UNIT 1 - Wiley
... outer edge of the atom would be 50 000 millimetres or 50 metres away. When discussing the sizes of atoms, a more useful unit is the nanometre. Nano- is a prefix like milli- and micro-: • A millimetre is one thousandth of a metre: mm = 10-3 m • A micrometre is one millionth of a metre: µm = 10-6 m • ...
... outer edge of the atom would be 50 000 millimetres or 50 metres away. When discussing the sizes of atoms, a more useful unit is the nanometre. Nano- is a prefix like milli- and micro-: • A millimetre is one thousandth of a metre: mm = 10-3 m • A micrometre is one millionth of a metre: µm = 10-6 m • ...
Assignment # 6 Atomic Structure Drill
... The atomic mass values listed on the periodic table are what are known as “weighted” averages of the naturally occurring masses of the isotopes. You are somewhat familiar with the notion of a weighted average. Many of your course grades are determined this way. If your teacher says to you “tests are ...
... The atomic mass values listed on the periodic table are what are known as “weighted” averages of the naturally occurring masses of the isotopes. You are somewhat familiar with the notion of a weighted average. Many of your course grades are determined this way. If your teacher says to you “tests are ...
Medical Chemistry Lecture By : Asst. Lect. Tariq-H-Almgheer
... of the helium atom contains two protons, whereas the nucleus of an oxygen atom contains eight protons. The nucleus of an atom has a positive charge because the nucleus contains protons. The charge of a nucleus is equal to the number or protons it contains. Thus, the helium nucleus has a charge of +2 ...
... of the helium atom contains two protons, whereas the nucleus of an oxygen atom contains eight protons. The nucleus of an atom has a positive charge because the nucleus contains protons. The charge of a nucleus is equal to the number or protons it contains. Thus, the helium nucleus has a charge of +2 ...
Problems - El Camino College
... c) The mass or an electron 1s about the same as the mass ofa proton. d) There are subatom ic particles in addition to the electron, proton. and neutron. e) The mass of an atom i~ uniformly distributed throughout the atom. f) Most of the particles fucd i11to the gold foi l in the Rutherford experimen ...
... c) The mass or an electron 1s about the same as the mass ofa proton. d) There are subatom ic particles in addition to the electron, proton. and neutron. e) The mass of an atom i~ uniformly distributed throughout the atom. f) Most of the particles fucd i11to the gold foi l in the Rutherford experimen ...
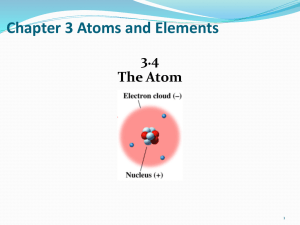
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... occurring sulfur contains several isotopes with the following abundances Isotope % abundance 32S ...
... occurring sulfur contains several isotopes with the following abundances Isotope % abundance 32S ...
Masses of Atoms
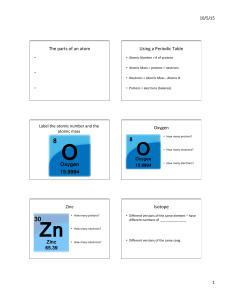
... Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Atomic Mass ~ number of neutrons AND number of protons Isotope ~ atoms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons Carbon - 12 (6 protons, 6 neutrons) Carbon - 14 (6 protons, 8 neutrons) ...
... Atomic Number ~ number of protons in the atom of an element Atomic Mass ~ number of neutrons AND number of protons Isotope ~ atoms of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons Carbon - 12 (6 protons, 6 neutrons) Carbon - 14 (6 protons, 8 neutrons) ...
Periodic Table (Wiki)
... gases).[13] Previously, they were known by roman numerals. In America, the roman numerals were followed by either an "A" if the group was in the s- or p-block, or a "B" if the group was in the d-block. The roman numerals used correspond to the last digit of today's naming convention (e.g. the group ...
... gases).[13] Previously, they were known by roman numerals. In America, the roman numerals were followed by either an "A" if the group was in the s- or p-block, or a "B" if the group was in the d-block. The roman numerals used correspond to the last digit of today's naming convention (e.g. the group ...
Chapter 3 Atoms and Elements
... Isotopes of Some Elements and Their Atomic Mass Most elements have two or more isotopes that contribute to the atomic mass of that element. ...
... Isotopes of Some Elements and Their Atomic Mass Most elements have two or more isotopes that contribute to the atomic mass of that element. ...
Mass/Mole Conversions
... • __________: atoms of the same element that have _______________ due to different numbers of __________. • _____________: the total number of _______ and _________ that make up the nucleus of an isotope ~ Isotopes are written with the _____________ written after the element name or symbol with a __ ...
... • __________: atoms of the same element that have _______________ due to different numbers of __________. • _____________: the total number of _______ and _________ that make up the nucleus of an isotope ~ Isotopes are written with the _____________ written after the element name or symbol with a __ ...
CHEMISTRY Test 3: Atomic Structure
... ____ 14. Atoms of the same element that have different masses are called a. moles. c. nuclides. b. isotopes. d. neutrons. ____ 15. Isotopes of an element contain different numbers of a. electrons. c. neutrons. b. protons. d. nuclides. ____ 16. All isotopes of hydrogen contain a. one neutron. b. two ...
... ____ 14. Atoms of the same element that have different masses are called a. moles. c. nuclides. b. isotopes. d. neutrons. ____ 15. Isotopes of an element contain different numbers of a. electrons. c. neutrons. b. protons. d. nuclides. ____ 16. All isotopes of hydrogen contain a. one neutron. b. two ...
1 CHAPTER 3. INSIDE THE ATOM What Is an Atom? A Closer View
... proton in its nucleus. Similarly, helium, atomic number 2, has two protons, lithium, atomic number 3, three protons. The atomic number gives not only the number of protons, but also the number of electrons in the neutral atom, since the number of negatively charged particles, or electrons, must be e ...
... proton in its nucleus. Similarly, helium, atomic number 2, has two protons, lithium, atomic number 3, three protons. The atomic number gives not only the number of protons, but also the number of electrons in the neutral atom, since the number of negatively charged particles, or electrons, must be e ...
Period:______ Table Number
... 46. The smallest particle of any element that you can have which still possesses all of the physical and chemical properties of that element is a single ATOM of that element. P. 10, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 47. Nearly 2000 years ago the Greek philosopher DEMOCRITUS gave us the word atom when he said ...
... 46. The smallest particle of any element that you can have which still possesses all of the physical and chemical properties of that element is a single ATOM of that element. P. 10, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 47. Nearly 2000 years ago the Greek philosopher DEMOCRITUS gave us the word atom when he said ...
Practice Packet Unit 3: Atomics - Mr. Palermo`s Flipped Chemistry
... that of a noble gas. For example, look at the electron configuration of oxygen. The unstable atom of oxygen has an electron configuration of 2-‐6. ...
... that of a noble gas. For example, look at the electron configuration of oxygen. The unstable atom of oxygen has an electron configuration of 2-‐6. ...
Aleksander Herman
... Our approach differs from the common method in that, the optimal exchange parameter αex was estimated for each atom in the periodic table [11,12]. Originally, this idea was introduced by Slater and Johnson [13]. In section IV of their paper, they have suggested a criterion for determining a value of ...
... Our approach differs from the common method in that, the optimal exchange parameter αex was estimated for each atom in the periodic table [11,12]. Originally, this idea was introduced by Slater and Johnson [13]. In section IV of their paper, they have suggested a criterion for determining a value of ...
CHAPTER 8 PERIODIC RELATIONSHIPS AMONG THE ELEMENTS
... Strategy: In the formation of a cation from the neutral atom of a representative element, one or more electrons are removed from the highest occupied n shell. In the formation of an anion from the neutral atom of a representative element, one or more electrons are added to the highest partially fill ...
... Strategy: In the formation of a cation from the neutral atom of a representative element, one or more electrons are removed from the highest occupied n shell. In the formation of an anion from the neutral atom of a representative element, one or more electrons are added to the highest partially fill ...
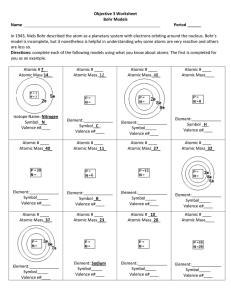
Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name Period In 1943, Niels
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
Chapter 10
... Bohr also suggested energy absorbed or emitted by an atom is quantized (has discrete fixed units). Bohr proposed that electrons can orbit the nucleus at different distances. Each orbit is a distinct, discrete (quantized) energy level. When an atom absorbs energy, the electrons can be promoted to hig ...
... Bohr also suggested energy absorbed or emitted by an atom is quantized (has discrete fixed units). Bohr proposed that electrons can orbit the nucleus at different distances. Each orbit is a distinct, discrete (quantized) energy level. When an atom absorbs energy, the electrons can be promoted to hig ...
10/2/2013 1 10 Modern Atomic Theory and the Periodic Table
... Each orbit is a distinct, discrete (quantized) energy level. When an atom absorbs energy, the electrons can be promoted to higher energy levels. When an atom emits energy, the electrons can decays to a lower energy level. ...
... Each orbit is a distinct, discrete (quantized) energy level. When an atom absorbs energy, the electrons can be promoted to higher energy levels. When an atom emits energy, the electrons can decays to a lower energy level. ...
Chapter 10
... A form of energy that runs a continuum from radio to X-rays, visible light to microwaves. Each form of radiation shares common characteristics: they display wavelike properties and travel at the same speed. Basic Properties of Waves Wavelength (λ): the distance between consecutive peaks (or troughs) ...
... A form of energy that runs a continuum from radio to X-rays, visible light to microwaves. Each form of radiation shares common characteristics: they display wavelike properties and travel at the same speed. Basic Properties of Waves Wavelength (λ): the distance between consecutive peaks (or troughs) ...