ion channel activity found in cytoplasmic droplets of n…
... Patch clamp technique employs a microelectrode to seal an area of a chosen membrane to create a high resistance (usually larger than 1 GΩ) contact. Thus any electrical current passing through the sealed area can be easily detected in high resolution – activity of a single ion channel can be recorded ...
... Patch clamp technique employs a microelectrode to seal an area of a chosen membrane to create a high resistance (usually larger than 1 GΩ) contact. Thus any electrical current passing through the sealed area can be easily detected in high resolution – activity of a single ion channel can be recorded ...
Name Date The Structure and Function of Cells Cell Part Structure
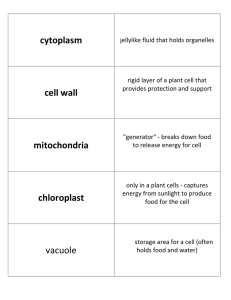
... reticulum or floating free in cytoplasm; produced in nucleolus Rod shaped organelle; located in the cytoplasm; has a smooth outer membrane and a greatly folded inner membrane ...
... reticulum or floating free in cytoplasm; produced in nucleolus Rod shaped organelle; located in the cytoplasm; has a smooth outer membrane and a greatly folded inner membrane ...
Cell Analogies Worksheet
... Cell Structure Extra Credit Instructions: Fill in the spaces below for each cell part in order to create a one-sentence analogy that shows the similarity between the cell part and another object. Be sure to explain the reasoning behind your analogies (see the underlined section of the example). Exem ...
... Cell Structure Extra Credit Instructions: Fill in the spaces below for each cell part in order to create a one-sentence analogy that shows the similarity between the cell part and another object. Be sure to explain the reasoning behind your analogies (see the underlined section of the example). Exem ...
Chapter 3 Lesson 3.2
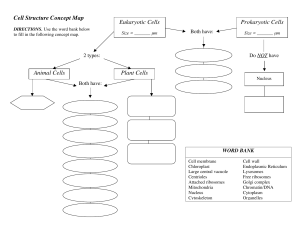
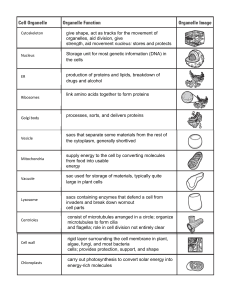
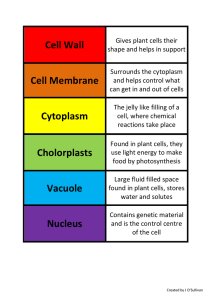
... Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Chloroplasts Golgi Complex Vesicle Lysosomes Vacuoles ...
... Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Chloroplasts Golgi Complex Vesicle Lysosomes Vacuoles ...
Organelle Notes #2
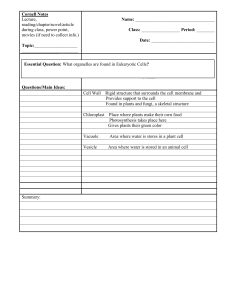
... Cornell Notes Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
... Cornell Notes Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
MICROTUBULES Tracks guide motor proteins to destination
... – Crosslinks with microtubules (cell shape) – Muscle cells: Actin filaments interact with myosin motor proteins to create muscle contraction – Amoeboid movement – Cytoplasmic streaming ...
... – Crosslinks with microtubules (cell shape) – Muscle cells: Actin filaments interact with myosin motor proteins to create muscle contraction – Amoeboid movement – Cytoplasmic streaming ...
Cell Organelle
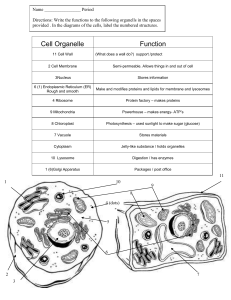
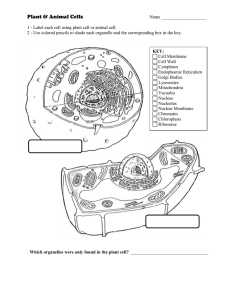
... Name ________________ Period Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
... Name ________________ Period Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
Slide 1
... To optimize conditions for photosynthesis chloroplasts are in constant motion in most plants. They accumulate in weakly illuminated regions of the cell and avoid regions exposed to strong light. In the mesophyll of vascular land plants, these orientation movements are controlled only by blue light. ...
... To optimize conditions for photosynthesis chloroplasts are in constant motion in most plants. They accumulate in weakly illuminated regions of the cell and avoid regions exposed to strong light. In the mesophyll of vascular land plants, these orientation movements are controlled only by blue light. ...
Chapter 3 Cells
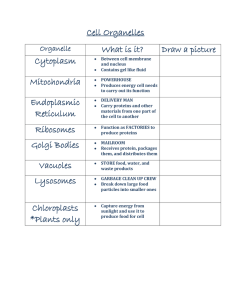
... •stack of flattened, membranous sacs •modifies, packages and delivers proteins Vesicles •membranous sacs •store substances Mitochondria •membranous sacs with inner partitions •generate energy ...
... •stack of flattened, membranous sacs •modifies, packages and delivers proteins Vesicles •membranous sacs •store substances Mitochondria •membranous sacs with inner partitions •generate energy ...
Unit 3 Chapter 7 A View of the Cell
... Vacuoles Membrane-bound compartments for temporary storage of materials May be very large in plant cells ...
... Vacuoles Membrane-bound compartments for temporary storage of materials May be very large in plant cells ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Orange Coast College
... Prepares proteins for export Makes lysosomes Packages material to add to plasma membrane ...
... Prepares proteins for export Makes lysosomes Packages material to add to plasma membrane ...
Cytoplasm!
... • Provides a medium for organelles to remain suspended • Promotes cell efficiency and movement through cytoplasmic streaming • Transports genetic material and products of cellular respiration • Protects genetic material and organelles from damage caused by collisions with other cells ...
... • Provides a medium for organelles to remain suspended • Promotes cell efficiency and movement through cytoplasmic streaming • Transports genetic material and products of cellular respiration • Protects genetic material and organelles from damage caused by collisions with other cells ...
carry out photosynthesis to convert solar energy into energy
... sacs that separate some materials from the rest of the cytoplasm, generally shortlived ...
... sacs that separate some materials from the rest of the cytoplasm, generally shortlived ...
I`m a real “powerhouse” That`s plain to see. I break down food To
... Found only in plant cells, I’m green as can be. I make food for the plant Using the sun’s energy. CHLOROPLASTS ...
... Found only in plant cells, I’m green as can be. I make food for the plant Using the sun’s energy. CHLOROPLASTS ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑