Assisted Conception Unit
... Please contact the Assisted Conception Unit for prices related to Sperm washing services Please request advice for prices that are not included on this list ...
... Please contact the Assisted Conception Unit for prices related to Sperm washing services Please request advice for prices that are not included on this list ...
Hormones and puberty
... Hormones and puberty Hormones play an important role in controlling or regulating many processes in the body, including physical development during youth. They are often referred to as ‘chemical messengers’ because they circulate in the bloodstream and act on various sites in the body, stimulating a ...
... Hormones and puberty Hormones play an important role in controlling or regulating many processes in the body, including physical development during youth. They are often referred to as ‘chemical messengers’ because they circulate in the bloodstream and act on various sites in the body, stimulating a ...
Menstrual Cycle Pains and Discomforts
... Potentially significant decrease in quality of life Loss of time at work/school Health care provider visits Expenses for OTC medications ...
... Potentially significant decrease in quality of life Loss of time at work/school Health care provider visits Expenses for OTC medications ...
B2BGynecologyLamensa2016
... Menopause occurs at ~51 years of age as a result of a genetically determined depletion of ovarian follicles responsive to gonadotropins. ...
... Menopause occurs at ~51 years of age as a result of a genetically determined depletion of ovarian follicles responsive to gonadotropins. ...
B2B Gynecology
... Menopause occurs at ~51 years of age as a result of a genetically determined depletion of ovarian follicles responsive to gonadotropins. ...
... Menopause occurs at ~51 years of age as a result of a genetically determined depletion of ovarian follicles responsive to gonadotropins. ...
INFERTILITY
... cervical cap, which the patient uses at home by placing the sperm inside the cap and putting the conception device on the cervix, or intrauterine insemination (IUI), in which the doctor introduces sperm into the uterus during ovulation, via a catheter. In these methods, fertilization occurs inside t ...
... cervical cap, which the patient uses at home by placing the sperm inside the cap and putting the conception device on the cervix, or intrauterine insemination (IUI), in which the doctor introduces sperm into the uterus during ovulation, via a catheter. In these methods, fertilization occurs inside t ...
Hormone Review Guide
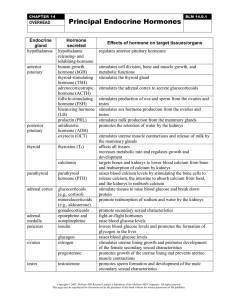
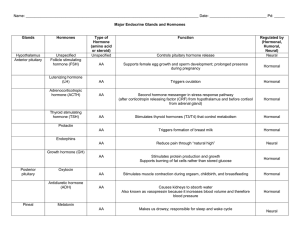
... Influences the metabolism of glucose, protein, and fat in response to conditions that stress the body and require a greater supply of energy in the bloodstream Production of androgens; stimulate male characteristics and precursor for estrogen Increases blood levels of glucose by stimulating the brea ...
... Influences the metabolism of glucose, protein, and fat in response to conditions that stress the body and require a greater supply of energy in the bloodstream Production of androgens; stimulate male characteristics and precursor for estrogen Increases blood levels of glucose by stimulating the brea ...
File - Patricia Schwandt Courses
... stimulates cell division, bone and muscle growth, and metabolic functions stimulates the thyroid gland stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids stimulates production of ova and sperm from the ovaries and testes stimulates sex hormone production from the ovaries and testes stimulates ...
... stimulates cell division, bone and muscle growth, and metabolic functions stimulates the thyroid gland stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids stimulates production of ova and sperm from the ovaries and testes stimulates sex hormone production from the ovaries and testes stimulates ...
Egg Donor Consent
... during egg retrievals. The incidence of major bleeding problems has been estimated to be less than 0.1%. Major bleeding will frequently require surgical repair and possibly loss of the ovary. The need for blood transfusion is rare. (Although very rare, review of the world experience with IVF indicat ...
... during egg retrievals. The incidence of major bleeding problems has been estimated to be less than 0.1%. Major bleeding will frequently require surgical repair and possibly loss of the ovary. The need for blood transfusion is rare. (Although very rare, review of the world experience with IVF indicat ...
FERTIVITRO that was founded in March, 2001 has the goa
... that implantation takes place (when the pre•embryo fixes itself in the uterus) and where the fetus develops. Uterine alterations are formed inside the uterus per se, as well inside the endometrium. Inside the uterus it is possible to find malformations (alterations in its embrionary development), tu ...
... that implantation takes place (when the pre•embryo fixes itself in the uterus) and where the fetus develops. Uterine alterations are formed inside the uterus per se, as well inside the endometrium. Inside the uterus it is possible to find malformations (alterations in its embrionary development), tu ...
REGULATION cont. THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... males (deep voice, facial and body hair, and the male body form) ...
... males (deep voice, facial and body hair, and the male body form) ...
REGULATION cont. THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... males (deep voice, facial and body hair, and the male body form) ...
... males (deep voice, facial and body hair, and the male body form) ...
File
... Stimulates reabsorption of sodium (and therefore water) into the blood and the release of potassium into the urine ...
... Stimulates reabsorption of sodium (and therefore water) into the blood and the release of potassium into the urine ...
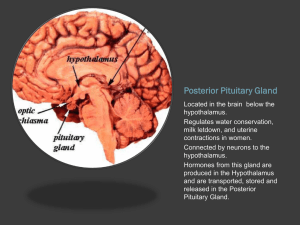
Pituitary gland
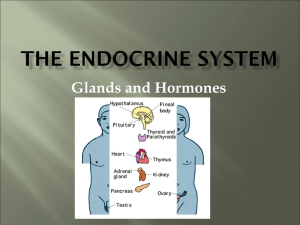
... Basic Endocrine Anatomy Some important endocrine glands 1. Hypothalamus – located in floor and walls of third ventricle, secretes hormones which affect pituitary gland secretion 2. Pituitary gland – sort of a “master gland”, hormones affect many other glands 3. Thyroid – located anterior to larynx, ...
... Basic Endocrine Anatomy Some important endocrine glands 1. Hypothalamus – located in floor and walls of third ventricle, secretes hormones which affect pituitary gland secretion 2. Pituitary gland – sort of a “master gland”, hormones affect many other glands 3. Thyroid – located anterior to larynx, ...
Lecture 22 - Abnormal uterine bleeding
... Abnormal uterine bleeding: change in the frequency of menses, the duration of flow (>7days), and the amount of blood loss (>80ml) Present in ~10-20% of women >30 y. old Menorrhagia: heavy or prolonged, but regular bleeding Metrorrhagia: irregular bleeding, intermenstrual bleeding, spotting, or ...
... Abnormal uterine bleeding: change in the frequency of menses, the duration of flow (>7days), and the amount of blood loss (>80ml) Present in ~10-20% of women >30 y. old Menorrhagia: heavy or prolonged, but regular bleeding Metrorrhagia: irregular bleeding, intermenstrual bleeding, spotting, or ...
Endocrine system notes
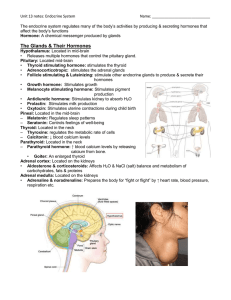
... Parathyroid: Located in the neck – Parathyroid hormone: ↑ blood calcium levels by releasing calcium from bone. • Goiter: An enlarged thyroid Adrenal cortex: Located on the kidneys • Aldosterone & corticosteroids: Affects H2O & NaCl (salt) balance and metabolism of carbohydrates, fats & proteins Adre ...
... Parathyroid: Located in the neck – Parathyroid hormone: ↑ blood calcium levels by releasing calcium from bone. • Goiter: An enlarged thyroid Adrenal cortex: Located on the kidneys • Aldosterone & corticosteroids: Affects H2O & NaCl (salt) balance and metabolism of carbohydrates, fats & proteins Adre ...
Normal Menstrual Physiology
... P concentrations during the luteal phase Inhibin A is also produced by the corpus luteum, and serum concentrations of inhibin A peak in the mid-luteal phase Inhibin B secretion is virtually absent and serum leptins are highest during luteal phase ...
... P concentrations during the luteal phase Inhibin A is also produced by the corpus luteum, and serum concentrations of inhibin A peak in the mid-luteal phase Inhibin B secretion is virtually absent and serum leptins are highest during luteal phase ...
Dear Patient - Center for Reproductive Medicine
... side effects, including hot flashes, abdominal distention, bloating, headaches and visual changes. Gonadotropins (e.g., Repronex, Menopur, Gonal-F, Follistim, Bravelle) may have side effects, including over-stimulation of the ovaries, leading to a condition called Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome ( ...
... side effects, including hot flashes, abdominal distention, bloating, headaches and visual changes. Gonadotropins (e.g., Repronex, Menopur, Gonal-F, Follistim, Bravelle) may have side effects, including over-stimulation of the ovaries, leading to a condition called Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome ( ...
endocrine system review – answer key
... cells be located? The adrenal cortex to stimulate the release of its hormones. 6. What types of feedback mechanisms are involved in the maintenance of homeostasis? 7. How would a person be affected if their pancreas produced no insulin? What disease would that person have? How could that disease be ...
... cells be located? The adrenal cortex to stimulate the release of its hormones. 6. What types of feedback mechanisms are involved in the maintenance of homeostasis? 7. How would a person be affected if their pancreas produced no insulin? What disease would that person have? How could that disease be ...
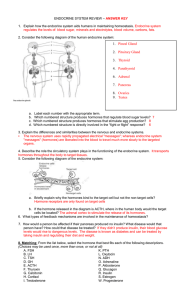
1. Pineal Gland 2. Pituitary Gland 3. Thyroid 4. Parathyroid 6
... cells be located? The adrenal cortex to stimulate the release of its hormones. 6. What types of feedback mechanisms are involved in the maintenance of homeostasis? 7. How would a person be affected if their pancreas produced no insulin? What disease would that person have? How could that disease be ...
... cells be located? The adrenal cortex to stimulate the release of its hormones. 6. What types of feedback mechanisms are involved in the maintenance of homeostasis? 7. How would a person be affected if their pancreas produced no insulin? What disease would that person have? How could that disease be ...
Chemical Regulation Endocrine System communication
... insulin which leads to increase blood sugar coma death if not medicated ...
... insulin which leads to increase blood sugar coma death if not medicated ...
Vocabulary for Test: Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... Effectors - structures that carry out responses to stimuli; muscles and glands Endocrine Gland - the ductless glands that make and release hormones into the blood Estrogen - a hormone secreted by the ovaries that promotes development of female secondary sexual characteristics and regulates the repro ...
... Effectors - structures that carry out responses to stimuli; muscles and glands Endocrine Gland - the ductless glands that make and release hormones into the blood Estrogen - a hormone secreted by the ovaries that promotes development of female secondary sexual characteristics and regulates the repro ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.