Osmosis in Plant Cells - Middlesex High School
... pressure increases. The protoplast begs to press on the cell wall. (c) Greatest turgor pressure. The tendency to take up water is ultimately restricts by the cell wall, creating a back pressure on the protoplast. Water enters and leaves the cell at the same rate. ...
... pressure increases. The protoplast begs to press on the cell wall. (c) Greatest turgor pressure. The tendency to take up water is ultimately restricts by the cell wall, creating a back pressure on the protoplast. Water enters and leaves the cell at the same rate. ...
1st 6 Test Review Notes 2012
... Mitochondrion- the cell organelle that produces energy used within the cell Chloroplast- plant cell organelle that contains chlorophyll and were plant cell photosynthesis occurs Vacuole- storage organelle for the cell. Stores items such as water and proteins. Large in plant cells, small but usually ...
... Mitochondrion- the cell organelle that produces energy used within the cell Chloroplast- plant cell organelle that contains chlorophyll and were plant cell photosynthesis occurs Vacuole- storage organelle for the cell. Stores items such as water and proteins. Large in plant cells, small but usually ...
(1.2) Cell Division (p22-27)
... • DNA in the nucleus of the cell contains the hereditary material. • DNA molecules have a shape like that of a ladder. • To fit inside the nucleus DNA forms compact coiled threads called chromatin. • To reproduce the chromatin packs together to form chromosomes. • Chromosomes pass on hereditary info ...
... • DNA in the nucleus of the cell contains the hereditary material. • DNA molecules have a shape like that of a ladder. • To fit inside the nucleus DNA forms compact coiled threads called chromatin. • To reproduce the chromatin packs together to form chromosomes. • Chromosomes pass on hereditary info ...
Biology Test 1 Review Three domains: Archae
... This makes the Cell Membrane Selectively Permeable -It allows small, uncharged molecules through with the concentration gradient – Passive Transport -While keeping out large, charged particles ...
... This makes the Cell Membrane Selectively Permeable -It allows small, uncharged molecules through with the concentration gradient – Passive Transport -While keeping out large, charged particles ...
pogil 9
... This exercise explores a theory that biologists use to explain a set of observations and facts. The theory you will be exploring today is the endosymbiotic theory of the eukaryotic cell. You will explore this theory through a set of questions that you will answer using your learning objective note s ...
... This exercise explores a theory that biologists use to explain a set of observations and facts. The theory you will be exploring today is the endosymbiotic theory of the eukaryotic cell. You will explore this theory through a set of questions that you will answer using your learning objective note s ...
cell analogy
... The city roads are like the endoplasmic reticulum. Roads are the transport system which allows materials to be carried throughout the city. The ER is a transport system that carries materials throughout the cell. The machine shops are like the cell's ribosomes. The machine shops are built along the ...
... The city roads are like the endoplasmic reticulum. Roads are the transport system which allows materials to be carried throughout the city. The ER is a transport system that carries materials throughout the cell. The machine shops are like the cell's ribosomes. The machine shops are built along the ...
Creative Activities
... Make an animal or plant cell cartoon. Use any information form the systems lessons. Make the analogy between the real-world and the cell world. Make sure the analogy is appropriate- that it makes sense. The cartoon should be drawn and colored on a single sheet of unlined paper. ...
... Make an animal or plant cell cartoon. Use any information form the systems lessons. Make the analogy between the real-world and the cell world. Make sure the analogy is appropriate- that it makes sense. The cartoon should be drawn and colored on a single sheet of unlined paper. ...
Cell Farm - Denair Unified School District
... conditions are designed to let anaerobic bacteria thrive and do the work of breaking the manure down. The large volume of "biogas" released ...
... conditions are designed to let anaerobic bacteria thrive and do the work of breaking the manure down. The large volume of "biogas" released ...
Slide ()
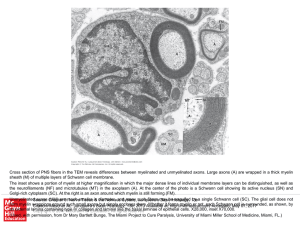
... Golgi-rich cytoplasm (SC). At the right is an axon around which myelin is still forming (FM). UnmyelinatedSource: axons Chapter (UM) are9.much diameter, and many such fibers may engulfed 13e by a single Schwann cell (SC). The glial cell does not Nervesmaller Tissue in & the Nervous System, Junqueira ...
... Golgi-rich cytoplasm (SC). At the right is an axon around which myelin is still forming (FM). UnmyelinatedSource: axons Chapter (UM) are9.much diameter, and many such fibers may engulfed 13e by a single Schwann cell (SC). The glial cell does not Nervesmaller Tissue in & the Nervous System, Junqueira ...
Botany 1st Semester Exam Study Guide ANSWERS
... 16. Prokaryotes lack _______________.a nucleus 17. Eukaryotes usually contain a _______________ which contains _______________ material. They also have specialized _______________. Nucleus, genetic, cell organelles 18. _______________ are examples or prokaryotes. Bacteria 19. _______________ & _____ ...
... 16. Prokaryotes lack _______________.a nucleus 17. Eukaryotes usually contain a _______________ which contains _______________ material. They also have specialized _______________. Nucleus, genetic, cell organelles 18. _______________ are examples or prokaryotes. Bacteria 19. _______________ & _____ ...
Document
... chromosome coiled structures of genetic material in the nucleus, made of long chains of DNA. mitochondrion transforms the unusable energy in food molecules, into a form of usable energy. prokaryotic cell a cell without a nucleus and most other organelles. cell wall a rigid wall that surrounds the ce ...
... chromosome coiled structures of genetic material in the nucleus, made of long chains of DNA. mitochondrion transforms the unusable energy in food molecules, into a form of usable energy. prokaryotic cell a cell without a nucleus and most other organelles. cell wall a rigid wall that surrounds the ce ...
Calculus Investigation
... is important in molecular biology and this problem introduces you to molecular modeling which is very important in medical research. In bacterial growth models, when the nutrient concentration is low, the bacterial growth rate is proportional to the concentration; when the nutrient level is high, th ...
... is important in molecular biology and this problem introduces you to molecular modeling which is very important in medical research. In bacterial growth models, when the nutrient concentration is low, the bacterial growth rate is proportional to the concentration; when the nutrient level is high, th ...
a. Cell membrane
... 2. Which of the following organisms do not have cell walls? a. humans b. squid c. spiders d. all of the above 3. Which of the following is true of membranes? a. Folded membranes decrease surface area for efficiency. b. Folded membranes do not form compartments in the cell. c. Endoplasmic reticulum i ...
... 2. Which of the following organisms do not have cell walls? a. humans b. squid c. spiders d. all of the above 3. Which of the following is true of membranes? a. Folded membranes decrease surface area for efficiency. b. Folded membranes do not form compartments in the cell. c. Endoplasmic reticulum i ...
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
... a) Hostile conditions cause the vegetative cell to convert to a sporeforming cell known as a sporangium b) The DNA of the cell is duplicated c) A septum forms dividing the cell into unequal parts each with its own DNA d) The larger portion engulfs the smaller portion resulting in a forespore e) A th ...
... a) Hostile conditions cause the vegetative cell to convert to a sporeforming cell known as a sporangium b) The DNA of the cell is duplicated c) A septum forms dividing the cell into unequal parts each with its own DNA d) The larger portion engulfs the smaller portion resulting in a forespore e) A th ...
Cell Structure
... made of cellulose, pectin or silica • Nutrition: photosynthetic autotrophs and heterotrophs that use ingestion or absorption • Habitat: freshwater and ocean water, in and on organisms ...
... made of cellulose, pectin or silica • Nutrition: photosynthetic autotrophs and heterotrophs that use ingestion or absorption • Habitat: freshwater and ocean water, in and on organisms ...
Jeopardy Transport
... Movement of molecules across a membrane from high low through a protein ...
... Movement of molecules across a membrane from high low through a protein ...
Cell Structure Project
... summary of their project. You should answer the following questions: What is your project? How did you represent each organelle? How did you represent their functions? At least 2 interesting facts that you learned while completing this project. What is unique about your project? Include anything els ...
... summary of their project. You should answer the following questions: What is your project? How did you represent each organelle? How did you represent their functions? At least 2 interesting facts that you learned while completing this project. What is unique about your project? Include anything els ...
exam_review_2_answers_0
... they reach equilibrium. This means that molecules do not “clump” naturally, but rather spread out until evenly distributed, even across membranes. 5. Osmosis is a type of diffusion related specifically to the movement of water across a cell membrane AGAINST the concentration gradient of a particular ...
... they reach equilibrium. This means that molecules do not “clump” naturally, but rather spread out until evenly distributed, even across membranes. 5. Osmosis is a type of diffusion related specifically to the movement of water across a cell membrane AGAINST the concentration gradient of a particular ...
Biology Midterm Review Sheet
... a. Does enzyme number one function at a pH of 5.5? ______ b. What is the best pH for enzyme number two? _______ c. Which enzyme has the broadest ph range? ___________ ...
... a. Does enzyme number one function at a pH of 5.5? ______ b. What is the best pH for enzyme number two? _______ c. Which enzyme has the broadest ph range? ___________ ...
Chapter 6: Concept 6.6
... techniques revealed a cytoskeleton (cyto means "cell"), a network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm. Unlike your body's skeleton, the skeleton of most cells does not keep the same structural pattern all the time. It is always changing, with new extensions building at the same time that ot ...
... techniques revealed a cytoskeleton (cyto means "cell"), a network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm. Unlike your body's skeleton, the skeleton of most cells does not keep the same structural pattern all the time. It is always changing, with new extensions building at the same time that ot ...
Bioenergetics Structures and Functions of Cells
... 6. contain oxidases and catalases 7. provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to another 8. sites of protein synthesis 9. plastids containing pigments other than chlorophyll 10.allow bacteria to exchange DNA during conjugation ...
... 6. contain oxidases and catalases 7. provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to another 8. sites of protein synthesis 9. plastids containing pigments other than chlorophyll 10.allow bacteria to exchange DNA during conjugation ...
i Know This
... cells to common non-living things (enzyme -substrate = lock and key, cell membrane works like a wall, nucleus is like a brain, etc) I know how cells were discovered I know the Cell Theory I can related cell shape and size to cell function I know what a prokaryotic cell is and can give examples of pr ...
... cells to common non-living things (enzyme -substrate = lock and key, cell membrane works like a wall, nucleus is like a brain, etc) I know how cells were discovered I know the Cell Theory I can related cell shape and size to cell function I know what a prokaryotic cell is and can give examples of pr ...
Cell Organelle and Levels of Organization STUDY GUIDE
... the following analogy for review: a. cell: letter b. tissue: ______________________________ c. organ: ______________________________ d. organ system: ________________________ ...
... the following analogy for review: a. cell: letter b. tissue: ______________________________ c. organ: ______________________________ d. organ system: ________________________ ...
Cell wall
The cell wall is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. In addition, the cell wall acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. Cell walls are found in plants, fungi and prokaryotic cells but not in mycoplasmas.The composition of the cell wall varies between species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. In bacteria, peptidoglycan forms the cell wall. Archaean cell walls have various compositions, and may be formed of glycoprotein S-layers, pseudopeptidoglycan, or polysaccharides. Fungi possess cell walls made of the glucosamine polymer chitin, and algae typically possess walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Unusually, diatoms have a cell wall composed of biogenic silica. Often, other accessory molecules are found anchored to the cell wall.