Lecture 5-Variation
... Importance of genetic variations in evolution • Mutations are usually lethal so that they are naturally removed from a population. • Recombination (and crossing over) alone will generate a large number of variations • They only mix characters. A large number variants with slight changes are produce ...
... Importance of genetic variations in evolution • Mutations are usually lethal so that they are naturally removed from a population. • Recombination (and crossing over) alone will generate a large number of variations • They only mix characters. A large number variants with slight changes are produce ...
... accepted in many forms of biology and medicine. Among these is real time-PCR (RT-PCR) or quantitative PCR (qPCR). Technology advances in qPCR have realised its potential in many applications including allelic discrimination, gene expression, forensic science, analysis of chromosome aberrations and p ...
Diapositiva 1
... Gene family must evolve as a block. This model is not able to explain the high diversity. ...
... Gene family must evolve as a block. This model is not able to explain the high diversity. ...
Secrets of Life Video Questions
... 6. Every one of the billion cells in the body contain the same instructions. These instructions are written in 7. the _________________________________. ...
... 6. Every one of the billion cells in the body contain the same instructions. These instructions are written in 7. the _________________________________. ...
the element makes na RNA copy of itself which is reversed
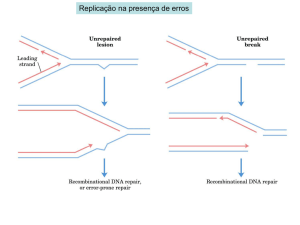
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
Cancer Research Project
... 2. You will research this gene. 3. You will create a 1 page document that answers each of the following questions: ● Is the gene a proto-oncogene, tumor suppressor, DNA repair enzyme, or something else (tell me what it is, don’t just say “something else”)? ● What does the normal (functional) version ...
... 2. You will research this gene. 3. You will create a 1 page document that answers each of the following questions: ● Is the gene a proto-oncogene, tumor suppressor, DNA repair enzyme, or something else (tell me what it is, don’t just say “something else”)? ● What does the normal (functional) version ...
Annelise Mah - New Genomics Technology: Copy Number Variation Analysis Methods
... (Fanciful illustration of oligonucleotide probes with tagged DNA attached, Illumina) ...
... (Fanciful illustration of oligonucleotide probes with tagged DNA attached, Illumina) ...
Biotechnoloy :Guides for Exam 2
... 8. Genetic fingerprinting or DNA testing was invented by Sir Alec Jeffreys at the University of Leicester and was announced in A.1984 B.1986 C.2000 D.1985 9. The virus that causes the common cold is an adenovirus. A. True B. False 10. The-----------is the government organization to approve any human ...
... 8. Genetic fingerprinting or DNA testing was invented by Sir Alec Jeffreys at the University of Leicester and was announced in A.1984 B.1986 C.2000 D.1985 9. The virus that causes the common cold is an adenovirus. A. True B. False 10. The-----------is the government organization to approve any human ...
2007.6. JW
... HERV-M (the human endogenous retrovirus M), related to the super family of HERV-K, has a Whole Genome sequence (Golden Path, hg16) ...
... HERV-M (the human endogenous retrovirus M), related to the super family of HERV-K, has a Whole Genome sequence (Golden Path, hg16) ...
Supplementary Information (doc 33K)
... and 5ng/µl genomic DNA: 2µl). The qPCR thermal cycling conditions were as follows: initiation at 95 °C for 10 minutes for hot start, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 seconds and 60 °C for 1 minute. The PCR efficiency of each assay was extracted from the calibration curves of mixed DNA from thre ...
... and 5ng/µl genomic DNA: 2µl). The qPCR thermal cycling conditions were as follows: initiation at 95 °C for 10 minutes for hot start, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 seconds and 60 °C for 1 minute. The PCR efficiency of each assay was extracted from the calibration curves of mixed DNA from thre ...
Traits: The Puppeteering of Genetics
... Example include height, weight, and skin color, cancer risk, or any trait in which multiple factors come into play (generally quantitative values) ...
... Example include height, weight, and skin color, cancer risk, or any trait in which multiple factors come into play (generally quantitative values) ...
Garland E. Allen, Washington University, St. Louis: "Mechanistic
... sciences in general and biology in particular in the first half of the twentieth century. It provided a highly quantitative way to understand hereditary transmission between generations and evolution in populations, even as it excluded embryonic development from its concerns. It also fit well with a ...
... sciences in general and biology in particular in the first half of the twentieth century. It provided a highly quantitative way to understand hereditary transmission between generations and evolution in populations, even as it excluded embryonic development from its concerns. It also fit well with a ...
Do now - MrSimonPorter
... In what ways are we different from each other (“variations”)? Can you now divide these differences between those that are inherited and those which are environmental and those which might be both. ...
... In what ways are we different from each other (“variations”)? Can you now divide these differences between those that are inherited and those which are environmental and those which might be both. ...
Sexual conflict and imprinting
... The best strategy for mating and rearing offspring is not the same for males and females. As a result, sexual conflicts can evolve, producing traits and behaviors that can seem downright destructive—such as the habit some birds have of abandoning their young (page 285). David Haig and other research ...
... The best strategy for mating and rearing offspring is not the same for males and females. As a result, sexual conflicts can evolve, producing traits and behaviors that can seem downright destructive—such as the habit some birds have of abandoning their young (page 285). David Haig and other research ...
6.4 Manipulating the Genome - Hutchison
... mammals, but plasmid vectors are not. • A cold virus is a good choice to target lung cells but not bone cells. ...
... mammals, but plasmid vectors are not. • A cold virus is a good choice to target lung cells but not bone cells. ...
No Slide Title
... disease in order to understand the basis of disease and be able to diagnose and treat it more effectively. Even with sequence in hand, there are major problems in gene identification and cloning – need knowledge of map position therefore linkage analysis continues to be of major importance – ultimat ...
... disease in order to understand the basis of disease and be able to diagnose and treat it more effectively. Even with sequence in hand, there are major problems in gene identification and cloning – need knowledge of map position therefore linkage analysis continues to be of major importance – ultimat ...
Copy-number variation

Copy-number variations (CNVs)—a form of structural variation—are alterations of the DNA of a genome that results in the cell having an abnormal or, for certain genes, a normal variation in the number of copies of one or more sections of the DNA. CNVs correspond to relatively large regions of the genome that have been deleted (fewer than the normal number) or duplicated (more than the normal number) on certain chromosomes. For example, the chromosome that normally has sections in order as A-B-C-D might instead have sections A-B-C-C-D (a duplication of ""C"") or A-B-D (a deletion of ""C"").This variation accounts for roughly 13% of human genomic DNA and each variation may range from about one kilobase (1,000 nucleotide bases) to several megabases in size. CNVs contrast with single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which affect only one single nucleotide base.