introductory chemistry
... Elements are substances that contain only one type of atom. Hydrogen gas is an element as it contains only hydrogen atoms. Compounds contain the atoms of two or more different elements joined together. Water is a compound that consists of hydrogen and oxygen atoms joined together. There are nearly 1 ...
... Elements are substances that contain only one type of atom. Hydrogen gas is an element as it contains only hydrogen atoms. Compounds contain the atoms of two or more different elements joined together. Water is a compound that consists of hydrogen and oxygen atoms joined together. There are nearly 1 ...
The New Alchemy
... Protons – one of the parts of an atom. Protons have a (+) charge and are found in the nucleus. Neutrons – one of the parts of an atom. Neutrons have no charge and are found in the nucleus. Nucleus – found in the center of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons. Nuclei is the plural of nucleus. Nu ...
... Protons – one of the parts of an atom. Protons have a (+) charge and are found in the nucleus. Neutrons – one of the parts of an atom. Neutrons have no charge and are found in the nucleus. Nucleus – found in the center of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons. Nuclei is the plural of nucleus. Nu ...
Small Business Success on the Web
... Pair of electrons not shared equally by 2 atoms Water = O + H oxygen has stronger “attraction” for the shared electrons than hydrogen oxygen has higher ...
... Pair of electrons not shared equally by 2 atoms Water = O + H oxygen has stronger “attraction” for the shared electrons than hydrogen oxygen has higher ...
05 Chemistry Basics with Flips 2011
... Pair of electrons not shared equally by 2 atoms Water = O + H oxygen has stronger “attraction” for the shared electrons than hydrogen oxygen has higher ...
... Pair of electrons not shared equally by 2 atoms Water = O + H oxygen has stronger “attraction” for the shared electrons than hydrogen oxygen has higher ...
TEST II Study Guide-Atomic Theory Honors Chemistry
... 1. ______________ This person was developed the Law of Conservation of Mass stating “matter cannot be created or destroyed.” 2. _____________ Using the line spectrum of the hydrogen atom and his knowledge of quantum theory and physics, this scientist proposed an atomic model where electrons orbit th ...
... 1. ______________ This person was developed the Law of Conservation of Mass stating “matter cannot be created or destroyed.” 2. _____________ Using the line spectrum of the hydrogen atom and his knowledge of quantum theory and physics, this scientist proposed an atomic model where electrons orbit th ...
Extra Credit Test Review
... 29. How is the bonding of Cl2 different from the bonding in NaCl? Cl2 is a diatomic / covalent bond whereas NaCl is an ionic bond 30. Explain how Helium can be in Group 18, but doesn’t have 8 valence electrons? Helium only has 2 electrons, so they will fill up the first energy level/shell and theref ...
... 29. How is the bonding of Cl2 different from the bonding in NaCl? Cl2 is a diatomic / covalent bond whereas NaCl is an ionic bond 30. Explain how Helium can be in Group 18, but doesn’t have 8 valence electrons? Helium only has 2 electrons, so they will fill up the first energy level/shell and theref ...
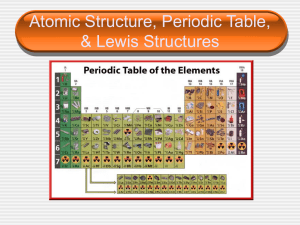
Summary of the Periodic Table of Elements: 1. Elements in the same
... c. Atomic size d. Metallic properties 6. Valence electrons are involved in the chemical combining of elements in the forming of molecules. 7. Elements to the left in the periodic table tend to lose electrons. 8. Elements to the right in the periodic table tend to gain electrons. 9. The amount of ene ...
... c. Atomic size d. Metallic properties 6. Valence electrons are involved in the chemical combining of elements in the forming of molecules. 7. Elements to the left in the periodic table tend to lose electrons. 8. Elements to the right in the periodic table tend to gain electrons. 9. The amount of ene ...
File
... 32. Give an example of a compound. H2O 33. What is a molecule? An element with more than one atom attached to it 34. Give an example of a molecule. O₂- air we breathe O₃- ozone layer 35. As you go from left to right on the periodic table, describe the changes that occur to element's atomic structure ...
... 32. Give an example of a compound. H2O 33. What is a molecule? An element with more than one atom attached to it 34. Give an example of a molecule. O₂- air we breathe O₃- ozone layer 35. As you go from left to right on the periodic table, describe the changes that occur to element's atomic structure ...
Chem Unit 2 Review Guide ANSWERS
... Chemical reactions only involve the atoms’ valence electrons. In a nuclear reaction, the nucleus is actually altered. The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true during chemical reactions, but is not during a nuclear reaction, as mass is converted directly to energy and vice versa. 18.) Define what v ...
... Chemical reactions only involve the atoms’ valence electrons. In a nuclear reaction, the nucleus is actually altered. The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true during chemical reactions, but is not during a nuclear reaction, as mass is converted directly to energy and vice versa. 18.) Define what v ...
Looking for Patterns in Chemical Reactivity
... to the energy changes that take place when their atoms lose, gain, or share electrons to obtain a filled valence shell. Metals are elements that tend to lose their valence electrons relatively easily and this accounts for many of their physical and chemical properties. One important property of ...
... to the energy changes that take place when their atoms lose, gain, or share electrons to obtain a filled valence shell. Metals are elements that tend to lose their valence electrons relatively easily and this accounts for many of their physical and chemical properties. One important property of ...
Study Guide - Honors Chemistry
... degree of penetrability. Draw a diagram indicating the individual degree of penetrability of these particles. Be sure to include what materials can impede or retard these particles. beta ...
... degree of penetrability. Draw a diagram indicating the individual degree of penetrability of these particles. Be sure to include what materials can impede or retard these particles. beta ...
Basics of Chemistry
... chemical behavior of an atom depends on number of electrons in its outermost shell ...
... chemical behavior of an atom depends on number of electrons in its outermost shell ...
Chemistry Exam Review
... Isotope • an atom with a different number of neutrons and therefore a different mass ...
... Isotope • an atom with a different number of neutrons and therefore a different mass ...
atoms - Trinity Regional School
... John Dalton (aka Jack) 1. Atoms are the smallest form of matter 2. Atoms make up all matter 3. Atoms of the same element are the same 4. Atoms cannot be broken down 5. Atoms combine in specific ratios ...
... John Dalton (aka Jack) 1. Atoms are the smallest form of matter 2. Atoms make up all matter 3. Atoms of the same element are the same 4. Atoms cannot be broken down 5. Atoms combine in specific ratios ...
Cornell notes template
... - Take sufficient notes with selective (not too many words) & accurate paraphrasing - Skip a line between ideas and topics - Use bulleted lists and abbreviations - Correctly sequence information - Include diagrams or tables if needed for clarification or length The atomic number of proton and electr ...
... - Take sufficient notes with selective (not too many words) & accurate paraphrasing - Skip a line between ideas and topics - Use bulleted lists and abbreviations - Correctly sequence information - Include diagrams or tables if needed for clarification or length The atomic number of proton and electr ...
2015 Final Exam Study Guide
... Moving from left to right across a row of the periodic table, which of the following values increases by exactly one from element to element? ...
... Moving from left to right across a row of the periodic table, which of the following values increases by exactly one from element to element? ...
Remember Question words
... nucleus (protons, neutrons) shells (electrons) shell = a particular region where electrons can orbit the nucleus of an atom valence electron = an electron in the outermost shell of an atom charges (positive = proton; neutral = neutron; negative = ...
... nucleus (protons, neutrons) shells (electrons) shell = a particular region where electrons can orbit the nucleus of an atom valence electron = an electron in the outermost shell of an atom charges (positive = proton; neutral = neutron; negative = ...
Periodic Table
... Atoms remain unchanged, but the may be rearranged Involve only valence electrons Have small energy changes Reaction rates are influenced by temperature, pressure, concentration, and catalysts ...
... Atoms remain unchanged, but the may be rearranged Involve only valence electrons Have small energy changes Reaction rates are influenced by temperature, pressure, concentration, and catalysts ...
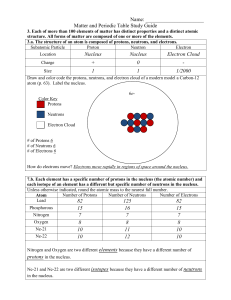
Matter and the Periodic Table Study Guide Answer Key
... Semimetals/Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. 3.b. Compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 3.f. Use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. Compound ...
... Semimetals/Metalloids have properties of both metals and non-metals. 3.b. Compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 3.f. Use the periodic table to identify elements in simple compounds. Compound ...
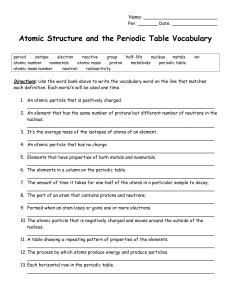
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Vocabulary
... 2. An element that has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in the nucleus. __________________________________________________________________ 3. It’s the average mass of the isotopes of atoms of an element. __________________________________________________________________ 4. ...
... 2. An element that has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons in the nucleus. __________________________________________________________________ 3. It’s the average mass of the isotopes of atoms of an element. __________________________________________________________________ 4. ...