Nuclear Physics Ch 30-31 Atom - word comes from the ancient
... 2 types: beta negative - electron and anti-neutrino produced in the nucleus from a neutron changing into a proton. beta positive - positron (anti matter electron) and a neutrino produced from a proton changing into a neutron. anti-matter - like matter but with opposite charge and quantum numbers but ...
... 2 types: beta negative - electron and anti-neutrino produced in the nucleus from a neutron changing into a proton. beta positive - positron (anti matter electron) and a neutrino produced from a proton changing into a neutron. anti-matter - like matter but with opposite charge and quantum numbers but ...
Topic 3 Review
... • Atoms are divisible into even smaller particles (by a nuclear change) • A given element can have atoms with different masses (isotopes) ...
... • Atoms are divisible into even smaller particles (by a nuclear change) • A given element can have atoms with different masses (isotopes) ...
Atomic Theory
... Atomic number = number of protons in the nucleus Atomic number determines the identity of the element Mass number = protons + neutrons Number of electrons = number of protons Isotopes: two atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons C-12 and C-13 are isotopes of carbon ...
... Atomic number = number of protons in the nucleus Atomic number determines the identity of the element Mass number = protons + neutrons Number of electrons = number of protons Isotopes: two atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons C-12 and C-13 are isotopes of carbon ...
File - Rogers` Rocket Science
... different from those of any other element. 3) Atoms of different elements __________in simple ________-number ratios to form _____________ compounds. 4) In chemical reactions, atoms are_________________, ________________, or ____________– but never changed into atoms of another element. Sizing up th ...
... different from those of any other element. 3) Atoms of different elements __________in simple ________-number ratios to form _____________ compounds. 4) In chemical reactions, atoms are_________________, ________________, or ____________– but never changed into atoms of another element. Sizing up th ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Chapter 2 Handout 1 The Atom Dalton`s
... For Full Atomic Theory Read: Section 2.2 in Textbook Modern Knowledge of Atomic Structure ...
... For Full Atomic Theory Read: Section 2.2 in Textbook Modern Knowledge of Atomic Structure ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
Integrated Science 3
... What state is this element in at room temperature?_________ Draw the electron distribution of an atom of this element. ...
... What state is this element in at room temperature?_________ Draw the electron distribution of an atom of this element. ...
Chapter 4
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are made of atoms that can not be divided. 2. All atoms of the same element are EXACTLY alike and have the same mass. 3. Atoms of one element CAN NOT change into another type of element. In a chemical reaction, they can not be created or destroyed, only rearra ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. All elements are made of atoms that can not be divided. 2. All atoms of the same element are EXACTLY alike and have the same mass. 3. Atoms of one element CAN NOT change into another type of element. In a chemical reaction, they can not be created or destroyed, only rearra ...
Chemistry 1 – Tollett Chapter 5 – Atomic Structure & The Periodic
... Rutherford's atomic structure by assuming that electrons travel in stationary orbits defined by their angular momentum. • This led to the calculation of possible energy levels for these orbits and the hypothesis that the emission of light occurs when an electron moves into a lower energy orbit. ...
... Rutherford's atomic structure by assuming that electrons travel in stationary orbits defined by their angular momentum. • This led to the calculation of possible energy levels for these orbits and the hypothesis that the emission of light occurs when an electron moves into a lower energy orbit. ...
Chapter 4: Concept 4.2
... the cloud model is helpful. An electron may visit every point around a nucleus over time. Thus you can think of the electron's negative charge as spread out, like a cloud, in all the places the electron might be. In a real atom, the electron cloud is much larger than the nucleus. To give you an idea ...
... the cloud model is helpful. An electron may visit every point around a nucleus over time. Thus you can think of the electron's negative charge as spread out, like a cloud, in all the places the electron might be. In a real atom, the electron cloud is much larger than the nucleus. To give you an idea ...
Subject - Currituck County Schools
... conclusions from experimentation changed atomic theory over time. Explain Dalton’s atomic theory, which states the following: o Chemical elements are made up of atoms. o The atoms of an element are identical in their masses. (Be sure students understand that this was shown to be false with the disco ...
... conclusions from experimentation changed atomic theory over time. Explain Dalton’s atomic theory, which states the following: o Chemical elements are made up of atoms. o The atoms of an element are identical in their masses. (Be sure students understand that this was shown to be false with the disco ...
Periodic Table Workbook NOTES
... Metals, Nonmetals and Metalloids Metals – elements that are shiny and conduct heat and electricity well, mostly solid at room temp., are malleable (able to be formed into different shapes, are ductile (able to be made into wires). Nonmetals – poor conductors of heat and electricity, often dull and b ...
... Metals, Nonmetals and Metalloids Metals – elements that are shiny and conduct heat and electricity well, mostly solid at room temp., are malleable (able to be formed into different shapes, are ductile (able to be made into wires). Nonmetals – poor conductors of heat and electricity, often dull and b ...
(Questions 1-10) Write the letter of the answer that best complet
... How many oxygen atoms are there in Al2(SO4)3? A. 2 B. 3 C. 7 D. 12 E. 14 ...
... How many oxygen atoms are there in Al2(SO4)3? A. 2 B. 3 C. 7 D. 12 E. 14 ...
Week 1 Grade 7 Thursday
... Atomic number = number of protons Atomic number = number of electrons in a neutral atom (not an ion) Atomic weight - atomic number = number of neutrons Isotopes have different numbers of neutrons, H normally has 0 neutrons ...
... Atomic number = number of protons Atomic number = number of electrons in a neutral atom (not an ion) Atomic weight - atomic number = number of neutrons Isotopes have different numbers of neutrons, H normally has 0 neutrons ...
Semester Exam Review - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
... Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated that electrons ...
Unit 2 - Chapter 3 Elements, Atoms, Ions The elements Can we
... • Can we name some? • A compound has a unique chemical formula, which indicates which elements and how many are in that particular substance. ...
... • Can we name some? • A compound has a unique chemical formula, which indicates which elements and how many are in that particular substance. ...
Atomic Structure
... atoms of one element are different from the atoms of another element. • 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simplewhole number ratios to form compounds. • 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined or rearranged. ...
... atoms of one element are different from the atoms of another element. • 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simplewhole number ratios to form compounds. • 4. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined or rearranged. ...
File
... 4. The number of ELECTRONS and where they are located (on which SHELLS they are located) around the nucleus. YOUR TURN! Draw the following Bohr Model Diagrams Sodium ...
... 4. The number of ELECTRONS and where they are located (on which SHELLS they are located) around the nucleus. YOUR TURN! Draw the following Bohr Model Diagrams Sodium ...
Scientific method
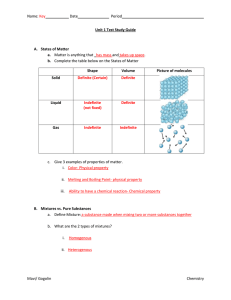
... measured or observed without changing the identity of matter are called Physical properties. Examples are density, specific heat, boiling ...
... measured or observed without changing the identity of matter are called Physical properties. Examples are density, specific heat, boiling ...
Study Guide Answer Key
... by which J.J. Thomson demonstrated that cathode rays could be deflected by a magnetic field, and that their negative charge was not a separate phenomenon. i. ...
... by which J.J. Thomson demonstrated that cathode rays could be deflected by a magnetic field, and that their negative charge was not a separate phenomenon. i. ...