Chapter 4 Early Atomic Theory
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical in size, shape and mass; atoms of different elements are different. 3. Atoms of different elements combine in whole number mass ratios to form compounds. This is known as Law of Definite Proportions. Each compound has a specific mass ratio of elements. Wate ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are identical in size, shape and mass; atoms of different elements are different. 3. Atoms of different elements combine in whole number mass ratios to form compounds. This is known as Law of Definite Proportions. Each compound has a specific mass ratio of elements. Wate ...
1 Which of the following has the least mass
... C isotope D quark 2 Which of the following has the least mass in an atom? A neutron B proton C electron D nucleus 3 Which of the following showed electrons in specific, fixed orbits? A Rutherford Model B Planck Model C Bohr Model D Quantum Model 4 An atom that is electrically neutral must contain A ...
... C isotope D quark 2 Which of the following has the least mass in an atom? A neutron B proton C electron D nucleus 3 Which of the following showed electrons in specific, fixed orbits? A Rutherford Model B Planck Model C Bohr Model D Quantum Model 4 An atom that is electrically neutral must contain A ...
INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY - Chapter 1
... Calvin Coolidge recognized that chemistry makes significant contributions to our quality of life. From the structural material provided by plastics to medicines, pesticides and combustion, we use the products of chemistry all the time. However, there also sometimes have been accompanying negative co ...
... Calvin Coolidge recognized that chemistry makes significant contributions to our quality of life. From the structural material provided by plastics to medicines, pesticides and combustion, we use the products of chemistry all the time. However, there also sometimes have been accompanying negative co ...
Document
... Subscripts in (parenthesis) • represents the physical states of the compounds (elements) • Ex: (s)= solid, (l)=liquid, (g)= gas, (aq)= aqueous (dissolved in water) ...
... Subscripts in (parenthesis) • represents the physical states of the compounds (elements) • Ex: (s)= solid, (l)=liquid, (g)= gas, (aq)= aqueous (dissolved in water) ...
Table of Contents Chapter 5 Objectives Chapter 5 Mendeleev and
... • lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium • In their pure state, all of the alkali metals have a silvery appearance and are soft enough to cut with a knife. ...
... • lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium • In their pure state, all of the alkali metals have a silvery appearance and are soft enough to cut with a knife. ...
What Are Atoms, and Why Do They Join Together?
... neutrons in the nucleus of an element may vary. Most oxygen atoms have seven neutrons, but some may have slightly more or less neutrons. You cannot tell what element an atom is just by the number of neutrons. The mass of an electron is much less than the mass of a proton or neutron, and it would tak ...
... neutrons in the nucleus of an element may vary. Most oxygen atoms have seven neutrons, but some may have slightly more or less neutrons. You cannot tell what element an atom is just by the number of neutrons. The mass of an electron is much less than the mass of a proton or neutron, and it would tak ...
Answer - Test banks
... 58. (T/F) The human body and the earth’s crust are predominantly composed of carbon. F 59. (T/F) Chemical compounds are composed of atoms of different elements combined in specific ratios, such as HO1/2. F 60. (T/F) A force called a covalent bond holds the atoms in a molecule together. T 61. (T/F) A ...
... 58. (T/F) The human body and the earth’s crust are predominantly composed of carbon. F 59. (T/F) Chemical compounds are composed of atoms of different elements combined in specific ratios, such as HO1/2. F 60. (T/F) A force called a covalent bond holds the atoms in a molecule together. T 61. (T/F) A ...
Unit 2: Atoms, Moles and The Periodic Table Notes (answers)
... Atomic Number and Mass Number: Recall from the Dalton’s Atomic Theory, one of its points is that different elements have different atoms. For a long time, it was believed that the main difference between atoms of different elements is the mass number (the total mass of an atom). This is the mass cha ...
... Atomic Number and Mass Number: Recall from the Dalton’s Atomic Theory, one of its points is that different elements have different atoms. For a long time, it was believed that the main difference between atoms of different elements is the mass number (the total mass of an atom). This is the mass cha ...
Answer - Test Bank wizard
... 58. (T/F) The human body and the earth’s crust are predominantly composed of carbon. F 59. (T/F) Chemical compounds are composed of atoms of different elements combined in specific ratios, such as HO1/2. F 60. (T/F) A force called a covalent bond holds the atoms in a molecule together. T 61. (T/F) A ...
... 58. (T/F) The human body and the earth’s crust are predominantly composed of carbon. F 59. (T/F) Chemical compounds are composed of atoms of different elements combined in specific ratios, such as HO1/2. F 60. (T/F) A force called a covalent bond holds the atoms in a molecule together. T 61. (T/F) A ...
Answer - TEST BANK 360
... 58. (T/F) The human body and the earth’s crust are predominantly composed of carbon. F 59. (T/F) Chemical compounds are composed of atoms of different elements combined in specific ratios, such as HO1/2. F 60. (T/F) A force called a covalent bond holds the atoms in a molecule together. T 61. (T/F) A ...
... 58. (T/F) The human body and the earth’s crust are predominantly composed of carbon. F 59. (T/F) Chemical compounds are composed of atoms of different elements combined in specific ratios, such as HO1/2. F 60. (T/F) A force called a covalent bond holds the atoms in a molecule together. T 61. (T/F) A ...
Answer - We can offer most test bank and solution manual you need.
... 58. (T/F) The human body and the earth’s crust are predominantly composed of carbon. F 59. (T/F) Chemical compounds are composed of atoms of different elements combined in specific ratios, such as HO1/2. F 60. (T/F) A force called a covalent bond holds the atoms in a molecule together. T 61. (T/F) A ...
... 58. (T/F) The human body and the earth’s crust are predominantly composed of carbon. F 59. (T/F) Chemical compounds are composed of atoms of different elements combined in specific ratios, such as HO1/2. F 60. (T/F) A force called a covalent bond holds the atoms in a molecule together. T 61. (T/F) A ...
Materials Required
... as the students take their seats. As class begins a bag of candy for the activity will be pulled out and the students will be asked what the bag contains while emphasizing what is written on the board. For today this candy will be subatomic particles. Stimulating the recall of prerequisite learning: ...
... as the students take their seats. As class begins a bag of candy for the activity will be pulled out and the students will be asked what the bag contains while emphasizing what is written on the board. For today this candy will be subatomic particles. Stimulating the recall of prerequisite learning: ...
Chapter 2.4 Periodic properties of the elements
... Ca(g) + 599 kJ → Ca+(g) + eThe second ionization energy (IE2) is the amount of energy required to remove the second electron. For calcium, it may be represented as: Ca+(g) + 1145 kJ → Ca2+1(g) + eFor a given element, IE2 is always greater than IE1 because it is always more difficult to remove a nega ...
... Ca(g) + 599 kJ → Ca+(g) + eThe second ionization energy (IE2) is the amount of energy required to remove the second electron. For calcium, it may be represented as: Ca+(g) + 1145 kJ → Ca2+1(g) + eFor a given element, IE2 is always greater than IE1 because it is always more difficult to remove a nega ...
periodic table
... – IA are called alkali metals because the react with water to from an alkaline solution – Group IIA are called the alkaline earth metals because they are reactive, but not as reactive as Group IA. • They are also soft metals like Earth. ...
... – IA are called alkali metals because the react with water to from an alkaline solution – Group IIA are called the alkaline earth metals because they are reactive, but not as reactive as Group IA. • They are also soft metals like Earth. ...
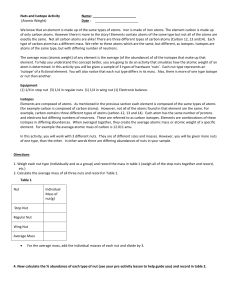
Nuts,Bolts and Isotopes- Average Atomic Mass Activity
... (for example carbon is composed of carbon atoms). However, not all of the atoms found in that element are the same. For example, carbon contains three different types of atoms (carbon-12, 13 and 14). Each atom has the same number of protons and electrons but differing numbers of neutrons. These are ...
... (for example carbon is composed of carbon atoms). However, not all of the atoms found in that element are the same. For example, carbon contains three different types of atoms (carbon-12, 13 and 14). Each atom has the same number of protons and electrons but differing numbers of neutrons. These are ...
Answer - Test Bank 1
... 58. (T/F) The human body and the earth’s crust are predominantly composed of carbon. F 59. (T/F) Chemical compounds are composed of atoms of different elements combined in specific ratios, such as HO1/2. F 60. (T/F) A force called a covalent bond holds the atoms in a molecule together. T 61. (T/F) A ...
... 58. (T/F) The human body and the earth’s crust are predominantly composed of carbon. F 59. (T/F) Chemical compounds are composed of atoms of different elements combined in specific ratios, such as HO1/2. F 60. (T/F) A force called a covalent bond holds the atoms in a molecule together. T 61. (T/F) A ...
weighted average atomic mass
... • Find out the names that 110, 111, 112, 114, and 116 have now been given. What is the latest news about element 118? • Who/what makes the decisions about element names? • How long does it take for a name to be decided upon? • Record your source(s) using MLA formatting. Read your notes about Chromat ...
... • Find out the names that 110, 111, 112, 114, and 116 have now been given. What is the latest news about element 118? • Who/what makes the decisions about element names? • How long does it take for a name to be decided upon? • Record your source(s) using MLA formatting. Read your notes about Chromat ...
printer-friendly version
... period. Moving from left to right across a given period, the valence electrons feel a stronger pull from the increased nuclear charge that pulls the valence electrons closer to the nucleus (atomic size decreases across the period). Ionization Energy. Ionization energy is the amount of energy requir ...
... period. Moving from left to right across a given period, the valence electrons feel a stronger pull from the increased nuclear charge that pulls the valence electrons closer to the nucleus (atomic size decreases across the period). Ionization Energy. Ionization energy is the amount of energy requir ...
Building Atoms Unit Interactive Science Notebook III
... 11.Hydrogen has the atomic number 1 because it has ________ proton. Itʼs symbol is ________. 12. _____________ electrons can fit in the first shell. ____________ electrons fit in the 2nd and 3rd shell. 13.______________________ have the same atomic number but different atomic mass and mass number. 1 ...
... 11.Hydrogen has the atomic number 1 because it has ________ proton. Itʼs symbol is ________. 12. _____________ electrons can fit in the first shell. ____________ electrons fit in the 2nd and 3rd shell. 13.______________________ have the same atomic number but different atomic mass and mass number. 1 ...
4 ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES __ /__ pts 1 1
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in ...
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in ...
notes - unit 2 - atomic theory_key_2012
... 1. Which of the following did Rutherford’s Gold Foil experiment prove? a. That the atom was a uniformly dense sphere. b. That the atom is mostly empty space with a dense, positive core. c. That most the atom consists of a uniform positive “pudding” with small negative particles called electrons embe ...
... 1. Which of the following did Rutherford’s Gold Foil experiment prove? a. That the atom was a uniformly dense sphere. b. That the atom is mostly empty space with a dense, positive core. c. That most the atom consists of a uniform positive “pudding” with small negative particles called electrons embe ...
Chapter 6 ppt
... • Protons, neutrons, and electrons make up atoms. • All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. • Isotopes of an element differ by the number of neutrons in the nucleus. • Atomic mass is an average of the masses of all of the naturally occurring isotopes of an elemen ...
... • Protons, neutrons, and electrons make up atoms. • All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. • Isotopes of an element differ by the number of neutrons in the nucleus. • Atomic mass is an average of the masses of all of the naturally occurring isotopes of an elemen ...
atom
... • From Aristotle to Modern Science Democritus was right, though: Matter is made of particles, which we call atoms. • An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical properties of that element. ...
... • From Aristotle to Modern Science Democritus was right, though: Matter is made of particles, which we call atoms. • An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical properties of that element. ...
10TH CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS CHEMISRY As a large
... With the developments in the field of Chemistry, various scientists attempted to classify the known elements of their times so that their study may become easier and more informative. Some of the attempts are mentioned as under: i) Division of elements into metals and non-metals: Earlier chemists re ...
... With the developments in the field of Chemistry, various scientists attempted to classify the known elements of their times so that their study may become easier and more informative. Some of the attempts are mentioned as under: i) Division of elements into metals and non-metals: Earlier chemists re ...