Chapter 3: Matter and Atomic Structure
... composed. For example, both oxygen and hydrogen are gases at room temperature, but in combination they form water, a liquid. For most elements, an atom is chemically stable when its outermost energy level is full. We know this is true because the most stable elements are the gases helium, neon, and ...
... composed. For example, both oxygen and hydrogen are gases at room temperature, but in combination they form water, a liquid. For most elements, an atom is chemically stable when its outermost energy level is full. We know this is true because the most stable elements are the gases helium, neon, and ...
chap03 Matter and Atomic Structure
... composed. For example, both oxygen and hydrogen are gases at room temperature, but in combination they form water, a liquid. For most elements, an atom is chemically stable when its outermost energy level is full. We know this is true because the most stable elements are the gases helium, neon, and ...
... composed. For example, both oxygen and hydrogen are gases at room temperature, but in combination they form water, a liquid. For most elements, an atom is chemically stable when its outermost energy level is full. We know this is true because the most stable elements are the gases helium, neon, and ...
Name Block Hon 1 Chemistry I – Ms. Elder Chapter 3 Atomic
... 3-4 Changes in the Nucleus What changes accompany nuclear reactions? What is radioactivity? Nuclear Reactions Change the Produces ...
... 3-4 Changes in the Nucleus What changes accompany nuclear reactions? What is radioactivity? Nuclear Reactions Change the Produces ...
Atomic Theory Slideshows
... Each line is part of the spectra, and is like a UNIQUE finger print for that atom or compound. Scientists (and you too) will be able to determine what atoms are present by what spectra is emitted by unknown substances. We just compare the spectra measured, to the known spectrographs. This can be use ...
... Each line is part of the spectra, and is like a UNIQUE finger print for that atom or compound. Scientists (and you too) will be able to determine what atoms are present by what spectra is emitted by unknown substances. We just compare the spectra measured, to the known spectrographs. This can be use ...
Topic 2 Atomic Structure File
... 6. If the mass number of the atom of a given element is known, the number of neutrons in its nucleus can be calculated by subtracting the _______________________ from the _______________________. For example, if an atom of the element sodium, atomic number 11, has a mass of 23, the atom has ________ ...
... 6. If the mass number of the atom of a given element is known, the number of neutrons in its nucleus can be calculated by subtracting the _______________________ from the _______________________. For example, if an atom of the element sodium, atomic number 11, has a mass of 23, the atom has ________ ...
Chapter 2 Expanded Notes
... it can be classified as, so an atom has and retains the identity of that element. Can atoms be broken down at all? Yes, they can be split into their smaller fundamental particles, but this is technically a nuclear reaction (fission or fusion), not chemical, and the atoms will no longer have the iden ...
... it can be classified as, so an atom has and retains the identity of that element. Can atoms be broken down at all? Yes, they can be split into their smaller fundamental particles, but this is technically a nuclear reaction (fission or fusion), not chemical, and the atoms will no longer have the iden ...
Masses of Atoms
... Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Atomic Mass ~ number of neutrons AND number of protons Isotope ~ atoms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons Carbon - 12 (6 protons, 6 neutrons) Carbon - 14 (6 protons, 8 neutrons) ...
... Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Atomic Mass ~ number of neutrons AND number of protons Isotope ~ atoms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons Carbon - 12 (6 protons, 6 neutrons) Carbon - 14 (6 protons, 8 neutrons) ...
atomic - Humble ISD
... mass of one proton or one neutron Because of this, an atom’s mass is nearly equal to the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus ...
... mass of one proton or one neutron Because of this, an atom’s mass is nearly equal to the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus ...
Atomic Structure Worksheet
... b. An orbital can contain a maximum of two electrons. c. An electron cloud represents all the orbitals in an atom. d. An atom’s lowest energy level has only one orbital. ____ 16. The glowing of a neon light is caused by electrons emitting energy as they a. move from lower to higher energy c. move fr ...
... b. An orbital can contain a maximum of two electrons. c. An electron cloud represents all the orbitals in an atom. d. An atom’s lowest energy level has only one orbital. ____ 16. The glowing of a neon light is caused by electrons emitting energy as they a. move from lower to higher energy c. move fr ...
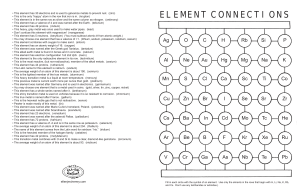
element connections
... • This heavy, gray metal was once used to make water pipes. (lead) • Don’t confuse this element with magnesium! (manganese) • This element has 5 neutrons. (beryllium) (You must subtract atomic # from atomic weight.) • You may choose one element that has a valence of +1. (lithium, sodium, potassium, ...
... • This heavy, gray metal was once used to make water pipes. (lead) • Don’t confuse this element with magnesium! (manganese) • This element has 5 neutrons. (beryllium) (You must subtract atomic # from atomic weight.) • You may choose one element that has a valence of +1. (lithium, sodium, potassium, ...
Name: 1) The modern model of the atom is based on the work of A
... B) An atom has hardly any empty space, and the nucleus has a positive charge. C) An atom is mainly empty space, and the nucleus has a negative charge. D) An atom has hardly any empty space, and the nucleus has a negative charge. ...
... B) An atom has hardly any empty space, and the nucleus has a positive charge. C) An atom is mainly empty space, and the nucleus has a negative charge. D) An atom has hardly any empty space, and the nucleus has a negative charge. ...
Historical Development of the Periodic Table Periodic Table of the
... properties of the elements vary periodically with increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the ga ...
... properties of the elements vary periodically with increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the ga ...
Historical Development of the Periodic Table
... increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the gaps he had left. ...
... increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the gaps he had left. ...
Chapter 1 (Matter and Measurement) Objectives
... The following California State Standards for Chemistry are met by the objectives above: 1. The periodic table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. As a basis for understanding ...
... The following California State Standards for Chemistry are met by the objectives above: 1. The periodic table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. As a basis for understanding ...
Atomic Electron Configurations and Chapter 8 Chemical Periodicity
... No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. ¾ Two electrons (max) per orbital ¾ Maximize parallel spins when filling a subshell ¾ If more than one orbital in a subshell is available, electrons will fill empty orbitals in the subshell first. (Hund’s Rul ...
... No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. ¾ Two electrons (max) per orbital ¾ Maximize parallel spins when filling a subshell ¾ If more than one orbital in a subshell is available, electrons will fill empty orbitals in the subshell first. (Hund’s Rul ...
Chapter42015.1 STUDENT
... A. Noble gases – Family of elements on the periodic table in ____________________. B. The noble gases all have their outermost energy levels filled with electrons. C. When an atom’s outermost energy level is filled, it is called “_________________.” D. Stable is a condition where change is not likel ...
... A. Noble gases – Family of elements on the periodic table in ____________________. B. The noble gases all have their outermost energy levels filled with electrons. C. When an atom’s outermost energy level is filled, it is called “_________________.” D. Stable is a condition where change is not likel ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... In 1869, a Russian chemist named Dmitri I. Mendeleev (1834–1907) discovered that elements exhibit a repeating pattern of properties when organized in order of increasing atomic mass. He called this observation the periodic law. Mendeleyev arranged the elements in different ways to determine if a rel ...
... In 1869, a Russian chemist named Dmitri I. Mendeleev (1834–1907) discovered that elements exhibit a repeating pattern of properties when organized in order of increasing atomic mass. He called this observation the periodic law. Mendeleyev arranged the elements in different ways to determine if a rel ...
Chapter 10 Section 1 Development of the Atomic Theory
... Rutherford proposed that: In the center of the atom is a tiny, positively charged part called the nucleus. ...
... Rutherford proposed that: In the center of the atom is a tiny, positively charged part called the nucleus. ...
The Mole - My CCSD
... We come here to be philosophers, and I hope you will always remember that whenever a result happens, especially if it be new, you should say, “What is the cause? Why does it occur?” and you will, in the course of time, find out the reason. -Michael Faraday Bires, 2010 ...
... We come here to be philosophers, and I hope you will always remember that whenever a result happens, especially if it be new, you should say, “What is the cause? Why does it occur?” and you will, in the course of time, find out the reason. -Michael Faraday Bires, 2010 ...
Valence Electrons - Warren County Public Schools
... •I can predict chemical reactivity for an element based on its number of valence electrons and location on periodic table. •I can predict the charge for an element (ion) to reach maximum stability. •I can distinguish between metallic and non-metallic properties. •I can understand how the periodic ta ...
... •I can predict chemical reactivity for an element based on its number of valence electrons and location on periodic table. •I can predict the charge for an element (ion) to reach maximum stability. •I can distinguish between metallic and non-metallic properties. •I can understand how the periodic ta ...
(Neon) - PowerPoint Presentation
... Discoverers: Sir William Ramsay and M.W. Travers Discovered in 1898 Predicted Existence: 1897 Discovered while studying air ...
... Discoverers: Sir William Ramsay and M.W. Travers Discovered in 1898 Predicted Existence: 1897 Discovered while studying air ...
OCR A Level Physics B Delivery Guide Learner Resource 1: Atomic
... The number x is often called the mass number and gives an indication of the relative mass of the atom. It can also be called the nucleon number because it is equal to the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of the atom. The word nucleon covers both neutrons and protons. The number z is the ...
... The number x is often called the mass number and gives an indication of the relative mass of the atom. It can also be called the nucleon number because it is equal to the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of the atom. The word nucleon covers both neutrons and protons. The number z is the ...
Section 2 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table Chapter 5
... • Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appeared at regular intervals. • Repeating patterns are referred to as periodic. • Mendeleev created a table in which elements with similar properties were g ...
... • Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass, certain similarities in their chemical properties appeared at regular intervals. • Repeating patterns are referred to as periodic. • Mendeleev created a table in which elements with similar properties were g ...
Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons, Neutrons, Electrons Proton
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...