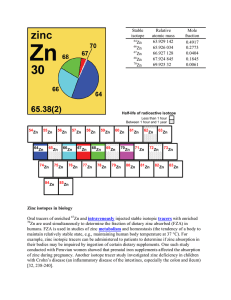
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... anthropogenic – resulting from human activity. [return] atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic weight (relative mean atomic mass) – the sum of the products of the relative atomic mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that ...
... anthropogenic – resulting from human activity. [return] atomic number (Z) – The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. atomic weight (relative mean atomic mass) – the sum of the products of the relative atomic mass and the mole fraction of each stable and long-lived radioactive isotope of that ...
Matter: A) Homogeneous Matter • Uniform and in 1 phase • Even
... Rutherford: Gold foil experiment with alpha particles (positive) bombarding a piece of gold. Most of them went through the foil, but some were deflected. Shows that the atom is mostly empty space and has a small, positive, dense center (nucleus). It disproved Thomson. Also discovered alpha, beta, an ...
... Rutherford: Gold foil experiment with alpha particles (positive) bombarding a piece of gold. Most of them went through the foil, but some were deflected. Shows that the atom is mostly empty space and has a small, positive, dense center (nucleus). It disproved Thomson. Also discovered alpha, beta, an ...
Name Period _____ Chemistry Review
... Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement true. ____ 13. A change that produces one or more new substances is called a physical change. _________________________ ____ 14. A(n) pure substance is made o ...
... Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement true. ____ 13. A change that produces one or more new substances is called a physical change. _________________________ ____ 14. A(n) pure substance is made o ...
Electron Arrangement
... • In an experiment working with neon atoms, Thomson discovered some of the atoms had different masses. • Because they all were neon, the number of protons and electrons were all the same. • Therefore, the difference in mass was due to different numbers of neutrons. • He called these different atoms ...
... • In an experiment working with neon atoms, Thomson discovered some of the atoms had different masses. • Because they all were neon, the number of protons and electrons were all the same. • Therefore, the difference in mass was due to different numbers of neutrons. • He called these different atoms ...
11/13 atoms powerpoint
... Cathode ray tubes pass electricity through a gas that is contained at a very low pressure. ...
... Cathode ray tubes pass electricity through a gas that is contained at a very low pressure. ...
chapter2 2012 (no naming) 2014
... Law of Conservation of Mass Matter is conserved in chemical reactions This applies to all chemical reactions but DOES NOT ...
... Law of Conservation of Mass Matter is conserved in chemical reactions This applies to all chemical reactions but DOES NOT ...
Chemistry Test Study Guide
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus.(Protons and Neutrons) 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? ...
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus.(Protons and Neutrons) 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom
... Bohr incorporated Rutherford’s planetary model but made some restrictions based on the spectra he observed 1) atoms have specific energy levels called stationary states (fixed circular orbit) 2) while in a specific energy state, the electrons do not emit energy 3) electrons can change orbits b ...
... Bohr incorporated Rutherford’s planetary model but made some restrictions based on the spectra he observed 1) atoms have specific energy levels called stationary states (fixed circular orbit) 2) while in a specific energy state, the electrons do not emit energy 3) electrons can change orbits b ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... Metals- Found on the left hand side of the stair step on the periodic table, usually in the solid form, (except mercury), are lustrous (shiny), ductile (drawn into wires), malleable (Pounded into sheets), and are good conductors of heat and electricity. Non-Metals- Found on the right hand side of th ...
... Metals- Found on the left hand side of the stair step on the periodic table, usually in the solid form, (except mercury), are lustrous (shiny), ductile (drawn into wires), malleable (Pounded into sheets), and are good conductors of heat and electricity. Non-Metals- Found on the right hand side of th ...
ChemFinalgeocities
... Which of the following has the greatest density? a. a rock c. oil b. oxygen d. ice A 26.0-g sample of a liquid was found to have a volume of 13.0 mL. What is the density of the liquid? a. 0.500 g/mL c. 39.0 g/mL b. 2.00 g/mL d. 338 g/mL Coal burns in a furnace, producing light and heat. This reactio ...
... Which of the following has the greatest density? a. a rock c. oil b. oxygen d. ice A 26.0-g sample of a liquid was found to have a volume of 13.0 mL. What is the density of the liquid? a. 0.500 g/mL c. 39.0 g/mL b. 2.00 g/mL d. 338 g/mL Coal burns in a furnace, producing light and heat. This reactio ...
AP Projectile Motion
... approximate mass of a single proton or neutron is 1 amu mass of an atom in atomic mass units is simply the sum of its protons and neutrons and is known as the atomic mass number mass of an electron is so small that it's disregarded ...
... approximate mass of a single proton or neutron is 1 amu mass of an atom in atomic mass units is simply the sum of its protons and neutrons and is known as the atomic mass number mass of an electron is so small that it's disregarded ...
Chemistry (B) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 50. How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? a. It decreases. c. It stays the same. b. It increases. d. It doubles. ____ 51. What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital? a. sphere c. bar b. dumbbell d. two perpendicular dumbbells ____ 52. What is ...
... ____ 50. How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? a. It decreases. c. It stays the same. b. It increases. d. It doubles. ____ 51. What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital? a. sphere c. bar b. dumbbell d. two perpendicular dumbbells ____ 52. What is ...
making models of atoms - Mater Academy Charter Middle/ High
... small particle that makes up most types of matter. Atoms are so mall it would take about 1 million of them lined up in a row to equal the thickness of a human hair. Atoms are made up of even smaller particles. The largest of these particles are protons, neutrons and electrons. The identity of a type ...
... small particle that makes up most types of matter. Atoms are so mall it would take about 1 million of them lined up in a row to equal the thickness of a human hair. Atoms are made up of even smaller particles. The largest of these particles are protons, neutrons and electrons. The identity of a type ...
Periodicity PowerPoint
... • The valence electrons (outer e-) in atoms are those shared/transferred to form bonds between atoms. • The number of valence electrons will affect the type(s) of bonds an atom can form with a specific element. • The number of valence electrons in an atom can be determined from the electron configur ...
... • The valence electrons (outer e-) in atoms are those shared/transferred to form bonds between atoms. • The number of valence electrons will affect the type(s) of bonds an atom can form with a specific element. • The number of valence electrons in an atom can be determined from the electron configur ...
CHAPTER 2
... • Bohr’s model of the atom when applied to atoms with more than one electron failed to explain their line spectra. • One major change from Bohr’s model is that electrons do not move in orbits. • Atomic orbitals - regions in space with a high probability of finding an electron. • Electrons move rapid ...
... • Bohr’s model of the atom when applied to atoms with more than one electron failed to explain their line spectra. • One major change from Bohr’s model is that electrons do not move in orbits. • Atomic orbitals - regions in space with a high probability of finding an electron. • Electrons move rapid ...
electron
... abundance of 19.91%. The isotope with mass 11.009 amu has a relative abundance of 80.09%. 1. Calculate the atomic mass of this element (show all work) and then name this element. ...
... abundance of 19.91%. The isotope with mass 11.009 amu has a relative abundance of 80.09%. 1. Calculate the atomic mass of this element (show all work) and then name this element. ...
Atomic Structure – Revision Pack (C4) Atoms: A nucleus is made up
... Arrangement of electrons: The elements of the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The amount of electrons is different for the shells of an atom: The maximum number of electrons for the first shell is 2. The maximum number of electrons for all of the shells from then is ...
... Arrangement of electrons: The elements of the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The amount of electrons is different for the shells of an atom: The maximum number of electrons for the first shell is 2. The maximum number of electrons for all of the shells from then is ...
C4 Atomic structure
... Arrangement of electrons: The elements of the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The amount of electrons is different for the shells of an atom: The maximum number of electrons for the first shell is 2. The maximum number of electrons for all of the shells from then is ...
... Arrangement of electrons: The elements of the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The amount of electrons is different for the shells of an atom: The maximum number of electrons for the first shell is 2. The maximum number of electrons for all of the shells from then is ...
The Atom - Exam #2 Review
... 17. How can you determine if the atom is the most common isotope? Most common isotope = atomic mass from the Periodic Table rounded to a whole number 18. What is the difference between mass number and average atomic mass? Mass # = mass of each specific isotope (protons + neutrons) Average atomic mas ...
... 17. How can you determine if the atom is the most common isotope? Most common isotope = atomic mass from the Periodic Table rounded to a whole number 18. What is the difference between mass number and average atomic mass? Mass # = mass of each specific isotope (protons + neutrons) Average atomic mas ...
chapter 2-1 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... What are elements? Elements: The fundamental units of matter What do we mean by fundamental? Necessary base or core ...
... What are elements? Elements: The fundamental units of matter What do we mean by fundamental? Necessary base or core ...
DALTON`S ATOMIC THEORY - 1808: Publication of Dalton`s "A New
... RATIO of water and oxygen would form: ...
... RATIO of water and oxygen would form: ...
ionization energies
... • As more and more elements were discovered, chemists began to notice patterns in the chemical properties of certain elements. • Consider the three metals Li, Na, and K • All 3 metals are soft • All 3 metals are less dense than water • All 3 metals have similar appearance and low melting points • Th ...
... • As more and more elements were discovered, chemists began to notice patterns in the chemical properties of certain elements. • Consider the three metals Li, Na, and K • All 3 metals are soft • All 3 metals are less dense than water • All 3 metals have similar appearance and low melting points • Th ...























