* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download INFERTILITY
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
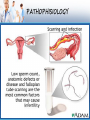
INFERTILITY د.الق سعيد العارضي INFERTILITY • Infertility is the inability to conceive a child. A couple may be considered infertile if, after two years of regular sexual intercourse, without contraception, the woman has not become pregnant (and there is no other reason, such as breastfeeding or postpartum amenorrhoea). Primary infertility is infertility in a couple who have never had a child. Secondary infertility is failure to conceive following a previous pregnancy. PREVALANCE • 15% of married couples complaining of inability to conceive . • By simple advise within 6 month , 60% will conceive , within 1 year . PATHOPHISIOLOGY INFERTILITY • The fertility depends on several factors : 1. Mother age > 35 year , sever decline in the ability to conceive . 2. FSH level in male and female . 3. If there is no previous pregnancy is worser . 4. BMI . 5. Smoking . 6. Drugs . 7. Male factors . PATHOPHISIOLOGY PATHOPHISIOLOGY General factors affecting both sex : • Diabetes mellitus, thyroid disorders, adrenal disease. • Hypothalamic-pituitary factors • Hyperprolactinemia • Hypopituitarism • The presence of anti-thyroid antibodies is associated with an increased risk of unexplained subfertility. • Environmental factors Toxins such as glues, volatile organic solvents or silicones, physical agents, chemical dusts, and pesticides, Tobacco smokers are 60% more likely to be infertile than non-smokers. PATHOPHISIOLOGY FEMALE FACTORS : Ovarian factors • Polycystic ovary syndrome. • Anovulation : Female infertility caused by anovulation is called "anovulatory infertility", as opposed to "ovulatory infertility" in which ovulation is present. • Diminished ovarian reserve. • Premature menopause • Menopause • Luteal dysfunction • Gonadal dysgenesis (Turner syndrome) • Ovarian cancer PATHOPHISIOLOGY PATHOPHISIOLOGY FEMALE FACTORS : Tubal (ectopic)/peritoneal factors • Endometriosis can lead to anatomical distortions and adhesions( has been suggested that endometriotic lesions release factors which are detrimental to gametes or embryos, or, alternatively, endometriosis may more likely develop in women who fail to conceive for other reasons and thus be a secondary phenomenon). • Pelvic adhesions • Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID, usually due to chlamydia) • Tubal occlusion • Tubal dysfunction PATHOPHISIOLOGY FEMALE FACTORS : Uterine factors 1.Uterine malformations 2.Uterine fibroids (leiomyoma) 3.Asherman's Syndrome] Cervical factors 1.Cervical stenosis 2.Antisperm antibodies 3.Non-receptive cervical mucus Vaginal factors 1.Vaginismus 2.Vaginal obstruction PATHOPHISIOLOGY Male factors : • Disorder of spermatogenesis • impaired sperm transport • Ejaculatory dysfunction • Immune factors • infections PATHOPHISIOLOGY MANAGEMENT Diagnosis of infertility begins with a medical history and physical exam : History about : • Duration of infertility • Age of female • Life style • Regularity of sexual intercourse • Any medical illness • Hx of pelvic surgery • Drug history of both male and female • Nutritional history • Menstrual history MANAGEMENT Examination : Examination of female : • Secondary sexual charecterstics • Abnormal fusion of labia majora and minora • Hypertrophy of clitoris Examination of male : • • • • Hypogonadism Abscent testis , undescended testis Abnormality of shape of external genitalia Abscense of pubic hair , axillary hair or gynaecomastia MANAGEMENT INVESTIGATION : • Lab tests • hormone testing, to measure levels of female hormones at certain times during a menstrual cycle • day 2 or 3 measure of FSH and estrogen, to assess ovarian reserve • measurements of thyroid function (a thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) level of between 1 and 2 is considered optimal for conception) • measurement of progesterone in the second half of the cycle to help confirm ovulation MANAGEMENT Examination and imaging : • • • • • • • an endometrial biopsy, to verify ovulation and inspect the lining of the uterus laparoscopy, which allows the provider to inspect the pelvic organs fertiloscopy, a relatively new surgical technique used for early diagnosis (and immediate treatment) Pap smear, to check for signs of infection pelvic exam, to look for abnormalities or infection a postcoital test, which is done soon after intercourse to check for problems with sperm surviving in cervical mucous (not commonly used now because of test unreliability) special X-ray tests MANAGEMENT Investigations for male : • Seminal fluid analysis • Hormonal analysis ( FSH , LH , prolactine and testesterone ) • Check for liver function • Check for renal function • Bloob sugar in case of DM MANAGEMENT TREATMENT : Medical treatments • Medical treatment of infertility generally involves the use of fertility medication, medical device, surgery, or a combination of the following. • If the sperm are of good quality and the mechanics of the woman's reproductive structures are good (patent fallopian tubes, no adhesions or scarring), physicians may start by prescribing a course of ovarian stimulating medication. MANAGEMENT • The physician may also suggest using a conception cap cervical cap, which the patient uses at home by placing the sperm inside the cap and putting the conception device on the cervix, or intrauterine insemination (IUI), in which the doctor introduces sperm into the uterus during ovulation, via a catheter. In these methods, fertilization occurs inside the body. • If conservative medical treatments fail to achieve a full term pregnancy, the physician may suggest the patient undergo in vitro fertilization (IVF). IVF and related technique (ICSI) are called assisted reproductive technology (ART) techniques. MANAGEMENT • ART techniques generally start with stimulating the ovaries to increase egg production. After stimulation, the physician surgically extracts one or more eggs from the ovary, and unites them with sperm in a laboratory setting, with the intent of producing one or more embryos. Fertilization takes place outside the body, and the fertilized egg is reinserted into the woman's reproductive tract, in a procedure called embryo transfer. • Other medical techniques are e.g. tuboplasty, assisted hatching, and Preimplantation genetic diagnosis.