week 13 - My CCSD
... THE STUDENT WILL RELATE THE PERIODIC LAW TO THE POSITIONS OF ELEMENTS ON THE PERIODIC TABLE. [P.12.A.2] 5.13 THE STUDENT WILL PREDICT THE VALENCE ORBITALS FILLED IN THE EIGHT MAIN GROUPS (REPRESENTATIVE ELEMENTS). [P.12.A.9] OBJECTIVE: The student will be able to: ...
... THE STUDENT WILL RELATE THE PERIODIC LAW TO THE POSITIONS OF ELEMENTS ON THE PERIODIC TABLE. [P.12.A.2] 5.13 THE STUDENT WILL PREDICT THE VALENCE ORBITALS FILLED IN THE EIGHT MAIN GROUPS (REPRESENTATIVE ELEMENTS). [P.12.A.9] OBJECTIVE: The student will be able to: ...
- Elliott Hudson College
... Atoms consist of a central ____________ containing protons and ___________. The nucleus is _______ compared to the size of the whole atom. The nucleus is surrounded by ___________ in energy levels (also called _________). Atoms have no electric charge because they contain the same number of protons ...
... Atoms consist of a central ____________ containing protons and ___________. The nucleus is _______ compared to the size of the whole atom. The nucleus is surrounded by ___________ in energy levels (also called _________). Atoms have no electric charge because they contain the same number of protons ...
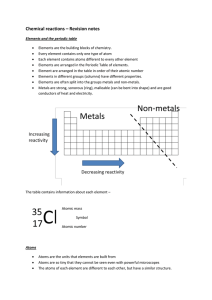
Chemical reactions revision
... A name ending in ‘...ide’ means that the compound contains two elements A name ending in ‘...ate’ means that the compound contains three elements and one is oxygen. ‘Oxygen’ does not show up in the name; the ‘ate’ is the only clue it is there You should be able to give the name of the compound forme ...
... A name ending in ‘...ide’ means that the compound contains two elements A name ending in ‘...ate’ means that the compound contains three elements and one is oxygen. ‘Oxygen’ does not show up in the name; the ‘ate’ is the only clue it is there You should be able to give the name of the compound forme ...
Isotopes
... • Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. • They can be a radioactive form of an element. – Atoms of the same element all have the same number of protons. – Isotopes of the element have different numbers of neutrons. ...
... • Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. • They can be a radioactive form of an element. – Atoms of the same element all have the same number of protons. – Isotopes of the element have different numbers of neutrons. ...
nuclear physics ppt
... A nucleon is a general term to denote a nuclear particle - that is, either a proton or a neutron. The atomic number Z of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of that element. The mass number A of an element is equal to the total number of nucleons (protons + neutrons). The mas ...
... A nucleon is a general term to denote a nuclear particle - that is, either a proton or a neutron. The atomic number Z of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of that element. The mass number A of an element is equal to the total number of nucleons (protons + neutrons). The mas ...
study guide - atomic srtucture/_classification of matter
... idea that all things were made of particles too small to see. He was laughed at. In the 1800’s John Dalton proposed the idea of the “Atomic Theory”. He had 5 theories, 3 of which are still believed today. They are: 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles too small to see 2. In reactio ...
... idea that all things were made of particles too small to see. He was laughed at. In the 1800’s John Dalton proposed the idea of the “Atomic Theory”. He had 5 theories, 3 of which are still believed today. They are: 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles too small to see 2. In reactio ...
File
... 3. An electron is a (positively charged/negatively charged) particle located outside the nucleus. 4. The modern model of an atom is called the (electron-cloud/nucleus-orbit) model. 5. Electrons that are close to the nucleus have (more energy/less energy) than electrons that are farther from the nucl ...
... 3. An electron is a (positively charged/negatively charged) particle located outside the nucleus. 4. The modern model of an atom is called the (electron-cloud/nucleus-orbit) model. 5. Electrons that are close to the nucleus have (more energy/less energy) than electrons that are farther from the nucl ...
Chapter 4: Atomic Structure
... Au is the chemical symbol for gold. How many electrons does a gold atom have ...
... Au is the chemical symbol for gold. How many electrons does a gold atom have ...
Inside the Atom
... 2. Isotopes – atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons 3. Mass number – number of protons plus number of neutrons 4. Atomic mass – the number found below the element symbol a. The average mass of an atom of an element b. The unit used for atomic mass is the atomic mass unit ...
... 2. Isotopes – atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons 3. Mass number – number of protons plus number of neutrons 4. Atomic mass – the number found below the element symbol a. The average mass of an atom of an element b. The unit used for atomic mass is the atomic mass unit ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... o Atoms are neither __________ nor _________ in any chemical reaction. o A given ____________ always has the same relative numbers and kinds of atoms. The Atom The smallest particle of an ___________ is an atom. The atom is made up of three ____________ particles: ___________, _____________, and ...
... o Atoms are neither __________ nor _________ in any chemical reaction. o A given ____________ always has the same relative numbers and kinds of atoms. The Atom The smallest particle of an ___________ is an atom. The atom is made up of three ____________ particles: ___________, _____________, and ...
30-2 Ch 3 Test Review Atomic Theory DEBRIEF KEY
... 8. Electron transitions between which 2 levels will produce the spectral line associated with the least energy? a. 2 and 1 ...
... 8. Electron transitions between which 2 levels will produce the spectral line associated with the least energy? a. 2 and 1 ...
Periodic Table - Ralph C. Mahar
... Going down a group, the ionization energy decreases due to increased atomic radius and the shielding effect. Going across a period it increases due to increasing nuclear charge. Second ionization energy- the energy required to remove a second electron from an atom. ...
... Going down a group, the ionization energy decreases due to increased atomic radius and the shielding effect. Going across a period it increases due to increasing nuclear charge. Second ionization energy- the energy required to remove a second electron from an atom. ...
Classifying Matter
... Compounds Compounds are groups of two or more elements that are bonded together. You have also seen us use the word molecule. Molecule is the general term used to describe atoms connected by chemical bonds. Every combination of atoms is a molecule. Compounds happen with atoms from different eleme ...
... Compounds Compounds are groups of two or more elements that are bonded together. You have also seen us use the word molecule. Molecule is the general term used to describe atoms connected by chemical bonds. Every combination of atoms is a molecule. Compounds happen with atoms from different eleme ...
Name: Per: ______ Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter Atoms
... etc…) from atoms of another element. 3.Atoms of different elements combine in simple, ________________________ ratios to form molecules. 4.In chemical reactions atoms can combine, ______________________ and rearrange, but not destroyed. Structure of the Atom Atoms consist of two regions: 1.Nucleus: ...
... etc…) from atoms of another element. 3.Atoms of different elements combine in simple, ________________________ ratios to form molecules. 4.In chemical reactions atoms can combine, ______________________ and rearrange, but not destroyed. Structure of the Atom Atoms consist of two regions: 1.Nucleus: ...
Unit 2 Review for Test
... 40. What elements make up a protein? 42. Name the building blocks of lipids. 43. Draw a structural diagram showing a simple representation of a fatty acid.. 44. List some types of lipids. 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule wh ...
... 40. What elements make up a protein? 42. Name the building blocks of lipids. 43. Draw a structural diagram showing a simple representation of a fatty acid.. 44. List some types of lipids. 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule wh ...
Chapter 11 and 12-2 Review/Study Guide for Test
... 5. What happens to the electrons in the atom when it becomes an ion? They are gained or lost to another atom. 6. What is an isotope? When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons from each other. 7. What determines the identity of an element? The number of protons in the nucleus ...
... 5. What happens to the electrons in the atom when it becomes an ion? They are gained or lost to another atom. 6. What is an isotope? When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons from each other. 7. What determines the identity of an element? The number of protons in the nucleus ...
chapter-7-explore-page-248-protons-neutrons
... wasn’t required. Radioactivity Becquerel shared his discovery with fellow scientists Pierre and Marie Curie. Marie Curie (1867-1934), called elements that spontaneously emit radiation radioactive. Becquerel and the Curies discovered that the radiation released by the uranium was made of energy a ...
... wasn’t required. Radioactivity Becquerel shared his discovery with fellow scientists Pierre and Marie Curie. Marie Curie (1867-1934), called elements that spontaneously emit radiation radioactive. Becquerel and the Curies discovered that the radiation released by the uranium was made of energy a ...
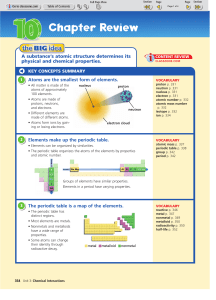
Chapter Review - BAschools.org
... 13. The modern periodic table is organized by a. size of atom b. atomic mass c. number of neutrons d. atomic number 14. Elements in a group have a. a wide range of chemical properties b. the same atomic radius c. similar chemical properties d. the same number of protons 15. Elements in a period have ...
... 13. The modern periodic table is organized by a. size of atom b. atomic mass c. number of neutrons d. atomic number 14. Elements in a group have a. a wide range of chemical properties b. the same atomic radius c. similar chemical properties d. the same number of protons 15. Elements in a period have ...
NANO-MODULE: Introduction to Chemistry Name: Date: Objectives
... • To understand what an atom is • To learn the trends that exist in the Periodic Table of Elements Key Concepts: atom, subatomic particle, nucleus, electron, proton, neutron, atomic number, atomic mass number, isotope, valence octet, metal, cation, anion, ionic bond, molecule, covalent bond, lone pa ...
... • To understand what an atom is • To learn the trends that exist in the Periodic Table of Elements Key Concepts: atom, subatomic particle, nucleus, electron, proton, neutron, atomic number, atomic mass number, isotope, valence octet, metal, cation, anion, ionic bond, molecule, covalent bond, lone pa ...
nuclear chemistry - Wood County Schools
... Fission: The splitting of an atomic nucleus into two or more smaller fragments. Fusion: The combining of two atoms to form an element of a larger atomic number. Releases more energy than fission. Chain Reaction: A self-sustaining fission process. Critical Mass: The minimum quantity of a radioactive ...
... Fission: The splitting of an atomic nucleus into two or more smaller fragments. Fusion: The combining of two atoms to form an element of a larger atomic number. Releases more energy than fission. Chain Reaction: A self-sustaining fission process. Critical Mass: The minimum quantity of a radioactive ...
Name Period Nuclear Study Packet Set 1 1. What subatomic
... sample contains 34.2 mg of K-42. How much did it contain yesterday at the same time. 4. What percent of a sample of a radioactive element whose half life is 5 years will decay after 25 years? 5. What are some ways that nuclear reactions are being used today? Do not list any ways that we have tal ...
... sample contains 34.2 mg of K-42. How much did it contain yesterday at the same time. 4. What percent of a sample of a radioactive element whose half life is 5 years will decay after 25 years? 5. What are some ways that nuclear reactions are being used today? Do not list any ways that we have tal ...
Protons
... Laura works as a consultant at a software company. The amount of her annual bonus is based upon the number of hours she works. Over summer vacation, Debbie has to read a novel for English class. She has decided to spend the same amount of time reading every day. The number of ...
... Laura works as a consultant at a software company. The amount of her annual bonus is based upon the number of hours she works. Over summer vacation, Debbie has to read a novel for English class. She has decided to spend the same amount of time reading every day. The number of ...
Development of atomic theory
... 1808. He held that all the atoms of an element are of exactly the same size and weight (see atomic weight) and are in these two respects unlike the atoms of any other element. He stated that atoms of the elements unite chemically in simple numerical ratios to form compounds. The best evidence for hi ...
... 1808. He held that all the atoms of an element are of exactly the same size and weight (see atomic weight) and are in these two respects unlike the atoms of any other element. He stated that atoms of the elements unite chemically in simple numerical ratios to form compounds. The best evidence for hi ...