Final Animal Organelles
... • Chloroplasts are what make plants their distinctive green color • The process of turning light into energy is called photosynthesis ...
... • Chloroplasts are what make plants their distinctive green color • The process of turning light into energy is called photosynthesis ...
Across 1. an organelle within the nucleus that produces ribosomes 3
... 3. an organelle formed by the centriole 5. an organelle unique to animal cells involved in cell replication 7. a rigid structure located on the outside of plant cells 10. large membrane-bound space in the cytoplasm of plant cells 13. composed of phospholipds, proteins, carbohydrates and cholesterol ...
... 3. an organelle formed by the centriole 5. an organelle unique to animal cells involved in cell replication 7. a rigid structure located on the outside of plant cells 10. large membrane-bound space in the cytoplasm of plant cells 13. composed of phospholipds, proteins, carbohydrates and cholesterol ...
ADVANCED BIOLOGY Exam III (Chapter 3: Cell Structure and
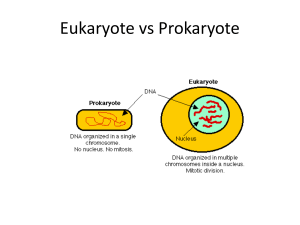
... cells and their function(s). (Refer to Cell Function Wkshts) 4. What are the functions of all organelles within both the animal and plant cells. 5. Describe one similarity and one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; cell wall and cell membrane; facilitated diffusion and diffusion. 6 ...
... cells and their function(s). (Refer to Cell Function Wkshts) 4. What are the functions of all organelles within both the animal and plant cells. 5. Describe one similarity and one difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; cell wall and cell membrane; facilitated diffusion and diffusion. 6 ...
Lecture 013--Organelles 4 (Cytoskeleton)
... twisted double chain of actin subunits about 7nm in diameter ...
... twisted double chain of actin subunits about 7nm in diameter ...
The “brains” of the cell, that directs cell activities and contains
... plant cells than in animal cells ...
... plant cells than in animal cells ...
S3O1 Curr Map
... Plant cells have a cell membrane and a cell wall. They have green chloroplasts. They are regular in shape, boxlike. Animals cells vary in shape because they do not have cell walls. The flexible cell membrane holds them together. They lack chloroplasts. Diffusion is the movement of atoms and molecule ...
... Plant cells have a cell membrane and a cell wall. They have green chloroplasts. They are regular in shape, boxlike. Animals cells vary in shape because they do not have cell walls. The flexible cell membrane holds them together. They lack chloroplasts. Diffusion is the movement of atoms and molecule ...
Lysosome small round structures that break down large food
... small round structures that break down large food molecules ...
... small round structures that break down large food molecules ...
Cell wall Single large vacuole Chloroplasts
... While both animal and plant cells have a thin cell membrane that controls what goes in and out, plants differ in that they also have a cell wall made of cellulose. This rigid outer wall enables the plant to hold a lot of moisture under pressure without popping, while also providing essential structu ...
... While both animal and plant cells have a thin cell membrane that controls what goes in and out, plants differ in that they also have a cell wall made of cellulose. This rigid outer wall enables the plant to hold a lot of moisture under pressure without popping, while also providing essential structu ...
Biology Chapter 7
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
Centrioles are self-replicating organelles made up
... Centrioles - Centrioles are self-replicating organelles made up of nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. They appear to help in organizing cell division, but aren't essential to the process. Cilia and Flagella - For single-celled eukaryotes, cilia and flagella are essentia ...
... Centrioles - Centrioles are self-replicating organelles made up of nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. They appear to help in organizing cell division, but aren't essential to the process. Cilia and Flagella - For single-celled eukaryotes, cilia and flagella are essentia ...
Vacuoles
... Keeps harmful materials away from cell Holds cell waste Stores protein for seeds Lets plants have leaves and flowers because of the high pressure in the cell • Vacuoles are found in plant and fungi cells ...
... Keeps harmful materials away from cell Holds cell waste Stores protein for seeds Lets plants have leaves and flowers because of the high pressure in the cell • Vacuoles are found in plant and fungi cells ...
Cell Membrane Animal Cell Controls what enters and leaves the cell
... Controls what enters and leaves the cell ...
... Controls what enters and leaves the cell ...
Cell membrane
... The gel-like fluid inside of a cell made of mostly water. The other organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm. Nucleus ...
... The gel-like fluid inside of a cell made of mostly water. The other organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm. Nucleus ...
Cells - biologybi
... Cell membrane- separates the cell from other cells and allows molecules to pass through. Cell wall- protects and supports the cell. (Plant cells only) ...
... Cell membrane- separates the cell from other cells and allows molecules to pass through. Cell wall- protects and supports the cell. (Plant cells only) ...
Lectures 18-21 - Biology Courses Server
... 3. Explain the mechanism of muscular contraction using actin, myosin, and ATPase. a. Would a muscle contract in the absence of calcium? Explain. 4. If both the thick and thin filaments of muscle are made up of subunits held together by weak non-covalent bonds, how is it possible for a human being to ...
... 3. Explain the mechanism of muscular contraction using actin, myosin, and ATPase. a. Would a muscle contract in the absence of calcium? Explain. 4. If both the thick and thin filaments of muscle are made up of subunits held together by weak non-covalent bonds, how is it possible for a human being to ...
Organelles - SchoolRack
... organelles – help cells do their work. Green organelles in plant cells contain chloroplasts to make food. Organelles which release energy from food are called mitochondria. ...
... organelles – help cells do their work. Green organelles in plant cells contain chloroplasts to make food. Organelles which release energy from food are called mitochondria. ...
Ch 3 - Fort Bend ISD
... • Made up of a PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER: outside is hydrophilic and inside is hydrophobic • Selectively Permeable, but naturally impermeable to large objects • Concentration Gradient – Concentration of sodium ions can attract and repel charged substances into and out of cells. ...
... • Made up of a PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER: outside is hydrophilic and inside is hydrophobic • Selectively Permeable, but naturally impermeable to large objects • Concentration Gradient – Concentration of sodium ions can attract and repel charged substances into and out of cells. ...
Cell Organelle Review - Jamestown School District
... Name the cell organelle known to perform “protein synthesis” (makes proteins) ...
... Name the cell organelle known to perform “protein synthesis” (makes proteins) ...
answers - Biology Resources
... substances entering and leaving the cell. 4 (a) Plant and animal cells have cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, nucleus and chromosomes. (b) Only plant cells have a cell wall, central vacuole and cell sap. 5 The most likely sequence is as shown below. ...
... substances entering and leaving the cell. 4 (a) Plant and animal cells have cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, nucleus and chromosomes. (b) Only plant cells have a cell wall, central vacuole and cell sap. 5 The most likely sequence is as shown below. ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑