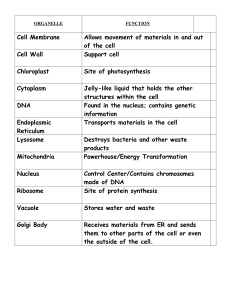
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... Formed of RNA and proteins. During protein synthesis, ribosomes and RNA translated from DNA leave the nucleus through the nuclear envelope and enter the cytoplasm ...
... Formed of RNA and proteins. During protein synthesis, ribosomes and RNA translated from DNA leave the nucleus through the nuclear envelope and enter the cytoplasm ...
Diversity of Living Things Study Guide
... the rest of the organelles what to do. It also holds the DNA. ...
... the rest of the organelles what to do. It also holds the DNA. ...
cell organization
... The extensive folding of the inner membrane allows an increase in surface area, which allows higher efficiency in transforming energy for the cell. The folds are called cristae. The central cavity is filled with liquid, called the matrix. ...
... The extensive folding of the inner membrane allows an increase in surface area, which allows higher efficiency in transforming energy for the cell. The folds are called cristae. The central cavity is filled with liquid, called the matrix. ...
TOPIC 2: Cells and Cellular Organization Please use the Khan
... Please use the Khan Academy Parts of a Cell video (compliments of Council Rock High School) to guide you. This video can be found at http://www.crsd.org/Page/31715 ...
... Please use the Khan Academy Parts of a Cell video (compliments of Council Rock High School) to guide you. This video can be found at http://www.crsd.org/Page/31715 ...
Slide 1
... 4. In the cell membrane model shown below, the molecules which move large molecules into and out of the cell are known as — A cholesterol B proteins C lipids D carbohydrates ...
... 4. In the cell membrane model shown below, the molecules which move large molecules into and out of the cell are known as — A cholesterol B proteins C lipids D carbohydrates ...
Plant and Animal Cells Booklet
... Plant and Animal Cells Booklet Directions: Using the drawings of the cell on p. 192 in the whale text book, make a booklet presenting information about the cell. Your book may showcase the plant cell or the animal cell. The cover needs to contain 1. a title (“Animal Cells” or “Plant Cells” will be f ...
... Plant and Animal Cells Booklet Directions: Using the drawings of the cell on p. 192 in the whale text book, make a booklet presenting information about the cell. Your book may showcase the plant cell or the animal cell. The cover needs to contain 1. a title (“Animal Cells” or “Plant Cells” will be f ...
Slide ()
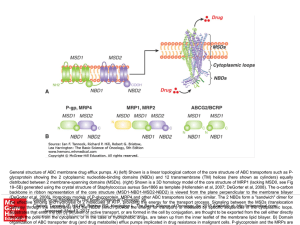
... (DeGorter et al, 2008). Homology models of P-glycoprotein, MRP4 and other ABC transporters look very similar. The 2 NBDs form a "sandwich" dimer for Source: Drug Resistance, The Basic Science of Oncology, 5e the effective binding and hydrolysis of 2 molecules of ATP, providing the energy for the tra ...
... (DeGorter et al, 2008). Homology models of P-glycoprotein, MRP4 and other ABC transporters look very similar. The 2 NBDs form a "sandwich" dimer for Source: Drug Resistance, The Basic Science of Oncology, 5e the effective binding and hydrolysis of 2 molecules of ATP, providing the energy for the tra ...
STAAR Review, Friday, Jan 20
... e. Rudolf Virchow – developed cell theory B. Cell Theory a. All living things are made of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced only from existing cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells A. Both have a. Cell membranes b. Cytoplasm c ...
... e. Rudolf Virchow – developed cell theory B. Cell Theory a. All living things are made of cells. b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. c. New cells are produced only from existing cells. Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells A. Both have a. Cell membranes b. Cytoplasm c ...
Cell Unit Project (Chapters 1-2)
... Directions: Be sure to add colored pictures (provide websites) and be creative. All foldables must be colored. Characteristics of all Living Things 1. List the characteristics of all living things (4) 2. List the needs of all living things (3) 3. What are the components of the Cell Theory? Contribut ...
... Directions: Be sure to add colored pictures (provide websites) and be creative. All foldables must be colored. Characteristics of all Living Things 1. List the characteristics of all living things (4) 2. List the needs of all living things (3) 3. What are the components of the Cell Theory? Contribut ...
engulf bacteria to change its shape has A white blood cell nourish
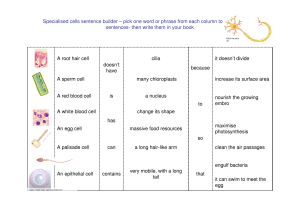
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
... Specialised cells sentence builder – pick one word or phrase from each column to make 7 correct sentences- then write them in your book ...
CELLS: What are they?
... Here are the parts you need to know: cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, and chloroplasts. The cell membrane protects the cell and controls what substances enter and leave it. The nucleus is the cell’s control center. Genetic information is stored in the nucleus. The cell wall gives the pl ...
... Here are the parts you need to know: cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, and chloroplasts. The cell membrane protects the cell and controls what substances enter and leave it. The nucleus is the cell’s control center. Genetic information is stored in the nucleus. The cell wall gives the pl ...
sParamecium: Paramecium is a genus of unicellular ciliate protozoa
... turns slightly and goes forward again. If it runs into the solid object again, it will repeat this process until it can get past the object. There is a deep mouthlike groove containing almost invisible tongue-like cilia, which are used to draw food inside. In general, they feed on bacteria and other ...
... turns slightly and goes forward again. If it runs into the solid object again, it will repeat this process until it can get past the object. There is a deep mouthlike groove containing almost invisible tongue-like cilia, which are used to draw food inside. In general, they feed on bacteria and other ...
File
... Cell Structure and Functions UNDERSTANDING CELLS: What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? List them in to order from least to most complex. What is cell specialization (differentiation)? How is ...
... Cell Structure and Functions UNDERSTANDING CELLS: What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? List them in to order from least to most complex. What is cell specialization (differentiation)? How is ...
micro intro organelles
... • form hair-like extensions on cell surface for movement (cilia or flagella) • Centrioles – rings of microtubules which form spindle fibers to aide in cell division ...
... • form hair-like extensions on cell surface for movement (cilia or flagella) • Centrioles – rings of microtubules which form spindle fibers to aide in cell division ...
Lecture 3 Prokaryotic Cell Biology Part I 1) How does the
... Lecture 3 Prokaryotic Cell Biology Part I 1) How does the arrangement of DNA differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 2) What is coupled transcription-translation, and why does it happen only in prokaryotes? What’s a benefit to coupling these two processes? 3) What types of things are stored in cy ...
... Lecture 3 Prokaryotic Cell Biology Part I 1) How does the arrangement of DNA differ between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 2) What is coupled transcription-translation, and why does it happen only in prokaryotes? What’s a benefit to coupling these two processes? 3) What types of things are stored in cy ...
SI Session 09/19/2014 Note: Know how to do molarity questions
... 3. Of the following, what do both mitochondria and chloroplasts have in common? A) ATP is produced. B) DNA is present. C) Ribosomes are present. D) B and C only E) A, B, and C are correct. 4. Which of the following is not a known function of the cytoskeleton? A) to maintain a critical limit on cell ...
... 3. Of the following, what do both mitochondria and chloroplasts have in common? A) ATP is produced. B) DNA is present. C) Ribosomes are present. D) B and C only E) A, B, and C are correct. 4. Which of the following is not a known function of the cytoskeleton? A) to maintain a critical limit on cell ...
Lecture 7: Intro to the cell, cont
... • maintain cell shape by resisting compression • motility via flagella/cilia • anchor nucleus • move organelles and some other organelles • move chromosomes during cell division ...
... • maintain cell shape by resisting compression • motility via flagella/cilia • anchor nucleus • move organelles and some other organelles • move chromosomes during cell division ...
Discover Cell Cycle Video
... 7. During prophase nuclear membranes __________________and spindle fibers ____________. 8. Where do the chromosomes line up during metaphase? 9. What happens to the twin chromatids in anaphase? 10. During telophase spindle fibers ____________ nuclear membrane ____________, and ___________________ un ...
... 7. During prophase nuclear membranes __________________and spindle fibers ____________. 8. Where do the chromosomes line up during metaphase? 9. What happens to the twin chromatids in anaphase? 10. During telophase spindle fibers ____________ nuclear membrane ____________, and ___________________ un ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑