The cytoskeletal system, motor proteins Cyto + SKELETON
... most concentrated just beneath the cell membrane Functions: • force production (contractile and protrusive forces) • cell movement (20µm/sec.) • wound healing • defend against infection • maintaining cellular shape • participation in some cell-to-cell or cell-to-matrix junctions (signal transduction ...
... most concentrated just beneath the cell membrane Functions: • force production (contractile and protrusive forces) • cell movement (20µm/sec.) • wound healing • defend against infection • maintaining cellular shape • participation in some cell-to-cell or cell-to-matrix junctions (signal transduction ...
Name: Date: Biology Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Review Sheet
... 3. What is the difference between passive and active transport? Describe using terms: concentration gradient, energy 4. What are three examples of passive transport? 5. Relate diffusion and equilibrium. 6. What is osmosis? 7. Explain what happens to a cell in a hypotonic vs a hypertonic solution. In ...
... 3. What is the difference between passive and active transport? Describe using terms: concentration gradient, energy 4. What are three examples of passive transport? 5. Relate diffusion and equilibrium. 6. What is osmosis? 7. Explain what happens to a cell in a hypotonic vs a hypertonic solution. In ...
LIFE CELLS
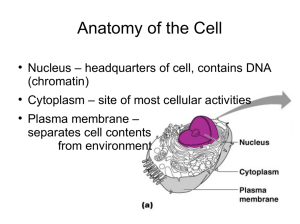
... • Nucleus= control centre, with nucleolus, nucleoplasm inside, doublemembrane nuclear envelope to contain everything, chromatin (DNA molecules and proteins) • Ribosomes= no membrane, translate RNA in to protein • Mitochondria= for energy (ATP production) • Chloroplasts= in plants only, for photo ...
... • Nucleus= control centre, with nucleolus, nucleoplasm inside, doublemembrane nuclear envelope to contain everything, chromatin (DNA molecules and proteins) • Ribosomes= no membrane, translate RNA in to protein • Mitochondria= for energy (ATP production) • Chloroplasts= in plants only, for photo ...
Chapter 7 The Cell
... Nucleus-Brain of cell/controls all cell activities. Cell division. Chromatin-DNA spread out in nucleus Nucleolus-Dark spot. Makes ribosomes. ...
... Nucleus-Brain of cell/controls all cell activities. Cell division. Chromatin-DNA spread out in nucleus Nucleolus-Dark spot. Makes ribosomes. ...
Slide 1
... •NUCLEUS– circular, located in the center of the cell, contains the DNA which is attached to proteins forming chromatin •Information stored in the DNA directs the activities of the cell •Nuclear membrane, with pores, surrounds nucleus •Nucleolus – ball like mass of fibers and granules that make ...
... •NUCLEUS– circular, located in the center of the cell, contains the DNA which is attached to proteins forming chromatin •Information stored in the DNA directs the activities of the cell •Nuclear membrane, with pores, surrounds nucleus •Nucleolus – ball like mass of fibers and granules that make ...
cell structure review sheet
... Distinguish between a prokaryote and a eukaryote. Distinguish between a unicellular organism and a multicellular organism State the three parts of the Cell theory. List and explain the characteristics of life. Discuss 3 main differences between plant and animal cells. Fill in the chart and be able t ...
... Distinguish between a prokaryote and a eukaryote. Distinguish between a unicellular organism and a multicellular organism State the three parts of the Cell theory. List and explain the characteristics of life. Discuss 3 main differences between plant and animal cells. Fill in the chart and be able t ...
BIOLOGY 2311 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PART I LECTURE 1
... Cytoplasmic organelles are metabolic machinery of the cell. ...
... Cytoplasmic organelles are metabolic machinery of the cell. ...
lab quiz 4 study guide sp 2015
... iv. Cytoplasmic streaming: the circular flow of a fluid layer of cytoplasm within a plant cell (one hypothesis is that myosin motors attached to organelles in the fluid cytoplasm drives the streaming by interacting with actin filaments). v. Function of cytoplasmic streaming? Speeds distribution of m ...
... iv. Cytoplasmic streaming: the circular flow of a fluid layer of cytoplasm within a plant cell (one hypothesis is that myosin motors attached to organelles in the fluid cytoplasm drives the streaming by interacting with actin filaments). v. Function of cytoplasmic streaming? Speeds distribution of m ...
Part B: Cell Organelles Structure and Function
... 1. State the three parts to the traditional cell theory: a. b. c. 2. Describe what Anton van Leeuwenhoek and Robert Hooke did to contribute to the cell theory. ...
... 1. State the three parts to the traditional cell theory: a. b. c. 2. Describe what Anton van Leeuwenhoek and Robert Hooke did to contribute to the cell theory. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... 1. Cell Wall Cell Wall -ALL Cells have a Cell membrane, but plant cells ALSO have a Cell Wall -It is made of cellulose -It gives shape, support, and structure to the plant cell ...
... 1. Cell Wall Cell Wall -ALL Cells have a Cell membrane, but plant cells ALSO have a Cell Wall -It is made of cellulose -It gives shape, support, and structure to the plant cell ...
Modeling sickle cells
... Sickle cell disease is a genetically inherited condition, in which a single amino acid change causes hemoglobin proteins to aggregate into stiff rods inside the red blood cells. Under certain conditions, regulated by oxigen concentration, these rods become very long, reach and deform the cell membra ...
... Sickle cell disease is a genetically inherited condition, in which a single amino acid change causes hemoglobin proteins to aggregate into stiff rods inside the red blood cells. Under certain conditions, regulated by oxigen concentration, these rods become very long, reach and deform the cell membra ...
Homeostasis Nucleus Decomposers Producers Consumer Abiotic
... Decomposers Producers Consumer Abiotic Biotic Asexual Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Chloroplasts Vacuole Echinoderm Bivalve Protozoa Flagella Pseudopod Mycelium Arthropod Turn over for more → ...
... Decomposers Producers Consumer Abiotic Biotic Asexual Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Chloroplasts Vacuole Echinoderm Bivalve Protozoa Flagella Pseudopod Mycelium Arthropod Turn over for more → ...
Cell Signaling Website Slides_10_4_11
... BIT 495/595: Cellular Signaling Techniques Overview: • Par9cipants will be introduced to a variety of methods for studying cellular signaling processes including theory, applica9ons and limita9ons. • Students wil ...
... BIT 495/595: Cellular Signaling Techniques Overview: • Par9cipants will be introduced to a variety of methods for studying cellular signaling processes including theory, applica9ons and limita9ons. • Students wil ...
Cell Organelles
... surface area for addition production of ATP’s Matrix inside contains hundreds of enzymes. ...
... surface area for addition production of ATP’s Matrix inside contains hundreds of enzymes. ...
Ch 3 Check Your Progress Answers BC Biology 12 3.1 p 67 1
... cilia and flagella: hair-like projections that can move like a whip or an oar. Cilia are shorter than flagella but have similar construction. Both are membrane bound cylinders. The cylinders are nine microtubule doublets arranged in a circle around two central microtubules. centrioles: short cylinde ...
... cilia and flagella: hair-like projections that can move like a whip or an oar. Cilia are shorter than flagella but have similar construction. Both are membrane bound cylinders. The cylinders are nine microtubule doublets arranged in a circle around two central microtubules. centrioles: short cylinde ...
7.2 Organelles
... Modify, sort, and package proteins and other materials from er for storage in cell or secretion What does it look like? Pancake stacks ...
... Modify, sort, and package proteins and other materials from er for storage in cell or secretion What does it look like? Pancake stacks ...
Unit 5 Cells Study Guide
... 7. What do ribosomes do? Are they found freely floating in the cytoplasm? OR are they found attached to another organelle? OR both. Explain why this occurs. ...
... 7. What do ribosomes do? Are they found freely floating in the cytoplasm? OR are they found attached to another organelle? OR both. Explain why this occurs. ...
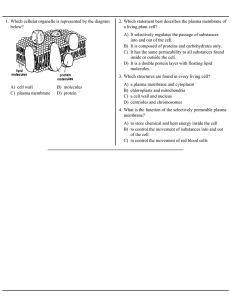
A) cell wall B) molecules C) plasma membrane D) protein 1. Which
... A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) It is a double protein layer with floating lipid molecules. 3. Which structures ...
... A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) It is a double protein layer with floating lipid molecules. 3. Which structures ...
topic 5 -part 3 guided notes -plant vs animal cells - student
... 9. vacuole (much bigger in plant cells!) 10. lysosomes 11. mitochondria 12. cytoplasm ...
... 9. vacuole (much bigger in plant cells!) 10. lysosomes 11. mitochondria 12. cytoplasm ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑