For SNP microarray analysis processed before Oct. 15, 2012
... approximately 1,140,419 probes including both single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) and non-SNP alleles. The test is used to identify chromosomal imbalances throughout the human genome. These imbalances include deletions, duplications and aneuploidy. Microarray testing is not designed to detect bala ...
... approximately 1,140,419 probes including both single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) and non-SNP alleles. The test is used to identify chromosomal imbalances throughout the human genome. These imbalances include deletions, duplications and aneuploidy. Microarray testing is not designed to detect bala ...
handout
... c) Variation in distribution of repeats: regions show either a high repeat density (e.g. chromosome Xp11 – a 525kb region shows 89% repeat density) or a low repeat density (e.g. HOX homeobox gene cluster (<2% repeats), indicative of regulatory elements which have low tolerance for insertions) d) Dis ...
... c) Variation in distribution of repeats: regions show either a high repeat density (e.g. chromosome Xp11 – a 525kb region shows 89% repeat density) or a low repeat density (e.g. HOX homeobox gene cluster (<2% repeats), indicative of regulatory elements which have low tolerance for insertions) d) Dis ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint Slides
... backgrounds working together in teams. As you might guess, software development for genome analysis is a very hot research area in computer science, mathematics, engineering, and biology. Few people can master more than one or two of these areas, so collaborations are common. If you learn both math ...
... backgrounds working together in teams. As you might guess, software development for genome analysis is a very hot research area in computer science, mathematics, engineering, and biology. Few people can master more than one or two of these areas, so collaborations are common. If you learn both math ...
3000-13-3d
... genes to get duplicated, and for the new copy to be rewired for a new job. Snake venom, to pick one example, also evolved common for ...
... genes to get duplicated, and for the new copy to be rewired for a new job. Snake venom, to pick one example, also evolved common for ...
No Slide Title
... •Exchanges of genetic information (crossing over, recombination) occur during meiosis ...
... •Exchanges of genetic information (crossing over, recombination) occur during meiosis ...
Study Questions – Chapter 1
... 15. In the late 1980s when the Huntington disease gene was mapped, it took years afterwards to find the gene. After the turn of the century, when the progeria gene was mapped, it took less than a year to find the gene. What had changed that made such a big difference in the timelines of these two p ...
... 15. In the late 1980s when the Huntington disease gene was mapped, it took years afterwards to find the gene. After the turn of the century, when the progeria gene was mapped, it took less than a year to find the gene. What had changed that made such a big difference in the timelines of these two p ...
genetics
... mother or father, rather than on the classic laws of Mendelian genetics, where genes are either dominant or recessive. It seems that certain genes are only functional with one active copy, not zero and not two. A gene is made inactive by adding a methyl groups that blocks access to RNA transcriptase ...
... mother or father, rather than on the classic laws of Mendelian genetics, where genes are either dominant or recessive. It seems that certain genes are only functional with one active copy, not zero and not two. A gene is made inactive by adding a methyl groups that blocks access to RNA transcriptase ...
BB30055: Genes and genomes
... • Haplotype is a set of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on a single chromatid that are statistically associated. • Haplotypes are generally shared between populations but their frequency can vary International HapMap Project (www.hapmap.org) – identifying common haplotypes in four populations ...
... • Haplotype is a set of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on a single chromatid that are statistically associated. • Haplotypes are generally shared between populations but their frequency can vary International HapMap Project (www.hapmap.org) – identifying common haplotypes in four populations ...
Human Genome Project
... • First produced a clone-based physical map of the genome that would serve as a scaffold for the later sequence data: – Broke genome into chunks of DNA whose position on chromosome was known from maps, clone into bacteria using BACs. – Digest BAC-inserted clonal chunks of DNA into small fragments. – ...
... • First produced a clone-based physical map of the genome that would serve as a scaffold for the later sequence data: – Broke genome into chunks of DNA whose position on chromosome was known from maps, clone into bacteria using BACs. – Digest BAC-inserted clonal chunks of DNA into small fragments. – ...
What are genomes and how are they studied
... Interspersed repeats or Transposon-derived repeats. They constitute 45% of genome and arise mainly as a result of transposition either through a DNA/RNA intermediate. They can be divided into 4 main types ...
... Interspersed repeats or Transposon-derived repeats. They constitute 45% of genome and arise mainly as a result of transposition either through a DNA/RNA intermediate. They can be divided into 4 main types ...
Genomic Annotation
... Many pseudogenes are mRNA’s that have been retro-transposed back into the genome; many of these will appear as single exon genes Increase vigilance for signs of a pseudogene for any single exon gene Alternatively, there may be missing exons ...
... Many pseudogenes are mRNA’s that have been retro-transposed back into the genome; many of these will appear as single exon genes Increase vigilance for signs of a pseudogene for any single exon gene Alternatively, there may be missing exons ...
Genetics Quiz Study Guide D6
... 2. The _________________ states that factors for different traits on different genes are independent of one another. 3. A ___________ is a plant pure for a specific trait. 4. A _________________ occurs between individuals with 2 contrasting traits. 5. A ______________ is the actual alleles that are ...
... 2. The _________________ states that factors for different traits on different genes are independent of one another. 3. A ___________ is a plant pure for a specific trait. 4. A _________________ occurs between individuals with 2 contrasting traits. 5. A ______________ is the actual alleles that are ...
State of BER
... Designing synthetic biofuel pathways with optimized and balanced enzyme levels can be challenging. Here we identified optimal gene expression elements for heterologous ethanol production from a combinatorial library of gene expression signals. ...
... Designing synthetic biofuel pathways with optimized and balanced enzyme levels can be challenging. Here we identified optimal gene expression elements for heterologous ethanol production from a combinatorial library of gene expression signals. ...
7.3 Gene Linkage and Mapping KEY CONCEPT chromosomes.
... KEY CONCEPT Genes can be mapped to specific locations on chromosomes. ...
... KEY CONCEPT Genes can be mapped to specific locations on chromosomes. ...
16-1 Genes and Variation - Lincoln Park High School
... alleles there are many different phenotypes that can ...
... alleles there are many different phenotypes that can ...
Candidate gene copy number analysis by PCR and multicapillary
... alternative for detection of copy number changes [16]. MLPAs probes consist of two oligonucleotides, hybridizing adjacent to each other and a sequence complementary to the target, known as the hybridization sequence. When the probes correctly hybridize to the target sequence, they are ligated by a t ...
... alternative for detection of copy number changes [16]. MLPAs probes consist of two oligonucleotides, hybridizing adjacent to each other and a sequence complementary to the target, known as the hybridization sequence. When the probes correctly hybridize to the target sequence, they are ligated by a t ...
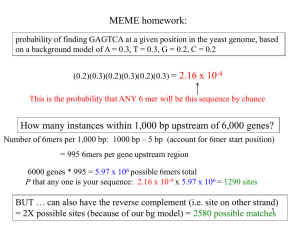
Fragile Sites and Cancer Powerpoint
... • Staining of metaphase chromosomes, one area failed to stain giving the appearance of a gap. • Gaps were susceptible to chromosome breakage. • Cause of fragility is unknown. ...
... • Staining of metaphase chromosomes, one area failed to stain giving the appearance of a gap. • Gaps were susceptible to chromosome breakage. • Cause of fragility is unknown. ...
ppt - Barley World
... The R locus (same position on each homologous chromosome) 2 copies of the absence of the R gene; each copy is one allele ...
... The R locus (same position on each homologous chromosome) 2 copies of the absence of the R gene; each copy is one allele ...
Copy-number variation

Copy-number variations (CNVs)—a form of structural variation—are alterations of the DNA of a genome that results in the cell having an abnormal or, for certain genes, a normal variation in the number of copies of one or more sections of the DNA. CNVs correspond to relatively large regions of the genome that have been deleted (fewer than the normal number) or duplicated (more than the normal number) on certain chromosomes. For example, the chromosome that normally has sections in order as A-B-C-D might instead have sections A-B-C-C-D (a duplication of ""C"") or A-B-D (a deletion of ""C"").This variation accounts for roughly 13% of human genomic DNA and each variation may range from about one kilobase (1,000 nucleotide bases) to several megabases in size. CNVs contrast with single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which affect only one single nucleotide base.