* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Scientific method
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
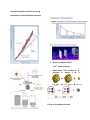
Study guide- 1st Bench mark Most abundant matter - Plasma: matter @ very high temp w/ positive and negative charges. Scientific method – a logical approach to solve technical/ nontechnical problems is called scientific method. Compound Pure substance Elements Making observation Hypothesis- a testable statement is called hypothesis Experiment-A procedure used to test hypothesis Developing theories- a theory is a well tested explaination for the broad set of observations. Scientific law- it is a concise statement that summarize the results of many observations and experiments. Metals Metalloids Shine Nonmetal partial No shine Ductile Parial Brittle Good conductor Good Bad cond. Malleanle & (Only good conduct.or At high temperature Conductance) Homogeneous (one phase & solution) Mixture (Blend of 2 or more) Heterogeneous (Non uniform) Classification of matte (Mass & Volume) Solid liquid Gas Plasma 1 Shape Definite Indefinite Indefinite Indefinite 2 Volume Definite Definite Indefinite Indefinite 3 Intermolecular forces Extensive property- properties which depends upon the amount of matter are called extensive properties. Mass, volume, amount of heat stored etc. Intensive properties- properties independent of amount of matter are called intensive properties. These are used to identify matter are like finger prints. Density, specific heat, boiling point, melting point etc are examples of Intensive properties. Very strong >>stronge > very weak 4 Compressible No No compressible Physical properties- properties which can be measured or observed without changing the identity of matter are called Physical properties. Examples are density, specific heat, boiling point, melting point, color, brittle, malleability, etc. Grinding _________, __________ Physical changes- during physical changes the composition (ID) of substance do not change. Grinding, melting, boiling, breaking into two parts, are examples of physical changes. Condensation __________, sublimation ( S - gas) ____ Chemical properties- Properties which are observed with change in composition of substance are called chemical properties. Flamability, combustion, rusting, corrosion, support combustion, neutralization, reactivity etc. are examples of chemical properties. Dalton’ atomic theory and Modern atomic theory Chemical changes – changes which can be observed with change in composition (change in ID). Color change, gas is produced, grass is growing green, digestion of food, formation of solids are examples of chemical changes. Identify the following as physical or chemical properties 1 Color____________ point_____________, Melting boiling point _______ ______________ Flammability Density ___________ of an acid _____ Neutralization React with ________ ___________ corrosion evaporation • Atoms of the given element are identical in size, mass and other properties • Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed. • Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole number ratio. • In chemical reactions, atoms combines, separates or rearranges • Modern Theory : Atoms of the same element can be different called isotopes • Atoms are subdivided into electrons, protons, and neutrons • Atoms can be destroyed Who discovered electron and proposed Plum pudding model of atom? JJ Thomson Supports combustion ___ Density___________ • Name Cathode rays were attracted towards positively charge electric plate indicating of experiment is cathode ray experiment ----- r Identify the following as physical or chemical changes Rusting _______ two pieces_______, , Breaking a wood into Burning of candle _______, Melting of wax ______ Grass is growing green _______, change of leaves ____ color negative charge of cathode ray particle called electrons. Who discovered nucleus – Ernest Rutherford Rutherford made a Gold foil Experiment Most of the Alpha particles passed through gold foil – Indicating atom has most of empty space Only few were deflected or bounced back- indicating positive charge at the center as Alpha particle has positive charge were deflected by positive nucleus. Name/ Symbol Charge Mass/ Location Proton p +1 1 In nucleus Electrons e -1 0 outside Neutrons n 0 1 Inide nucl. Why an atom is neutral? # positive charge(p) = # negative charges (e) A X Z A= mass # = ( #p + #n) Z = atomic number = #p 137 Ba #p = #e = 56, 56 #n =137 -56 = 81 1 Amu = 1/12 mass of Carbon-12 Two isotopes of chlorine 3517Cl and 37 Cl have % abundance of 70% and 17 30% respectively. What is its average atomic mass? It is closer to isotopes --3517Cl . Why? B/ of more abundance = 0.7 x 35 + 0.30 x 37 = 35.5 amu 1 mole C = 6.02 x 1023 atoms C 1 Mole C = 12 g C 1 Mole U = 6.02 x 1023 U atoms X-symbol of Element 1 Mole U = 238 g U 1 Mole H2O = 6.02 x 1023 molecules of H2O 1 molecules = 2H + O 1 mole molar mass = 2 + 16 =18 g # atoms in 1 molecule H2SO4 = 2H + 1 S + 4O = molar mass = 2x 1 = 1x32 + 4 x 16 =98 amu # atoms in 1 Molecule of Al2 (SO4)3 = 2Al + 3S + 12O Molar mass = 2x27 + 3 x 32 + 12x 16 = 342 amu Elements in Groups & Number of electrons in the highest orbit are called Valence electrons (VE). Groups Called main block elements Elemental Groups 1A 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A 1 # VE 1 8A 2 13 14 15 16 17 2 3 4 18 5 6 (Except He has VE -2) Nuclear chemistry • Nuclear Stability • Electrostatic force = the force that causes like electrical charges to repel each nucleus. other.Neutron stabilizes •Strong force = the force between nucleons (protons and neutrons). • Neutrons increase the attraction from the strong force without increasing electrostatic repulsion between nucleons. What is an alpha particle? ( He2+ - helium nucleus) Alpha decay = Loss of Mass # = 4, decrease in Atomic # by 2 Fission is the splitting of atoms These are usually very large, so that they are not as stable Fission chain has three general steps: 1. Initiation. Reaction of a single atom starts the chain (e.g., 235U + neutron) 2. Propagation. 236U fission releases neutrons that initiate other fissions 3. propagation of chain reaction. • Beta () particle = e- • How does nucleus emit an e-? • neutron changes into proton & emits e- called betta decay. • 10n 11p + 0-1e • Daughter nuclide = parent nuclide atomic number plus 1 137 55Cs 13756Ba + 0-1e-