node means ...
Document
... Phylogenetic analysis of gene families in Populus, Arabidopsis, and Oryza encoding selected lignin biosynthetic and related enzymes. (A) Cinnamate-4-hydroxylase (C4H) gene family. (B) 4-coumaroylshikimate/quinate-3-hydroxlase (C3H) gene family. (C) Cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD) and related m ...
... Phylogenetic analysis of gene families in Populus, Arabidopsis, and Oryza encoding selected lignin biosynthetic and related enzymes. (A) Cinnamate-4-hydroxylase (C4H) gene family. (B) 4-coumaroylshikimate/quinate-3-hydroxlase (C3H) gene family. (C) Cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD) and related m ...
A1981MD68300002
... after operon, only to discover that a single eukaryotic gene may, in some instances, be as large and complex as several operons or even an entire viral chromosome. "I believe this paper is frequently cited because it reported one of the most direct measures of gene size and number in a eukaryote. It ...
... after operon, only to discover that a single eukaryotic gene may, in some instances, be as large and complex as several operons or even an entire viral chromosome. "I believe this paper is frequently cited because it reported one of the most direct measures of gene size and number in a eukaryote. It ...
Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium and Evolution
... individuals that make up a population – think of the gene pool as the reservoir from which the next generation draws its genes – the population's gene pool is where genetic variation—the raw material of evolution—is stored ...
... individuals that make up a population – think of the gene pool as the reservoir from which the next generation draws its genes – the population's gene pool is where genetic variation—the raw material of evolution—is stored ...
comp - Imtech - Institute of Microbial Technology
... Figure 1 Regions of the human and mouse homologous genes: Coding exons (white), noncoding exons (gray}, introns (dark gray), and intergenic regions (black). Corresponding strong (white) and weak (gray) alignment regions of GLASS are shown connected with arrows. Dark lines connecting the alignment r ...
... Figure 1 Regions of the human and mouse homologous genes: Coding exons (white), noncoding exons (gray}, introns (dark gray), and intergenic regions (black). Corresponding strong (white) and weak (gray) alignment regions of GLASS are shown connected with arrows. Dark lines connecting the alignment r ...
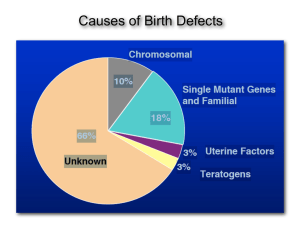
Causes of Birth Defects
... pleiotropy: refers to the multiple structures effected by one gene or one mutant gene. Haploinsufficiency occurs when a diploid organism only has a single functional copy of a gene (with the other copy inactivated by mutation) and the single functional copy of the gene does not produce enough of a g ...
... pleiotropy: refers to the multiple structures effected by one gene or one mutant gene. Haploinsufficiency occurs when a diploid organism only has a single functional copy of a gene (with the other copy inactivated by mutation) and the single functional copy of the gene does not produce enough of a g ...
How do we determine a genes function?
... These roles are not concrete without experimental data For Example:the NEW protein is a kinase (based on sequence) but without showing that the kinase domain is necessary for function this is not confirmed. How would this be possible using the techniques we have available? ...
... These roles are not concrete without experimental data For Example:the NEW protein is a kinase (based on sequence) but without showing that the kinase domain is necessary for function this is not confirmed. How would this be possible using the techniques we have available? ...
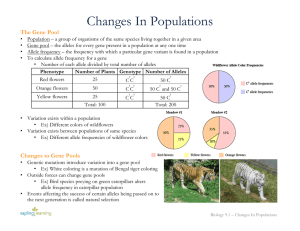
Changes In Populations
... Changes to Gene Pools • Genetic mutations introduce variation into a gene pool • Ex) White coloring is a mutation of Bengal tiger coloring • Outside forces can change gene pools • Ex) Bird species preying on green caterpillars alters allele frequency in caterpillar population • Events affecting the ...
... Changes to Gene Pools • Genetic mutations introduce variation into a gene pool • Ex) White coloring is a mutation of Bengal tiger coloring • Outside forces can change gene pools • Ex) Bird species preying on green caterpillars alters allele frequency in caterpillar population • Events affecting the ...
Heredity and Genetics Vocabulary
... 1. Cut the chart apart completely by cutting on all lines. 2. Have your child mix up the cards and try to match the correct definition with the correct vocabulary term. (A second chart can be printed to act as a key) ...
... 1. Cut the chart apart completely by cutting on all lines. 2. Have your child mix up the cards and try to match the correct definition with the correct vocabulary term. (A second chart can be printed to act as a key) ...
Copy-number variation

Copy-number variations (CNVs)—a form of structural variation—are alterations of the DNA of a genome that results in the cell having an abnormal or, for certain genes, a normal variation in the number of copies of one or more sections of the DNA. CNVs correspond to relatively large regions of the genome that have been deleted (fewer than the normal number) or duplicated (more than the normal number) on certain chromosomes. For example, the chromosome that normally has sections in order as A-B-C-D might instead have sections A-B-C-C-D (a duplication of ""C"") or A-B-D (a deletion of ""C"").This variation accounts for roughly 13% of human genomic DNA and each variation may range from about one kilobase (1,000 nucleotide bases) to several megabases in size. CNVs contrast with single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which affect only one single nucleotide base.