Solutions-Manual-General-Organic-Biological
... In, Sn, Sb, Te, I and Xe are main group elements. ...
... In, Sn, Sb, Te, I and Xe are main group elements. ...
4.1 Introduction to Atoms
... The Modern Atomic Model • In 1932, English scientist James Chadwick discovered another particle; the neutron. • This new particle was hard to discover because it had no charge, thus was named the neutron! • The new atomic model explains that at the center of the atom is a tiny, massive nucleus cont ...
... The Modern Atomic Model • In 1932, English scientist James Chadwick discovered another particle; the neutron. • This new particle was hard to discover because it had no charge, thus was named the neutron! • The new atomic model explains that at the center of the atom is a tiny, massive nucleus cont ...
Atomic Structure and Function
... • Gas (no definite shape nor definite volume) • Liquid (definite volume but no definite shape) • Solid (definite shape and definite volume) ...
... • Gas (no definite shape nor definite volume) • Liquid (definite volume but no definite shape) • Solid (definite shape and definite volume) ...
4 Structure of The Atom
... 1. Experiments on static electricity have proved that seemingly electrically neutral matter consists of electrically charged particles, such that positive charges in it are equal to the negative charges. 2. The electron was discovered by J.J. Thomson. 3. The proton was discovered by E. Gold ...
... 1. Experiments on static electricity have proved that seemingly electrically neutral matter consists of electrically charged particles, such that positive charges in it are equal to the negative charges. 2. The electron was discovered by J.J. Thomson. 3. The proton was discovered by E. Gold ...
BỘ GIÁO DỤC VÀ ĐÀO TẠO - THPT Chuyên Võ Nguyên Giáp
... its identity. For example, any atom containing only one proton in its nucleus is considered an atom of the element hydrogen, the number of protons in an atom is called the atomic number of that element. So, we can say that the atomic number of hydrogen is 1. A single proton is often represented by t ...
... its identity. For example, any atom containing only one proton in its nucleus is considered an atom of the element hydrogen, the number of protons in an atom is called the atomic number of that element. So, we can say that the atomic number of hydrogen is 1. A single proton is often represented by t ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... • The elements below the lanthanides are called actinides. Many of these elements are so unstable that they last for only a fraction of a second after they are made. ...
... • The elements below the lanthanides are called actinides. Many of these elements are so unstable that they last for only a fraction of a second after they are made. ...
Chemical Reactions
... Predict the products using the type of reaction as a model Balance the equation ...
... Predict the products using the type of reaction as a model Balance the equation ...
LEARNING WORKSHEET ON ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... For GCSE Chemistry you need to be able to give the FULL electron configurations for the elements up to and including Calcium (Atomic Number 20). The Periodic Table below shows the first four Periods (rows). The Atomic Number is given for each element. Remember that this tells you the number of elect ...
... For GCSE Chemistry you need to be able to give the FULL electron configurations for the elements up to and including Calcium (Atomic Number 20). The Periodic Table below shows the first four Periods (rows). The Atomic Number is given for each element. Remember that this tells you the number of elect ...
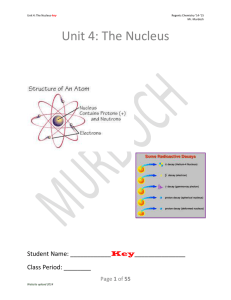
Unit 4: The Nucleus
... approximate mass of either a proton or neutron. 3. Atomic Number: The number that identifies an element, equal to an atom’s number of protons. 4. Deflect: Change in direction due to an outside force. 5. Emit: To give off something. 6. Half-life: The time it takes for half the mass of a radioactive i ...
... approximate mass of either a proton or neutron. 3. Atomic Number: The number that identifies an element, equal to an atom’s number of protons. 4. Deflect: Change in direction due to an outside force. 5. Emit: To give off something. 6. Half-life: The time it takes for half the mass of a radioactive i ...
Chapter 2
... Nuclear Stability There are many factors that determine whether a particular nucleus will radioactively decay (is unstable) or not. Based on observations, the following has been observed: 1) Nuclei with an even number of both protons and neutrons are generally more stable than those with an odd num ...
... Nuclear Stability There are many factors that determine whether a particular nucleus will radioactively decay (is unstable) or not. Based on observations, the following has been observed: 1) Nuclei with an even number of both protons and neutrons are generally more stable than those with an odd num ...
Electrons
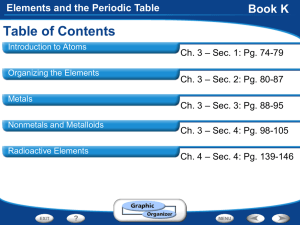
... the Periodic Table Section 1: Structure of the Atom Section 2: Masses of Atoms Section 3: The Periodic Table ...
... the Periodic Table Section 1: Structure of the Atom Section 2: Masses of Atoms Section 3: The Periodic Table ...
Science SOL CH
... Part Two – Determining the Average Mass for Different Samples of Beanium 1. Place TWO small plastic cups (one marked “A” and the other marked “B”) on the electronic scale and press the zero button. The scale should read “0.00 g” with the two cups on the pan. 2. Place 2 atoms of Isotope A into the A ...
... Part Two – Determining the Average Mass for Different Samples of Beanium 1. Place TWO small plastic cups (one marked “A” and the other marked “B”) on the electronic scale and press the zero button. The scale should read “0.00 g” with the two cups on the pan. 2. Place 2 atoms of Isotope A into the A ...
Hi Guys. Today we are going to be talking about the smallest part of
... either has to get rid of this one or has to gain 7 more. What do you think is easier for sodium to do? It is easier for sodium to lose and electron. If sodium loses an electron it is no longer a neutral charged atom, because sodium normally has 11 electrons. If it loses one it now only has 10 so th ...
... either has to get rid of this one or has to gain 7 more. What do you think is easier for sodium to do? It is easier for sodium to lose and electron. If sodium loses an electron it is no longer a neutral charged atom, because sodium normally has 11 electrons. If it loses one it now only has 10 so th ...
Lesson Plan
... Skill: students should be able to use the periodic table to determine various atomic properties such as atomic radius, ionic radius, effective nuclear charge, electron affinity, electronegativity, atomic mass and electron configuration using the periodic table. Students should also be able to descri ...
... Skill: students should be able to use the periodic table to determine various atomic properties such as atomic radius, ionic radius, effective nuclear charge, electron affinity, electronegativity, atomic mass and electron configuration using the periodic table. Students should also be able to descri ...
4 ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES __ /__ pts
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in ...
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in ...
Name
... chemical symbol, atomic number, atomic mass number, and physical and chemical properties is called the ______________________________ of elements. P. 82, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 50. The periodic table of elements was originally created by a Russian chemist named ____________________________________ ...
... chemical symbol, atomic number, atomic mass number, and physical and chemical properties is called the ______________________________ of elements. P. 82, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 50. The periodic table of elements was originally created by a Russian chemist named ____________________________________ ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2 (2015)
... 7) Which fourth period transition element has the highest atomic number? A) Ca B) Cd C) Kr D) Zn C) Sb and Te D) Po and At C) Ca D) none of the above 8) Which of the following elements are fourth period metalloids? A) Si and Ge B) Ge and As 9) Which of the following is an alkali metal? A) Al B) Fe 1 ...
... 7) Which fourth period transition element has the highest atomic number? A) Ca B) Cd C) Kr D) Zn C) Sb and Te D) Po and At C) Ca D) none of the above 8) Which of the following elements are fourth period metalloids? A) Si and Ge B) Ge and As 9) Which of the following is an alkali metal? A) Al B) Fe 1 ...
Period:______ Table Number
... 83. The number and arrangement of the electrons found in the electron cloud of an atom determines nearly all of an element’s _____________________________ properties. P. 125, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 84. The total number of electrons found in the electron cloud of an atom adds very little to the mas ...
... 83. The number and arrangement of the electrons found in the electron cloud of an atom determines nearly all of an element’s _____________________________ properties. P. 125, VCR: Atoms and Molecules 84. The total number of electrons found in the electron cloud of an atom adds very little to the mas ...
A an electron and an alpha particle B an electron and a proton C a
... empty space ® electrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus B the atom is a hard sphere ® electrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus ® most of the atom is empty space C most of the atom is empty space ® electrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus ® the atom is a hard sphere D most of the ...
... empty space ® electrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus B the atom is a hard sphere ® electrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus ® most of the atom is empty space C most of the atom is empty space ® electrons exist in orbitals outside the nucleus ® the atom is a hard sphere D most of the ...
Atoms and atomic structure - FQ-B
... down into pieces • all the atoms of a particular element are identical to each other and different from the atoms of other elements • atoms are rearranged in a chemical reaction • compounds are formed when two or more different kinds of atoms join together [molecules: a collection of two or more ato ...
... down into pieces • all the atoms of a particular element are identical to each other and different from the atoms of other elements • atoms are rearranged in a chemical reaction • compounds are formed when two or more different kinds of atoms join together [molecules: a collection of two or more ato ...
The Atom
... Each element has a limited number of isotopes that are found in nature. Some isotopes of an element have special properties because they are unstable. An unstable atom is an atom with a nucleus that will change over time. This type of isotope is radioactive. Radioactive atoms spontaneously fall apar ...
... Each element has a limited number of isotopes that are found in nature. Some isotopes of an element have special properties because they are unstable. An unstable atom is an atom with a nucleus that will change over time. This type of isotope is radioactive. Radioactive atoms spontaneously fall apar ...
Slide 1
... A Chlorine atom steals one from a sodium, forming ions and an attraction strong enough to bond them together. ...
... A Chlorine atom steals one from a sodium, forming ions and an attraction strong enough to bond them together. ...
The Periodic Table and The Periodic Law
... Noble gases are ignored. Fluorine has the largest E.N. Francium the smallest E.N. ...
... Noble gases are ignored. Fluorine has the largest E.N. Francium the smallest E.N. ...
electrons - Bryant School District
... CW: Complete all research of element/atom; be sure to research at least 3 websites and become an expert on your element... Work on your interactive poster from edu.Glogster.com site using your nickname and password that I gave you. You will include the information like your handout along with your s ...
... CW: Complete all research of element/atom; be sure to research at least 3 websites and become an expert on your element... Work on your interactive poster from edu.Glogster.com site using your nickname and password that I gave you. You will include the information like your handout along with your s ...