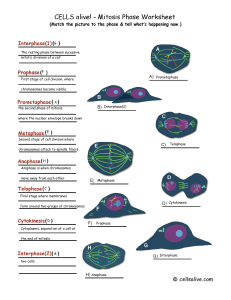
Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell Wall Ribosome Reticulum
... membrane, tubes, can be smooth or rough ...
... membrane, tubes, can be smooth or rough ...
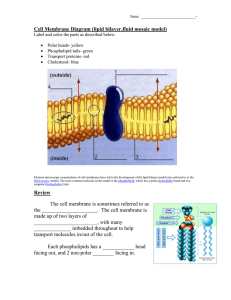
Cell Membrane Diagram (lipid bilayer,fluid mosaic model)
... Electron microscopic examinations of cell membranes have led to the development of the lipid bilayer model (also referred to as the fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
... Electron microscopic examinations of cell membranes have led to the development of the lipid bilayer model (also referred to as the fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
MICROSCOPE cell LEARNING TARGETS `16
... MS 01. I can identify the different parts of a compound microscope, and give the function of each. MS 02. I can determine the total magnification of an object I am viewing under a compound light microscope and accurately draw the object to scale based on my field of view. MS 03. I can use a compound ...
... MS 01. I can identify the different parts of a compound microscope, and give the function of each. MS 02. I can determine the total magnification of an object I am viewing under a compound light microscope and accurately draw the object to scale based on my field of view. MS 03. I can use a compound ...
1. The drawing shows part of a root hair cell. (a) Use words from the
... Name the process by which these gases move into and out of the cell. ...
... Name the process by which these gases move into and out of the cell. ...
Cell Theory
... All cells come from pre-existing cells. Important organelles in a cell Nucleus: Contains the cell’s DNA. ‘Brain’ of the cell. Mitochondrion: Site of respiration. Provides the energy for the cell to function. Ribosomes: Site where proteins are made (including enzymes) Vacuole: Storage. Cytoplasm: W ...
... All cells come from pre-existing cells. Important organelles in a cell Nucleus: Contains the cell’s DNA. ‘Brain’ of the cell. Mitochondrion: Site of respiration. Provides the energy for the cell to function. Ribosomes: Site where proteins are made (including enzymes) Vacuole: Storage. Cytoplasm: W ...
Cell Structure and Function1
... Two Main Types of Cells • Prokaryotic Cells – Lacks a cell nucleus (control center) or any other membrane-bound Organelles – Examples : Bacteria ...
... Two Main Types of Cells • Prokaryotic Cells – Lacks a cell nucleus (control center) or any other membrane-bound Organelles – Examples : Bacteria ...
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 5 Membrane Transport and
... organelles. Organelles in one of the heavier fractions could produce ATP in the light, whereas organelles in the lighter fraction could produce ATP in the dark. The heavier and lighter fractions are most likely to contain, respectively, A) mitochondria and chloroplasts. B) chloroplasts and peroxisom ...
... organelles. Organelles in one of the heavier fractions could produce ATP in the light, whereas organelles in the lighter fraction could produce ATP in the dark. The heavier and lighter fractions are most likely to contain, respectively, A) mitochondria and chloroplasts. B) chloroplasts and peroxisom ...
Cell membrane transport white board activity
... 1. Be able to define and locate each of the cell organelles. (Nucleus, cytoplasm, nucleolus, ER (smooth, rough), chloroplast, cell wall, lysosome, ribosomes, central vacuole, golgi apparatus, chromatin/DNA, cilia, flagella). 2. Diagram a phospholipid bilayer, and explain why the plasma membrane is s ...
... 1. Be able to define and locate each of the cell organelles. (Nucleus, cytoplasm, nucleolus, ER (smooth, rough), chloroplast, cell wall, lysosome, ribosomes, central vacuole, golgi apparatus, chromatin/DNA, cilia, flagella). 2. Diagram a phospholipid bilayer, and explain why the plasma membrane is s ...
Differences between the animal and plant cell: The plant cell has a
... The plant cell has a rigid cell wall for support and protection (1). If animal cells had cell walls, animals would not be able to move. ...
... The plant cell has a rigid cell wall for support and protection (1). If animal cells had cell walls, animals would not be able to move. ...
Cell structure and Function Practice Quiz
... Pick the choice that you think best answers the question If you get the answer correct you can move on to the next question If you get the answer wrong you will be returned to the question to try again ...
... Pick the choice that you think best answers the question If you get the answer correct you can move on to the next question If you get the answer wrong you will be returned to the question to try again ...
Biochemistry Review Sheet
... 3. Compare and contrast prokaryote and eukaryote cells. Cell Membrane 4. What is the function of the cell membrane? 5. Be able to identify the parts of the cell membrane from a diagram. 6. What are the four main components of the cell membrane, and what are the functions of each part? 7. Explain why ...
... 3. Compare and contrast prokaryote and eukaryote cells. Cell Membrane 4. What is the function of the cell membrane? 5. Be able to identify the parts of the cell membrane from a diagram. 6. What are the four main components of the cell membrane, and what are the functions of each part? 7. Explain why ...
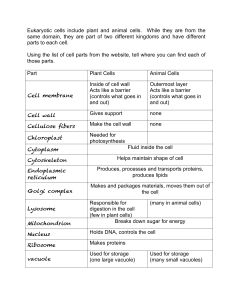
Cell membrane Cell wall Cellulose fibers Chloroplast Cytoplasm
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
7.3 Structures and Organelles
... RNA and ribosomes leave the nucleus and produce a protein on the ER. Proteins produced in the ER are sent to the Golding apparatus for packaging. Packaged proteins are delivered to other organelles where they serve a variety of functions. ...
... RNA and ribosomes leave the nucleus and produce a protein on the ER. Proteins produced in the ER are sent to the Golding apparatus for packaging. Packaged proteins are delivered to other organelles where they serve a variety of functions. ...
The Cell School to Home LESSON 2 1.
... Directions: Use your textbook to answer each question or respond to each statement. ...
... Directions: Use your textbook to answer each question or respond to each statement. ...
1. Which organelles are most closely associated with the process of
... 13. Most of the reactions of aerobic cellular respiration occur within the organelle known as the (1) lysosome (3) mitochondrion (2) nucleus (4) vacuole 14. Which organelles are usually found in both plant and animal cells? (1) cell walls (3) mitochondria (2) centrioles (4) chloroplasts 15. Which cy ...
... 13. Most of the reactions of aerobic cellular respiration occur within the organelle known as the (1) lysosome (3) mitochondrion (2) nucleus (4) vacuole 14. Which organelles are usually found in both plant and animal cells? (1) cell walls (3) mitochondria (2) centrioles (4) chloroplasts 15. Which cy ...
Cell wall: A protective layer external to the plasma membrane in
... Cell wall: A protective layer external to the plasma membrane in plant cells, bacteria, fungi, and some protists. In plant cells, the wall is formed of cellulose fibers embedded in a polysaccharide-protein matrix. The primary cell wall is thin and flexible, whereas the secondary cell wall is stronge ...
... Cell wall: A protective layer external to the plasma membrane in plant cells, bacteria, fungi, and some protists. In plant cells, the wall is formed of cellulose fibers embedded in a polysaccharide-protein matrix. The primary cell wall is thin and flexible, whereas the secondary cell wall is stronge ...
lecture 7 - cell biology I
... • internal elaborately folded specialised membrane system - thylakoid membrane • found in many plant cells exposed to light (leaves etc) • responsible for conversion of light energy to chemical energy - ATP and other energy currency cytoskeleton • movement of cells, movement of vesicles/organelles, ...
... • internal elaborately folded specialised membrane system - thylakoid membrane • found in many plant cells exposed to light (leaves etc) • responsible for conversion of light energy to chemical energy - ATP and other energy currency cytoskeleton • movement of cells, movement of vesicles/organelles, ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑