Unit 2 Cells Test Study Guide
... Unit 2 Cells Study Guide Answer the following questions using your textbook and notes. Study each of these questions and topics as all will appear on your test. ...
... Unit 2 Cells Study Guide Answer the following questions using your textbook and notes. Study each of these questions and topics as all will appear on your test. ...
Chpt 6 - San Diego Unified School District
... b. Rough ER 2. Golgi apparatus 3. Lysosome 4. Vacuoles a. food vacuole b. contractile vacuole c. central vacuole (plants) D. Mitochondrion E. Chloroplast (plants) III. Cytoskeleton A. Cilia B. Flagella IV. Extracellular components A. Cell wall (plants) Study Tips: Know … the differences between prok ...
... b. Rough ER 2. Golgi apparatus 3. Lysosome 4. Vacuoles a. food vacuole b. contractile vacuole c. central vacuole (plants) D. Mitochondrion E. Chloroplast (plants) III. Cytoskeleton A. Cilia B. Flagella IV. Extracellular components A. Cell wall (plants) Study Tips: Know … the differences between prok ...
Structures and Organelles
... digest excess organelles and/or food particles also digest bacteria and viruses ...
... digest excess organelles and/or food particles also digest bacteria and viruses ...
Unit of life MBBS Prof. Fridoon - King Edward Medical University
... phagocytosis (autophagy) to form secondary lysosomes, where engulfed materials are digested. Undigested materials are secreted from the cell when the secondary lysosome fuses with the plasma membrane.. ...
... phagocytosis (autophagy) to form secondary lysosomes, where engulfed materials are digested. Undigested materials are secreted from the cell when the secondary lysosome fuses with the plasma membrane.. ...
What Part of the Cell am I?
... Since I contain many enzymes, I can digest an injured cell. And I can make a large molecule into a smaller one as well. What am I? ...
... Since I contain many enzymes, I can digest an injured cell. And I can make a large molecule into a smaller one as well. What am I? ...
Cell Analogy Sheet
... Cell Analogy Sheet Purpose: To show mastery of each organelles function and role within a cell. Directions: Students will make their own unified analogy for the functions and roles of cell organelles. 1. Cell wall is: a plant cells outermost organelle. It is in charge of protecting the cell, as well ...
... Cell Analogy Sheet Purpose: To show mastery of each organelles function and role within a cell. Directions: Students will make their own unified analogy for the functions and roles of cell organelles. 1. Cell wall is: a plant cells outermost organelle. It is in charge of protecting the cell, as well ...
Cells and Organelles Chart
... Science North is an agency of the Government of Ontario and a registered charity #10796 2979 RR0001. ...
... Science North is an agency of the Government of Ontario and a registered charity #10796 2979 RR0001. ...
(null): Can You Identify These Cell Structures.doc, filename=Can
... Proteins are made here Even though I’m quite small You can find me in the cytoplasm Or attached to the E.R.’s wall What am I?__________________ I’ve been called a “storage tank” By those with little taste I’m a sac filled with water, Food, enzymes, or waste What am I?__________________ Since I cont ...
... Proteins are made here Even though I’m quite small You can find me in the cytoplasm Or attached to the E.R.’s wall What am I?__________________ I’ve been called a “storage tank” By those with little taste I’m a sac filled with water, Food, enzymes, or waste What am I?__________________ Since I cont ...
Cells and Tissues - Mrs. Hille`s FunZone
... Break down free radicals (highly reactive chemicals) Replicate by pinching in half Cytoplasmic Organelles Mitochondria “Powerhouses” of the cell Change shape continuously Carry out reactions where oxygen is used to break down food Provides ATP for cellular energy Cytoplasmic Organelles C ...
... Break down free radicals (highly reactive chemicals) Replicate by pinching in half Cytoplasmic Organelles Mitochondria “Powerhouses” of the cell Change shape continuously Carry out reactions where oxygen is used to break down food Provides ATP for cellular energy Cytoplasmic Organelles C ...
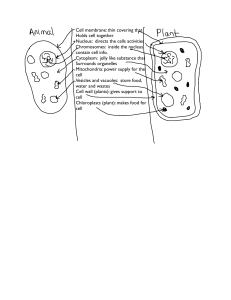
Cells Test What do I need to know???? Know the parts of a plant
... Know the parts of a plant and animal cell and their functions or jobs in the cell. Study flash cards and reading. Animal Cell ...
... Know the parts of a plant and animal cell and their functions or jobs in the cell. Study flash cards and reading. Animal Cell ...
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
... Prokaryotic cells lack autonomous plastids, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. The photosynthetic pigments (carotenoids, bacteriochlorophyll) of photosynthetic bacteria are contained in intracytoplasmic membrane systems of various morphologies. Bacteria often store reserve materials in the fo ...
... Prokaryotic cells lack autonomous plastids, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts. The photosynthetic pigments (carotenoids, bacteriochlorophyll) of photosynthetic bacteria are contained in intracytoplasmic membrane systems of various morphologies. Bacteria often store reserve materials in the fo ...
Cell Structure PPT Part 2
... Most cells have materials external to the plasma membrane. Cell walls are found in prokaryotes, plants, fungi and some protists. Cell walls of plants are made of cellulose; in fungi they are made of chitin; in prokaryotes they are murein (or muramic acid) and in protists they vary. ...
... Most cells have materials external to the plasma membrane. Cell walls are found in prokaryotes, plants, fungi and some protists. Cell walls of plants are made of cellulose; in fungi they are made of chitin; in prokaryotes they are murein (or muramic acid) and in protists they vary. ...
I`m a real “powerhouse.” That`s plain to see. I break down food to
... I’m a series of tubes, found throughout the cell. I transport proteins and other things as well ...
... I’m a series of tubes, found throughout the cell. I transport proteins and other things as well ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑