* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cardiac physiology wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
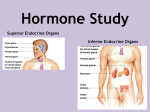
Name: __________________________________________________________________________________ Date: ___________________________ Pd: _____ Major Endocrine Glands and Hormones Glands Hormones Hypothalamus Anterior pituitary Unspecified Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) Type of Hormone (amino acid or steroid) Unspecified Function Controls pituitary hormone release Regulated by (Hormonal, Humoral, Neural) Neural AA Supports female egg growth and sperm development; prolonged presence during pregnancy Hormonal Lutenizing hormone (LH) AA Triggers ovulation Hormonal Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) AA Second hormone messenger in stress response pathway (after corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) from hypothalamus and before cortisol from adrenal gland) Hormonal AA Stimulates thyroid hormones (T3/T4) that control metabolism Hormonal AA Triggers formation of breast milk Hormonal AA Reduce pain through “natural high” Neural AA Stimulates protein production and growth Supports burning of fat cells rather than stored glucose Hormonal AA Stimulates muscle contraction during orgasm, childbirth, and breastfeeding Hormonal AA Causes kidneys to absorb water Also known as vasopressin because it increases blood volume and therefore blood pressure Hormonal Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) Prolactin Endorphins Growth hormone (GH) Posterior pituitary Oxytocin Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Pineal Melatonin AA Makes us drowsy; responsible for sleep and wake cycle Neural Thyroid Thyroid hormones (T3/T4) AA Triggers burning of glucose Hormonal Calcitonin Parathyroid Thymus Adrenal cortex Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Pancreas Reduces blood calcium by stimulating osteoblasts to deposit calcium into bone Humoral AA Increases blood calcium by stimulating osteoclasts to break down and release calcium in bone Humoral AA Triggers development of T lymphocytes (white blood cells) Unknown S Stimulates reabsorption of sodium (and therefore water) into the blood and the release of potassium into the urine Hormonal S Increases blood glucose (last step in stress response pathway) Also, reduces inflammation Hormonal (See below) (See below) S Stimulates fight or flight response Neural AA Decreases blood glucose by converting it to glycogen stored in kidney Humoral AA Increases blood glucose by converting glycogen stored in kidney to glucose Humoral S Triggers development of female secondary sex characteristics Also important in keeping a pregnancy Homornal S Triggers menstrual cycle or ensures body doesn’t naturally abort during pregnancy Hormonal Triggers sperm formation as well as the development of male secondary sex characteristics Hormonal Thymosin Aldosterone Cortisone/ Cortisol Adrenal medulla AA Androgens and estrogens Epinephrine/ Norepinephrine (See below) Insulin Glucagon Ovaries Estrogen Progesterone Testes Androgens Steroid