Document
... Valence Electrons • Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of the atom. • Valence electrons are the only electrons generally involved in bond formation. • The valence electrons in the s and p orbitals are written around the element symbol. • These electrons are the ...
... Valence Electrons • Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of the atom. • Valence electrons are the only electrons generally involved in bond formation. • The valence electrons in the s and p orbitals are written around the element symbol. • These electrons are the ...
Atom - Sites
... atoms join together chemically. •Combinations of two or more different elements are called compounds. •All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. (ex. H2O vs. O2) •Molecules can also join together to form larger molecules. •Many, many repeating small molecules joined together f ...
... atoms join together chemically. •Combinations of two or more different elements are called compounds. •All compounds are molecules but not all molecules are compounds. (ex. H2O vs. O2) •Molecules can also join together to form larger molecules. •Many, many repeating small molecules joined together f ...
Chapter 6 Vocabulary crossword puzzle
... Use the clues below to complete the crossword on the next page. Across 2. Set of elements that exhibit similar electron configurations in highest occupied energy level 4. Class of elements possessing the property of being ductile 5. Elements in which the highest occupied s and p sublevels are comple ...
... Use the clues below to complete the crossword on the next page. Across 2. Set of elements that exhibit similar electron configurations in highest occupied energy level 4. Class of elements possessing the property of being ductile 5. Elements in which the highest occupied s and p sublevels are comple ...
atoms, molecules, and matter (2)
... States of Matter 1. Solid – definite shape, atoms locked into position, most have regular pattern. 2. Liquid – atoms packed tightly but not as tight as to prohibit movement; has ...
... States of Matter 1. Solid – definite shape, atoms locked into position, most have regular pattern. 2. Liquid – atoms packed tightly but not as tight as to prohibit movement; has ...
BC1 Atoms Unit Standards
... of the protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom of an element. 2a For a given element, determine the number of protons 2b When given a number of protons, identify the element name and symbol 2c Identify the number of neutrons in an atom from atomic number and mass number 2d Identify the number of ...
... of the protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom of an element. 2a For a given element, determine the number of protons 2b When given a number of protons, identify the element name and symbol 2c Identify the number of neutrons in an atom from atomic number and mass number 2d Identify the number of ...
Chapter 5
... •Electron cloud is 10,000 times larger than the nucleus, but is still mostly empty. •Electrons are in the cloud but can not be pinpointed at an exact time because they move so quickly. ...
... •Electron cloud is 10,000 times larger than the nucleus, but is still mostly empty. •Electrons are in the cloud but can not be pinpointed at an exact time because they move so quickly. ...
Ch. 4: Atoms and the Periodic Table – Study Guide
... to form a lithium ion with a charge of 1+. A lithium ion is much less reactive than a lithium atom because it has a full outermost energy level. Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different atomic mass. Group 1 of the periodic table consists of the alkali metals, a highly reactiv ...
... to form a lithium ion with a charge of 1+. A lithium ion is much less reactive than a lithium atom because it has a full outermost energy level. Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different atomic mass. Group 1 of the periodic table consists of the alkali metals, a highly reactiv ...
atomic number - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. Different atoms of the same element can have a diffe ...
... An element is a substance made up of only one type of atom. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. The number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. Different atoms of the same element can have a diffe ...
The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this
... Group. The trends and patterns are captured in this version of the Periodic Table obtained from the Internet: ...
... Group. The trends and patterns are captured in this version of the Periodic Table obtained from the Internet: ...
The_Atoms_Family
... • When the number of neutrons in nuclei vary, you have an isotope • For example, chlorine always has 17 protons, but the number of neutrons could be either 18 or 20. This in turn, changes the atomic mass • The nuclei of some isotopes are unstable and release radiation • During the radioactive decay ...
... • When the number of neutrons in nuclei vary, you have an isotope • For example, chlorine always has 17 protons, but the number of neutrons could be either 18 or 20. This in turn, changes the atomic mass • The nuclei of some isotopes are unstable and release radiation • During the radioactive decay ...
CLASS TEST NAME Class IIB Date ______ 1 .Which atomic
... 21. The electrons ______________________________________________________ around the nucleus in shells. The first shell, which is _______________________________ the nucleus, can hold ________electrons, whereas the 2nd and 3rd shells can hold ...
... 21. The electrons ______________________________________________________ around the nucleus in shells. The first shell, which is _______________________________ the nucleus, can hold ________electrons, whereas the 2nd and 3rd shells can hold ...
Introduction to the Periodic Table
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...
Atoms and Their Electrons
... it can have a range of numbers of neutrons i.e. hydrogen can have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons to go with its 1 proton. These are called isotopes of hydrogen In real life there may be a number of different stable isotopes of each element. This makes it difficult to work out which mass number to put onto a pe ...
... it can have a range of numbers of neutrons i.e. hydrogen can have 0, 1, or 2 neutrons to go with its 1 proton. These are called isotopes of hydrogen In real life there may be a number of different stable isotopes of each element. This makes it difficult to work out which mass number to put onto a pe ...
C2- Topic 1: Atomic structure and the periodic table. Assessable
... - arranged the elements, known at that time, in a periodic table by using properties of these elements and their compounds - used his table to predict the existence and properties of some elements not then discovered ...
... - arranged the elements, known at that time, in a periodic table by using properties of these elements and their compounds - used his table to predict the existence and properties of some elements not then discovered ...
C2 Topic 1 Can Do Sheet
... a arranged the elements, known at that time, in a periodic table by using properties of these elements and their compounds b used his table to predict the existence and properties of some elements not then discovered 1.2 Classify elements as metals or non-metals according to their position in the pe ...
... a arranged the elements, known at that time, in a periodic table by using properties of these elements and their compounds b used his table to predict the existence and properties of some elements not then discovered 1.2 Classify elements as metals or non-metals according to their position in the pe ...
Periodic Table Vocabulary Periodic Table – a chart that organizes
... Inert – elements and/or compounds that when put together are unable to react chemically. The Law of Conservation of Matter – a scientific law that states that during a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed into a different form. Period law- The chemical properti ...
... Inert – elements and/or compounds that when put together are unable to react chemically. The Law of Conservation of Matter – a scientific law that states that during a chemical reaction, matter cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed into a different form. Period law- The chemical properti ...
Deconstructed HS-PS1-2
... trends in the periodic table, and knowledge of the patterns of chemical properties.[Clarification Statement: Examples of chemical reactions could include the reaction of sodium and chlorine, of carbon and oxygen, or of carbon and hydrogen.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment is limited to chemical rea ...
... trends in the periodic table, and knowledge of the patterns of chemical properties.[Clarification Statement: Examples of chemical reactions could include the reaction of sodium and chlorine, of carbon and oxygen, or of carbon and hydrogen.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment is limited to chemical rea ...
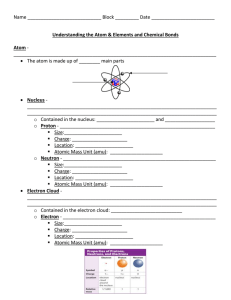
Understanding the Atom GN
... When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons they are called ____________________. Isotope – ________________________________________________________________________ Most elements have ______________________ isotopes. Mass Number - ________________________________________ ...
... When atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons they are called ____________________. Isotope – ________________________________________________________________________ Most elements have ______________________ isotopes. Mass Number - ________________________________________ ...
Chemistry Ch 5-3 Notes: Periodic Trends
... increases as we move from left to right, because the larger number of protons holds onto electrons more strongly. The most difficult elements to remove electrons from are the noble gases (full valence) Also: The more electrons we try to remove, the harder it is to remove them, so first Ionization en ...
... increases as we move from left to right, because the larger number of protons holds onto electrons more strongly. The most difficult elements to remove electrons from are the noble gases (full valence) Also: The more electrons we try to remove, the harder it is to remove them, so first Ionization en ...
Chemistry Review: Antoine Lavoisier (1743
... the same number of electrons, their chemical properties will be exactly the same. However, they have different masses due to the different number of neutrons; therefore, they will have slightly different properties that relate to mass. (Ex. Density , melting and boiling point). Also. Since the neutr ...
... the same number of electrons, their chemical properties will be exactly the same. However, they have different masses due to the different number of neutrons; therefore, they will have slightly different properties that relate to mass. (Ex. Density , melting and boiling point). Also. Since the neutr ...