Self-Organization and Functional Role of Lateral Connections and
... selectivity develop together, and perhaps because of the interactions between these two domains, does not produce a clear columnar organization of spatial frequency selectivity. Although the above models replicate the self-organization of a erent structures quite well, they are based on the simpli c ...
... selectivity develop together, and perhaps because of the interactions between these two domains, does not produce a clear columnar organization of spatial frequency selectivity. Although the above models replicate the self-organization of a erent structures quite well, they are based on the simpli c ...
Prefrontal abilities
... materials provided through primary cortex are distinguished, compared and patterned to form a percept, but only in a single modality. The step of unimodal perception is essential to higher mental functioning-all knowledge ofthe real world stems from sensing and perceiving. Intermixed with the unimod ...
... materials provided through primary cortex are distinguished, compared and patterned to form a percept, but only in a single modality. The step of unimodal perception is essential to higher mental functioning-all knowledge ofthe real world stems from sensing and perceiving. Intermixed with the unimod ...
Neural Compensations After Lesion of the Cerebral Cortex
... example, Whishaw (2000) has shown in an elegant series of studies that rats with small motor cortex lesions are initially severely impaired in skilled forelimb reaching tasks but over a 15-day period they show significant improvement (see also Rowntree & Kolb, 1997). Animals with larger lesions show ...
... example, Whishaw (2000) has shown in an elegant series of studies that rats with small motor cortex lesions are initially severely impaired in skilled forelimb reaching tasks but over a 15-day period they show significant improvement (see also Rowntree & Kolb, 1997). Animals with larger lesions show ...
APPsych2e_LecturePPTs_Unit06
... stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone. (Also calle ...
... stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone. (Also calle ...
Cognition`s Influence on Conditioning
... stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone. (Also calle ...
... stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone. (Also calle ...
Operant conditioning
... stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone. (Also calle ...
... stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone. (Also calle ...
Looking for the roots of cortical sensory computation in three
... diffuse organization represents the primordial structure of sensory cortex, prior to the evolution of isocortex in the synapsid and later, mammalian lineage [6]. (iii) That the computational properties of turtle primary visual cortex are more similar in essence to those of high-order cortices (e.g. ...
... diffuse organization represents the primordial structure of sensory cortex, prior to the evolution of isocortex in the synapsid and later, mammalian lineage [6]. (iii) That the computational properties of turtle primary visual cortex are more similar in essence to those of high-order cortices (e.g. ...
Unit 6 Power Point - Waterford Union High School
... stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone. (Also calle ...
... stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone. (Also calle ...
retina - Bakersfield College
... • In lower layer IV of the striate cortex, neurons with circular receptive fields (as in retinal ganglion cells and LGN) are rare • Most neurons in V1 are either – Simple – receptive fields are rectangular with “on” and “off” regions, or – Complex – also rectangular, larger receptive fields, respond ...
... • In lower layer IV of the striate cortex, neurons with circular receptive fields (as in retinal ganglion cells and LGN) are rare • Most neurons in V1 are either – Simple – receptive fields are rectangular with “on” and “off” regions, or – Complex – also rectangular, larger receptive fields, respond ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... Thus, M ganglion cells transmit signals representing movement to the two inferior layers of LGN neurons. These LGN neurons synapse in a subsection of layer 4 of V1. 2. Two Pathways Beyond the Primary Visual Cortex (V1) Neurons in V1 project their axons into two pathways that carry different informa ...
... Thus, M ganglion cells transmit signals representing movement to the two inferior layers of LGN neurons. These LGN neurons synapse in a subsection of layer 4 of V1. 2. Two Pathways Beyond the Primary Visual Cortex (V1) Neurons in V1 project their axons into two pathways that carry different informa ...
Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Changing Directions in
... Figure 6.2 The sequence of events in classical conditioning ...
... Figure 6.2 The sequence of events in classical conditioning ...
The representation of Kanizsa illusory contours in the monkey
... and three which triggered only a moderate response or no response at all (‘noneffective stimuli’). (As IT cortical neurons are often selective for stimuli, the effective and noneffective stimuli differed from cell to cell, i.e., each cell was tested with a different set of six stimuli. See also Figs ...
... and three which triggered only a moderate response or no response at all (‘noneffective stimuli’). (As IT cortical neurons are often selective for stimuli, the effective and noneffective stimuli differed from cell to cell, i.e., each cell was tested with a different set of six stimuli. See also Figs ...
HYPOTHALAMUS and EPITHALAMUS
... Sites around the third ventricle where the nervous system interacts with the vascular system without a blood-brain barrier. Site of release of neurohormones into the systemic (neurohypophysis) or pituitary portal circulation (median eminence). Neurohypophysis - extension of the hypothalamic floor fo ...
... Sites around the third ventricle where the nervous system interacts with the vascular system without a blood-brain barrier. Site of release of neurohormones into the systemic (neurohypophysis) or pituitary portal circulation (median eminence). Neurohypophysis - extension of the hypothalamic floor fo ...
Doberman Headbobbing Syndrome
... compressed, proprioceptive deficits (ataxia) are usually the first signs observed, because these pathways are located more superficially in the white matter and their larger-sized axons are more susceptible to compression than other tracts. Because of the early concomitant upper motor neuron involve ...
... compressed, proprioceptive deficits (ataxia) are usually the first signs observed, because these pathways are located more superficially in the white matter and their larger-sized axons are more susceptible to compression than other tracts. Because of the early concomitant upper motor neuron involve ...
From Nerve Cells to Cognition: The Internal
... activity of specific populations of neurons with specific perceptual and motor processes. From these microelectrode studies we have been able to see that the mechanisms of perception are much the same in humans, monkeys, and even simpler animals. These cellular studies in monkeys also made it possib ...
... activity of specific populations of neurons with specific perceptual and motor processes. From these microelectrode studies we have been able to see that the mechanisms of perception are much the same in humans, monkeys, and even simpler animals. These cellular studies in monkeys also made it possib ...
PDF
... columns, with cell dense cores, are typical of the main posteromedial field in rats (Rice, 1995). Variability is not reported for other columnar systems of connections, but this is likely because many of the systems are harder to visualize globally or require specialized tissue processing. In primar ...
... columns, with cell dense cores, are typical of the main posteromedial field in rats (Rice, 1995). Variability is not reported for other columnar systems of connections, but this is likely because many of the systems are harder to visualize globally or require specialized tissue processing. In primar ...
Basal Ganglia and Cerebellar Inputs to `AIP`
... a unique subregion of area 7b within inferior parietal cortex termed the anterior intraparietal area (AIP). AIP neurons either have visual responses to the three-dimensional features of objects, motor responses to object manipulation or the combination of the two types of responses (Godschalk and Le ...
... a unique subregion of area 7b within inferior parietal cortex termed the anterior intraparietal area (AIP). AIP neurons either have visual responses to the three-dimensional features of objects, motor responses to object manipulation or the combination of the two types of responses (Godschalk and Le ...
Predictability Modulates Human Brain Response to Reward
... temporal-differences (TD), which postulates that a synaptically reinforcing substance, e.g. dopamine, is released in response to errors in reward prediction (Schultz et al., 1997). This model has been used in a wide variety of applications including complex learning tasks, like backgammon (Sutton, 1 ...
... temporal-differences (TD), which postulates that a synaptically reinforcing substance, e.g. dopamine, is released in response to errors in reward prediction (Schultz et al., 1997). This model has been used in a wide variety of applications including complex learning tasks, like backgammon (Sutton, 1 ...
Article Link - Cortical Systems and Behavior Laboratory
... histograms of neuronal firing for trains of either 20- or 75-ms light pulses characterize the responses of an individual excited neuron (Fig. 2, C and E) and suppressed neuron (Fig. 2, D and F). In both cases, neurons exhibited rapid changes in neural activity closely coupled to the onset and offset ...
... histograms of neuronal firing for trains of either 20- or 75-ms light pulses characterize the responses of an individual excited neuron (Fig. 2, C and E) and suppressed neuron (Fig. 2, D and F). In both cases, neurons exhibited rapid changes in neural activity closely coupled to the onset and offset ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... eye field will generate action potentials to execute an appropriate saccade. These neurons project their axons both to the superior colliculus and directly into the RiMLF and PPRF via the corticobulbar tracts. Persons suffering lesions of the frontal eye fields (eg. strokes) find it very difficult t ...
... eye field will generate action potentials to execute an appropriate saccade. These neurons project their axons both to the superior colliculus and directly into the RiMLF and PPRF via the corticobulbar tracts. Persons suffering lesions of the frontal eye fields (eg. strokes) find it very difficult t ...
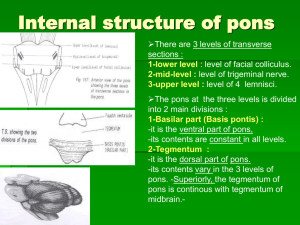
08. pons + midbrain
... -it has ascending fibres to cerebellum, thalamus,hypothalamus, limbic system and cerebral cortex. -its descending fibres project to brain stem & spinal cord. -involved in neural mechanisms regulating sleep. ...
... -it has ascending fibres to cerebellum, thalamus,hypothalamus, limbic system and cerebral cortex. -its descending fibres project to brain stem & spinal cord. -involved in neural mechanisms regulating sleep. ...
Dopamine control of pyramidal neuron activity in the primary motor
... cortex (Cg), or in the deep layers of M1, by using 3H-DA labelling. More recently, Hosp et al. (2011) described in rats direct projections from the Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA) to M1. Although detectable dopaminergic tissue levels can be measured in the motor cortex, this DA innervation remains weak ...
... cortex (Cg), or in the deep layers of M1, by using 3H-DA labelling. More recently, Hosp et al. (2011) described in rats direct projections from the Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA) to M1. Although detectable dopaminergic tissue levels can be measured in the motor cortex, this DA innervation remains weak ...
T2 - Center for Neural Basis of Cognition
... Remapping in humans produces activity in the hemisphere ipsilateral to the stimulus. Remapped activity is present in human parietal, extrastriate and striate cortex. Remapped visual signals are more prevalent at higher levels of the visual system hierarchy. Remapping occurs in parietal and visual co ...
... Remapping in humans produces activity in the hemisphere ipsilateral to the stimulus. Remapped activity is present in human parietal, extrastriate and striate cortex. Remapped visual signals are more prevalent at higher levels of the visual system hierarchy. Remapping occurs in parietal and visual co ...