The Information Processing Mechanism of the Brain
... There is reason to recap the central properties of a neural network. A neural network can be modelled in a simple physical mechanism, which can be studied in computer simulations. This model captures the essential properties of a biological network, and the simplified mechanism shows the fundamental ...
... There is reason to recap the central properties of a neural network. A neural network can be modelled in a simple physical mechanism, which can be studied in computer simulations. This model captures the essential properties of a biological network, and the simplified mechanism shows the fundamental ...
Listening to Narrative Speech after Aphasic
... disrupting many of the subcortical--cortical auditory projections, impairs the onward polysynaptic transmission of encoded speech information to structurally intact regions in auditory association and polysensory temporal lobe neocortex. Further, if the infarct destroys the posterior part of auditor ...
... disrupting many of the subcortical--cortical auditory projections, impairs the onward polysynaptic transmission of encoded speech information to structurally intact regions in auditory association and polysensory temporal lobe neocortex. Further, if the infarct destroys the posterior part of auditor ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... The dendrites of the GABAergic medium spines neurons receive excitatory glutamatergic synapses from cortical cells in the limbic and other association cortices. Signals on these axons are believed to represent predictions of the saliency (importance) or urgency of actions based on past experience an ...
... The dendrites of the GABAergic medium spines neurons receive excitatory glutamatergic synapses from cortical cells in the limbic and other association cortices. Signals on these axons are believed to represent predictions of the saliency (importance) or urgency of actions based on past experience an ...
Local Field Potential in the Visual System
... A pertinent question related to LFP signals is their spatial specificity, reflecting the degree to which they represent local activation within a region of cortex rather than mirroring activation that actually occurs at a distant site. Electrical signals observed locally may thus be due to transmitted ...
... A pertinent question related to LFP signals is their spatial specificity, reflecting the degree to which they represent local activation within a region of cortex rather than mirroring activation that actually occurs at a distant site. Electrical signals observed locally may thus be due to transmitted ...
Microcircuits in visual cortex Kevan AC Martin
... stimulus placed anywhere in the receptive field gives the same ...
... stimulus placed anywhere in the receptive field gives the same ...
phys chapter 51 [3-20
... During reading, person usually makes several saccadic movements of eyes for each line; visual scene not moving past eyes, but eyes trained to move by several successive saccades across visual scene to extract important info o Same saccades occur when person observes painting (saccades follow lines o ...
... During reading, person usually makes several saccadic movements of eyes for each line; visual scene not moving past eyes, but eyes trained to move by several successive saccades across visual scene to extract important info o Same saccades occur when person observes painting (saccades follow lines o ...
Movement
... Figure 8.14 Cellular organization of the cerebellum. Parallel fibers (yellow) activate one Purkinje cell after another. Purkinje cells (red) inhibit a target cell in one of the nuclei of the cerebellum (not shown, but toward the bottom of the illustration). The more Purkinje cells that respond, the ...
... Figure 8.14 Cellular organization of the cerebellum. Parallel fibers (yellow) activate one Purkinje cell after another. Purkinje cells (red) inhibit a target cell in one of the nuclei of the cerebellum (not shown, but toward the bottom of the illustration). The more Purkinje cells that respond, the ...
review - NYU Psychology
... Taken together, this work implies that the basic associative learning processes that are responsible for acquisition and expression of learned fear are similar across species and across different learning procedures, such as social observation and verbal instruction. However, social, affective and c ...
... Taken together, this work implies that the basic associative learning processes that are responsible for acquisition and expression of learned fear are similar across species and across different learning procedures, such as social observation and verbal instruction. However, social, affective and c ...
An oscillation-based model for the neuronal basis
... We are here not concerned with a detailed, biophysitally plausible, mechanism by which this periodic modulation is forced upon the Vl neurons; this could be implemented, for instance, by oscillatory subthreshold input to the Vl neurons. The inferior pulvinar projects onto processes in the superficia ...
... We are here not concerned with a detailed, biophysitally plausible, mechanism by which this periodic modulation is forced upon the Vl neurons; this could be implemented, for instance, by oscillatory subthreshold input to the Vl neurons. The inferior pulvinar projects onto processes in the superficia ...
Saccade-induced activity of dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus X
... saccade was detected if the eye velocity exceeded 50 deg0s. Saccade onset was defined as the time when the velocity reached 10% of the peak velocity during the rising part of the velocity profile. Mean slow-phase eye velocity was calculated from “desaccaded” spontaneous nystagmic eye movements durin ...
... saccade was detected if the eye velocity exceeded 50 deg0s. Saccade onset was defined as the time when the velocity reached 10% of the peak velocity during the rising part of the velocity profile. Mean slow-phase eye velocity was calculated from “desaccaded” spontaneous nystagmic eye movements durin ...
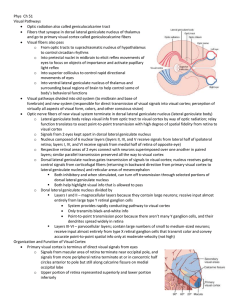
12 - Mrs. Jensen's Science Classroom
... – Part of primitive rhinencephalon, along with olfactory bulbs and tracts – Remainder of rhinencephalon in humans part of limbic system – Region of conscious awareness of odors ...
... – Part of primitive rhinencephalon, along with olfactory bulbs and tracts – Remainder of rhinencephalon in humans part of limbic system – Region of conscious awareness of odors ...
the cortical projection of the medial geniculate body
... described as being in such a state that for three or four weeks after the operation it is deaf. It then becomes able to hear, but does not understand what it hears. In the cortical zone immediately above the pseudo-sylvian sulcus Munk placed " tactile awareness " of the ear. Mann (1896) stimulated t ...
... described as being in such a state that for three or four weeks after the operation it is deaf. It then becomes able to hear, but does not understand what it hears. In the cortical zone immediately above the pseudo-sylvian sulcus Munk placed " tactile awareness " of the ear. Mann (1896) stimulated t ...
Medial medullary syndrome
... • The medulla oblongata is the lowest portion of the brainstem and continuous with the pons superiorly and spinal cord inferiorly. It is a vital anatomic structure as it is responsible for multiple autonomic functions necessary for life. It contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting, and vasomotor ...
... • The medulla oblongata is the lowest portion of the brainstem and continuous with the pons superiorly and spinal cord inferiorly. It is a vital anatomic structure as it is responsible for multiple autonomic functions necessary for life. It contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting, and vasomotor ...
The Auditory System
... Attached to the ossicles are two small muscles, the tensor tympani and the stapedius. The tensor tympani attaches to the malleus and the stapedius attaches to the stapes. The trigeminal nerve innervates the tensor tympani muscle while the facial nerve innervates the stapedius muscle. Contraction of ...
... Attached to the ossicles are two small muscles, the tensor tympani and the stapedius. The tensor tympani attaches to the malleus and the stapedius attaches to the stapes. The trigeminal nerve innervates the tensor tympani muscle while the facial nerve innervates the stapedius muscle. Contraction of ...
From sensorimotor learning to memory cells in prefrontal and
... several seconds (delayed matching to sample task), some neurons fire at an enhanced level throughout the delay (Fig. 1, Constantinidis, Franowicz, & Goldman-Rakic, 2001; Fuster, 1995; Fuster & Alexander, 1971; Kojima & Goldman-Rakic, 1982; Romanski & Goldman-Rakic, 2002). Intriguingly, the persisten ...
... several seconds (delayed matching to sample task), some neurons fire at an enhanced level throughout the delay (Fig. 1, Constantinidis, Franowicz, & Goldman-Rakic, 2001; Fuster, 1995; Fuster & Alexander, 1971; Kojima & Goldman-Rakic, 1982; Romanski & Goldman-Rakic, 2002). Intriguingly, the persisten ...
The Thalamus
... transmitters used by thalamic cells and the interactions of these transmitters with a wide range of receptor types and subtypes which not only govern the responses of thalamic cells to external and internally generated stimuli but also modulate their activities during changes in conscious state. In ...
... transmitters used by thalamic cells and the interactions of these transmitters with a wide range of receptor types and subtypes which not only govern the responses of thalamic cells to external and internally generated stimuli but also modulate their activities during changes in conscious state. In ...
Stimulus-Specific Adaptation in Auditory Cortex Is an NMDA
... • MMN is a human scalp recorded event related potential (ERP) component elicited by a sound which deviates from a repeating pattern of recent sounds, and thought to be generated by a temporo-prefrontal network including auditory cortex. • This claim implies that auditory cortex units themselves play ...
... • MMN is a human scalp recorded event related potential (ERP) component elicited by a sound which deviates from a repeating pattern of recent sounds, and thought to be generated by a temporo-prefrontal network including auditory cortex. • This claim implies that auditory cortex units themselves play ...
The thalamus as a monitor of motor outputs
... behaviour that these messages produce, but we have to address a possibly more difficult issue, which is to think about how reports of visual perceptions relate to messages sent to the superior colliculus or, in general, how perceptual processes relate to the messages that are being passed to motor c ...
... behaviour that these messages produce, but we have to address a possibly more difficult issue, which is to think about how reports of visual perceptions relate to messages sent to the superior colliculus or, in general, how perceptual processes relate to the messages that are being passed to motor c ...
BCM Theory
... not see any significant contribution of the short time scale in learned cerebellar timing (Supplementary Figure S1). See text for further explanations. Note 2. Normal behavior of the cerebellar network Supplementary Figure S2 shows three groups of neurons in the simulated cerebellar network in a hea ...
... not see any significant contribution of the short time scale in learned cerebellar timing (Supplementary Figure S1). See text for further explanations. Note 2. Normal behavior of the cerebellar network Supplementary Figure S2 shows three groups of neurons in the simulated cerebellar network in a hea ...
University of Groningen Ascending projections from spinal
... research, is to learn more about the human central nervous system, possibly contributing to solutions for disease. Although research techniques have been developed to study the living human brain, such as electro encephalograms (EEG), positron emission tomography (PET) and functional magnetic resona ...
... research, is to learn more about the human central nervous system, possibly contributing to solutions for disease. Although research techniques have been developed to study the living human brain, such as electro encephalograms (EEG), positron emission tomography (PET) and functional magnetic resona ...
Current Opinion in Neurobiology (2004)
... activation of representation of the outcome is used to guide behavior in addition to any stimulus–response associations. Recent studies of neural activity in rats, monkeys and humans in discrimination tasks provide another window through which to view learned expectancies in associative learning. In ...
... activation of representation of the outcome is used to guide behavior in addition to any stimulus–response associations. Recent studies of neural activity in rats, monkeys and humans in discrimination tasks provide another window through which to view learned expectancies in associative learning. In ...
General
... – A schedule in which a reinforcer is given following the first correct response after a fixed period of time has elapsed – Does not depend on the number of responses made, only on the one correct response made after the time interval has passed – Characteristic of the fixed-interval schedule is a p ...
... – A schedule in which a reinforcer is given following the first correct response after a fixed period of time has elapsed – Does not depend on the number of responses made, only on the one correct response made after the time interval has passed – Characteristic of the fixed-interval schedule is a p ...
Impaired associative learning in schizophrenia: behavioral and
... on this hippocampal activity are either not formed, or are formed to inadequate strength (Squire et al. 2004). Thus, memory is inadequately established and is unavailable at the fidelity needed when recall is required. In the human brain, the interplay between evolutionarily mature prefrontal and hi ...
... on this hippocampal activity are either not formed, or are formed to inadequate strength (Squire et al. 2004). Thus, memory is inadequately established and is unavailable at the fidelity needed when recall is required. In the human brain, the interplay between evolutionarily mature prefrontal and hi ...
DescendSC10
... 2nd component; for muscles of the limbs and trunk motor neurons and interneurons located in: ventral horn and internal zone of the spinal cord. A parallel exists for the muscles of the head: cranial nerve motor nuclei and reticular formation in the brainstem – these are analogous to above areas. 1 ...
... 2nd component; for muscles of the limbs and trunk motor neurons and interneurons located in: ventral horn and internal zone of the spinal cord. A parallel exists for the muscles of the head: cranial nerve motor nuclei and reticular formation in the brainstem – these are analogous to above areas. 1 ...
motor neurons
... 2. Inhibitory area –medullary reticular system (1) Extend the entire extent to the medulla, lying ventrally and medially near the middle. (2) Transmit inhibitory signals to the same antigravity anterior motor neurons (medullary reticulospinal tract). 1. motor cortex 2. Basal ganglia 3. Cerebellum 4 ...
... 2. Inhibitory area –medullary reticular system (1) Extend the entire extent to the medulla, lying ventrally and medially near the middle. (2) Transmit inhibitory signals to the same antigravity anterior motor neurons (medullary reticulospinal tract). 1. motor cortex 2. Basal ganglia 3. Cerebellum 4 ...