ISOSTOPE NOTES - Mr. Collier`s 9th Grade Physical Science
... • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses because they have different numbers of neutrons. –Subatomic particles are so small that we don’t use grams, we use AMU (atomic mass units) –Protons and Neutrons have about the same mass: 1AMU. –Electrons have so little mass they do ...
... • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses because they have different numbers of neutrons. –Subatomic particles are so small that we don’t use grams, we use AMU (atomic mass units) –Protons and Neutrons have about the same mass: 1AMU. –Electrons have so little mass they do ...
Taking a Look Inside the Atom
... What is stuff made of? Greek philosopher Democritus began the search for a description of matter more than 2400 years ago, wondering if matter could be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever. His theory: Eventually, there would be a smallest possible piece that couldn’t be divided. H ...
... What is stuff made of? Greek philosopher Democritus began the search for a description of matter more than 2400 years ago, wondering if matter could be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever. His theory: Eventually, there would be a smallest possible piece that couldn’t be divided. H ...
Ch 4 - USD305.com
... – Smallest unit of an element that has chemical properties of that element – Can it be broken down any farther? How big is an atom? ...
... – Smallest unit of an element that has chemical properties of that element – Can it be broken down any farther? How big is an atom? ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... but can calculate an area they are found 3. Just like a fan blade moving ...
... but can calculate an area they are found 3. Just like a fan blade moving ...
Periodic Table
... –Included elements Valence # (bonding power) •How many e- the atom can lose or gain when bonding •Pattern appeared - 1234321 ...
... –Included elements Valence # (bonding power) •How many e- the atom can lose or gain when bonding •Pattern appeared - 1234321 ...
Slide 1 - MrWilsonScience
... • Has no mass. (1/1840 or 9.11X10^-28 grams) • Found in orbit around the nucleus of an atom. ...
... • Has no mass. (1/1840 or 9.11X10^-28 grams) • Found in orbit around the nucleus of an atom. ...
INTRODUCTION TO THE PERIODIC TABLE
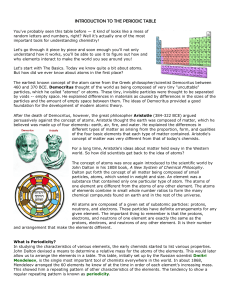
... For a long time, Aristotle's ideas about matter held sway in the Western world. So how did scientists get back to the idea of atoms? The concept of atoms was once again introduced to the scientific world by John Dalton in his 1808 book, A New System of Chemical Philosophy. Dalton put forth the conce ...
... For a long time, Aristotle's ideas about matter held sway in the Western world. So how did scientists get back to the idea of atoms? The concept of atoms was once again introduced to the scientific world by John Dalton in his 1808 book, A New System of Chemical Philosophy. Dalton put forth the conce ...
File
... Some metal atoms, depending on the nature of the chemical reaction, can form stable ions with more than one charge. For example copper atoms will lose either one or two electrons. ...
... Some metal atoms, depending on the nature of the chemical reaction, can form stable ions with more than one charge. For example copper atoms will lose either one or two electrons. ...
Unit 3 - Chemistry
... reaction, mass is neither created nor destroyed; it is conserved. • The mass of the reactants equals the mass of the products. ...
... reaction, mass is neither created nor destroyed; it is conserved. • The mass of the reactants equals the mass of the products. ...
Electron Behavior File
... • What is atomic radii? • It is defined as one half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together Period trends– the atomic radii across periods (rows) decreases due to increasing positive charge in the nucleus Group trends– the atomic radii down a group (column) in ...
... • What is atomic radii? • It is defined as one half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together Period trends– the atomic radii across periods (rows) decreases due to increasing positive charge in the nucleus Group trends– the atomic radii down a group (column) in ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... This proved that: the atom had a dense but very small positive core the electrons were far away from the nucleus Most of the atom is just EMPTY SPACE! ...
... This proved that: the atom had a dense but very small positive core the electrons were far away from the nucleus Most of the atom is just EMPTY SPACE! ...
Study Guide for test - Madison County Schools
... c. How can you determine how many neutrons will be in a given atom? d. For an atom to be neutral, what subatomic particles have to have been present in the same number? e. What number is unique for any given element? 10) Isotopes & Ions a. Define “isotope”: b. What is same about all isotopes of a gi ...
... c. How can you determine how many neutrons will be in a given atom? d. For an atom to be neutral, what subatomic particles have to have been present in the same number? e. What number is unique for any given element? 10) Isotopes & Ions a. Define “isotope”: b. What is same about all isotopes of a gi ...
Drawing Atomic Structure
... Protons and Neutrons can both be broken down even farther into _______________. More info on pg. 508 ...
... Protons and Neutrons can both be broken down even farther into _______________. More info on pg. 508 ...
Thomson`s Atom
... metal foils with alpha particles (helium ions) • Most particles went through - only 1 alpha particle in 10.000 was deflected by the foil • This deflection indicated the existence of a small, dense, positively charged nucleus ...
... metal foils with alpha particles (helium ions) • Most particles went through - only 1 alpha particle in 10.000 was deflected by the foil • This deflection indicated the existence of a small, dense, positively charged nucleus ...
The Periodic table
... 2. They have very little mass compared to proton and Neutrons. 3. Located outside the nucleus. 4. Move around the nucleus in a volume that defines the Size of the atom. ...
... 2. They have very little mass compared to proton and Neutrons. 3. Located outside the nucleus. 4. Move around the nucleus in a volume that defines the Size of the atom. ...
Ch. 2 The Chemical Basis of Life
... The Distribution of Electrons Determines an Atoms Chemical Properties Electrons occupy up to seven electron shells (energy levels) around nucleus Octet rule: Except for the first shell which is full with two electrons, atoms interact in order to have eight electrons in their outermost energy le ...
... The Distribution of Electrons Determines an Atoms Chemical Properties Electrons occupy up to seven electron shells (energy levels) around nucleus Octet rule: Except for the first shell which is full with two electrons, atoms interact in order to have eight electrons in their outermost energy le ...
Bohr´s atomic model (1913)
... Between the nucleus and the electron shell there is empty space. Most of the atom is empty space. The nucleus of an atom is positively charged and contains almost all the mass of the atom. We know now that it is composed of protons and neutrons. Electrons orbit around the nucleus in circular orbits. ...
... Between the nucleus and the electron shell there is empty space. Most of the atom is empty space. The nucleus of an atom is positively charged and contains almost all the mass of the atom. We know now that it is composed of protons and neutrons. Electrons orbit around the nucleus in circular orbits. ...
Document
... all of the particles in the atom. • In the center are circles. Each circle represents a single neutron or proton. Protons should have a plus or “p” written on them. Neutrons should an “n” or zero. • In a circle around the nucleus are the electrons. Electrons should have a minus sign or an e. ...
... all of the particles in the atom. • In the center are circles. Each circle represents a single neutron or proton. Protons should have a plus or “p” written on them. Neutrons should an “n” or zero. • In a circle around the nucleus are the electrons. Electrons should have a minus sign or an e. ...
Chemical Bonding
... • Going across the row, atomic radius decreases. • Going down the group, atomic radius increases because the more electrons around the nucleus, the greater the volume needed to contain them (since electrons repel each other and can’t easily be “compacted”. ...
... • Going across the row, atomic radius decreases. • Going down the group, atomic radius increases because the more electrons around the nucleus, the greater the volume needed to contain them (since electrons repel each other and can’t easily be “compacted”. ...
Chapter 5
... o Thomson knew that opposite charges attract and like charges repel, so he sent a stream of negatively charged particles (originally called corpuscles) at high speed. The particles were deflected toward the positive plate - Robert Millikan found the charge on an electron to be one negative unit. Its ...
... o Thomson knew that opposite charges attract and like charges repel, so he sent a stream of negatively charged particles (originally called corpuscles) at high speed. The particles were deflected toward the positive plate - Robert Millikan found the charge on an electron to be one negative unit. Its ...
atoms - SP Moodle
... Most of the volume (space) of an atom is made up of electrons Electrons have very little mass and take up very little space SO, atoms are mainly empty space We are made of atoms SO we are empty mainly made up of Empty ...
... Most of the volume (space) of an atom is made up of electrons Electrons have very little mass and take up very little space SO, atoms are mainly empty space We are made of atoms SO we are empty mainly made up of Empty ...