10/2/2013 1 5 Early Atomic Theory and Structure Chapter Outline
... Dalton’s theory of atoms, proposed in the early 1800s, states: 1. Elements are composed of small, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical in mass and size. 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their mass and size. 4. Compounds are formed by combining two or ...
... Dalton’s theory of atoms, proposed in the early 1800s, states: 1. Elements are composed of small, indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical in mass and size. 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their mass and size. 4. Compounds are formed by combining two or ...
Chapter 5
... Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. Electrons are dispersed throughout the remainder of the atom (mainly open space). Neutral atoms contain the same number of protons and neutrons to maintain charge balance. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. Electrons are dispersed throughout the remainder of the atom (mainly open space). Neutral atoms contain the same number of protons and neutrons to maintain charge balance. © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
Advanced Chemistry Midterm
... d. electrons 72. Under what conditions can two electrons occupy the same orbital? a. never b. if they have opposite spins c. if they have parallel spins d. if they have different principal quantum numbers 73. The relationship in which the physical and chemical properties of elements show a periodic ...
... d. electrons 72. Under what conditions can two electrons occupy the same orbital? a. never b. if they have opposite spins c. if they have parallel spins d. if they have different principal quantum numbers 73. The relationship in which the physical and chemical properties of elements show a periodic ...
ppt notes
... different than A and BA element Atoms of element A and B can be can be physically chemically combined mixed together as a compound ...
... different than A and BA element Atoms of element A and B can be can be physically chemically combined mixed together as a compound ...
02 Atomic Structure [ppt 1MB]
... a substance that is made up of the same kind of atoms is an element I can describe the basic structure of an atom and state the location and charge of the proton, electron and neutron within the atom structure I can state the relative masses of the proton, neutron and electron. I can explain what is ...
... a substance that is made up of the same kind of atoms is an element I can describe the basic structure of an atom and state the location and charge of the proton, electron and neutron within the atom structure I can state the relative masses of the proton, neutron and electron. I can explain what is ...
Name
... 2. A nighttime cold medicine is 22% alcohol (by volume). How many mL of alcohol are in a 250 mL bottle of this cold medicine? 3. Hydrogen peroxide is sold as a 3.0% (by mass) solution. The rest of the solution is water. How many grams of hydrogen peroxide are in 250 g of this solution? 4. A compound ...
... 2. A nighttime cold medicine is 22% alcohol (by volume). How many mL of alcohol are in a 250 mL bottle of this cold medicine? 3. Hydrogen peroxide is sold as a 3.0% (by mass) solution. The rest of the solution is water. How many grams of hydrogen peroxide are in 250 g of this solution? 4. A compound ...
UNIT NUM="1" ID="UN
... three isotopes of carbon have 6 protons; otherwise, they would not be carbon. Although the isotopes of an element have slightly different masses, they behave identically in chemical reactions. (The number usually given as the atomic mass of an element, such as 22.9898 daltons for sodium, is actually ...
... three isotopes of carbon have 6 protons; otherwise, they would not be carbon. Although the isotopes of an element have slightly different masses, they behave identically in chemical reactions. (The number usually given as the atomic mass of an element, such as 22.9898 daltons for sodium, is actually ...
Student Copy Study Guide Introduction to Periodic
... 19.The atomic number of an element is the total number of which particles in the nucleus? a. neutrons b. protons c. electrons d. protons and electrons 20. Who was the man who lived from 460 B.C.–370 B.C. and was among the first to suggest the idea of atoms? a. Atomos b. Dalton c. Democritus d. Thoms ...
... 19.The atomic number of an element is the total number of which particles in the nucleus? a. neutrons b. protons c. electrons d. protons and electrons 20. Who was the man who lived from 460 B.C.–370 B.C. and was among the first to suggest the idea of atoms? a. Atomos b. Dalton c. Democritus d. Thoms ...
electrons and the structure of atoms
... Early Models of the Atom The scientific study of the atom began with John Dalton in the early 1800s. The ancient Greek Democritus first proposed that matter is made up of small, indivisible particles that he called atoms. John Dalton made the first accepted theory on atoms almost 2000 years after th ...
... Early Models of the Atom The scientific study of the atom began with John Dalton in the early 1800s. The ancient Greek Democritus first proposed that matter is made up of small, indivisible particles that he called atoms. John Dalton made the first accepted theory on atoms almost 2000 years after th ...
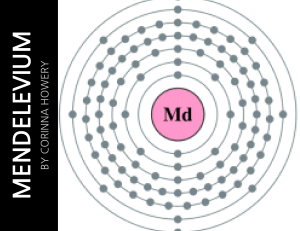
Mendelevium
... table so its atomic number is 101. There are 101 protons/electrons in the nucleus and 157 neutrons. It also has 2 valence electrons. Mendelevium has 7 shells. On the periodic table, mendelevium is in the group actinide and it is radioactive. Mendeleviums state of matter is radioactive. ...
... table so its atomic number is 101. There are 101 protons/electrons in the nucleus and 157 neutrons. It also has 2 valence electrons. Mendelevium has 7 shells. On the periodic table, mendelevium is in the group actinide and it is radioactive. Mendeleviums state of matter is radioactive. ...
Introduction to Chemical Bonding
... opposite charges attract and so they stick together. The Oxidation number is the overall charge of an element once it becomes an ion. Because elements in the same family (column) have the same number of valence electrons, they will also have the same oxidation number. In your own words define and an ...
... opposite charges attract and so they stick together. The Oxidation number is the overall charge of an element once it becomes an ion. Because elements in the same family (column) have the same number of valence electrons, they will also have the same oxidation number. In your own words define and an ...
Unit 1 Notes
... 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms, which cannot be broken into smaller particles, created nor destroyed. 2. The atoms of any given element are all identical to each other and different from the atoms of other elements. 3. Atoms of different elements combine in speci ...
... 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms, which cannot be broken into smaller particles, created nor destroyed. 2. The atoms of any given element are all identical to each other and different from the atoms of other elements. 3. Atoms of different elements combine in speci ...
Плеханов В
... oxygen [51]. In the magnetic field 0,2 T maximal concentration 13CO 1,41% is observed when magnet (height 10 cm) placed on 13–16 cm from the plasma flow onset. In the magnetic field 1,2 T maximal concentration 13CO 1,7% is observed when magnet (height 5 cm) placed on 16–27 cm from the plasma flow on ...
... oxygen [51]. In the magnetic field 0,2 T maximal concentration 13CO 1,41% is observed when magnet (height 10 cm) placed on 13–16 cm from the plasma flow onset. In the magnetic field 1,2 T maximal concentration 13CO 1,7% is observed when magnet (height 5 cm) placed on 16–27 cm from the plasma flow on ...
filled in teacher version, level 1 only
... • Nuclear reactions involve the nucleus of an atom and are different from chemical reactions in that chemical reactions only involve the electrons • The rays and particles emitted in nuclear reactions are called radiation, and are emitted because the nucleus of radioactive elements is unstable • Uns ...
... • Nuclear reactions involve the nucleus of an atom and are different from chemical reactions in that chemical reactions only involve the electrons • The rays and particles emitted in nuclear reactions are called radiation, and are emitted because the nucleus of radioactive elements is unstable • Uns ...
Chemistry General v. 2016
... Relate an element’s position on the periodic table to its electron configuration. Compare an element’s relativity to that of other elements. Describe chemical reactions in terms of atomic rearrangement and /or electron configuration. Explain how the periodicity of chemical properties led to the arra ...
... Relate an element’s position on the periodic table to its electron configuration. Compare an element’s relativity to that of other elements. Describe chemical reactions in terms of atomic rearrangement and /or electron configuration. Explain how the periodicity of chemical properties led to the arra ...
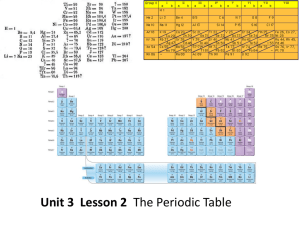
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table Essential Question: How are
... is called a group, or family. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. ...
... is called a group, or family. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. ...
Atomic Theory PPT
... 3. Atoms of different elements are different by virtue of their size and mass o 4. Chemical compounds are formed by the union of two or more atoms of different elements o 5. Atoms combine to form compounds in whole number ratios (1:2 or 2:2, etc] o 6. Atoms of two elements may combine in different r ...
... 3. Atoms of different elements are different by virtue of their size and mass o 4. Chemical compounds are formed by the union of two or more atoms of different elements o 5. Atoms combine to form compounds in whole number ratios (1:2 or 2:2, etc] o 6. Atoms of two elements may combine in different r ...
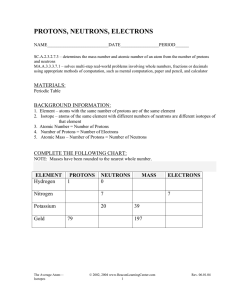
protons, neutrons, electrons
... Struggles with directions for using lab equipment. One or more safety rules are not followed. Struggles with directions for completing measurements. The student shows minimal accuracy in the use of numeric operations and is unable to complete the mass averages. The student shows minimal understandin ...
... Struggles with directions for using lab equipment. One or more safety rules are not followed. Struggles with directions for completing measurements. The student shows minimal accuracy in the use of numeric operations and is unable to complete the mass averages. The student shows minimal understandin ...
Chap 10
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
... of varying density surrounding the nucleus. • The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. ...
Ch 04 AtomicStructure
... A. amu B. gram C. angstrom D. nanogram ____ 50. Which of the following equals one atomic mass unit? A. the mass of one electron B. the mass of one helium-4 atom C. the mass of one carbon-12 atom D. one-twelfth the mass of one carbon-12 atom ____ 51. Which of the following statements is true? A. Prot ...
... A. amu B. gram C. angstrom D. nanogram ____ 50. Which of the following equals one atomic mass unit? A. the mass of one electron B. the mass of one helium-4 atom C. the mass of one carbon-12 atom D. one-twelfth the mass of one carbon-12 atom ____ 51. Which of the following statements is true? A. Prot ...
Atomic Mass
... was devised to express the masses of elements using simple numbers. The standard to which the masses of all other atoms are compared to was chosen to be the most abundant isotope of carbon, carbon-12. A mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) was assigned to the carbon12 atom. An amu is defined a ...
... was devised to express the masses of elements using simple numbers. The standard to which the masses of all other atoms are compared to was chosen to be the most abundant isotope of carbon, carbon-12. A mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) was assigned to the carbon12 atom. An amu is defined a ...
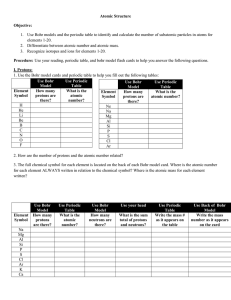
Atomic Structure_Bohr Flashcards
... 12. If protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged particles. What is the overall charge for each element listed above? 13. Suppose you do not have access to the Bohr models for the above elements. Describe how you can determine the number of electrons for a neutral element j ...
... 12. If protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged particles. What is the overall charge for each element listed above? 13. Suppose you do not have access to the Bohr models for the above elements. Describe how you can determine the number of electrons for a neutral element j ...
Elements and Compounds Chapter 3
... was devised to express the masses of elements using simple numbers. The standard to which the masses of all other atoms are compared to was chosen to be the most abundant isotope of carbon, carbon-12. A mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) was assigned to the carbon12 atom. An amu is defined a ...
... was devised to express the masses of elements using simple numbers. The standard to which the masses of all other atoms are compared to was chosen to be the most abundant isotope of carbon, carbon-12. A mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units (amu) was assigned to the carbon12 atom. An amu is defined a ...
periodic table
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...



![02 Atomic Structure [ppt 1MB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000821172_1-5bf1afd152b32026d524139a10b8292f-300x300.png)