The Basal Ganglia
... The basal ganglia may be viewed as the principa subcortical components of a family of circuits linkin the thalamus and cerebral cortex. These circuits ar The Skel to~otor Circuit Engages Specific Portions largely segregated, bath structurally and functionally. Each circuit originates in a specific a ...
... The basal ganglia may be viewed as the principa subcortical components of a family of circuits linkin the thalamus and cerebral cortex. These circuits ar The Skel to~otor Circuit Engages Specific Portions largely segregated, bath structurally and functionally. Each circuit originates in a specific a ...
Reticular Formation
... Sensory modalities are merged in a polysynaptic pathway Only provides a vague awareness of any particular sensory modality Results in cortical stimulation with profound effects on: levels of Consciousness and Alerting reactions to sensory stimuli ...
... Sensory modalities are merged in a polysynaptic pathway Only provides a vague awareness of any particular sensory modality Results in cortical stimulation with profound effects on: levels of Consciousness and Alerting reactions to sensory stimuli ...
Warren S. McCulloch: Why the Mind Is in the Head
... analogical contrivances a quantity of something, say a voltage or a distance, is replaced by a number of whatnots or, conversely, the quantity replaces the number. Sense organs and effectors are analogical. For example, the eye and the ear report the continuous variable of intensity by discrete impu ...
... analogical contrivances a quantity of something, say a voltage or a distance, is replaced by a number of whatnots or, conversely, the quantity replaces the number. Sense organs and effectors are analogical. For example, the eye and the ear report the continuous variable of intensity by discrete impu ...
neural mechanisms for detecting and remembering novel events
... effects can be detected after only minutes of experience, they probably continue to develop over longer periods of time (hours to days) and are thought to be mediated by synaptic plasticity28. Effects that are similar to the repetition-related phenomena observed in neural activity can also be seen i ...
... effects can be detected after only minutes of experience, they probably continue to develop over longer periods of time (hours to days) and are thought to be mediated by synaptic plasticity28. Effects that are similar to the repetition-related phenomena observed in neural activity can also be seen i ...
SECTION A.1 – ELECTRICAL IMBALANCE IN AUTISM A. Evidence
... increase the chance an infant will develop autism. Both of these chemicals inflict their damage, at least in part, by reducing the number of GABA dominated (highly inhibitory) synapses in an important portion of the brain called the cerebellum, a structure that provides an electrical filtering role ...
... increase the chance an infant will develop autism. Both of these chemicals inflict their damage, at least in part, by reducing the number of GABA dominated (highly inhibitory) synapses in an important portion of the brain called the cerebellum, a structure that provides an electrical filtering role ...
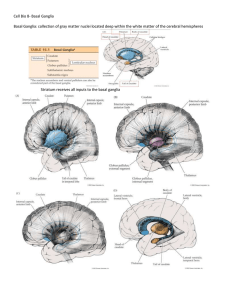
Cell Bio 8- Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia: collection of gray matter
... Huntington’s disease (hyperkinetic): uncontrolled involuntary movements produce a random pattern of jerks and twists Parkinson’s Disease Is a common idiopathic disease caused by loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. It is characterized by asymmetrical ‘pill-rolling’ res ...
... Huntington’s disease (hyperkinetic): uncontrolled involuntary movements produce a random pattern of jerks and twists Parkinson’s Disease Is a common idiopathic disease caused by loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. It is characterized by asymmetrical ‘pill-rolling’ res ...
Classical conditioning - Exp In Social Studies
... acquired a new behavior. Many factors affect acquisition. For instance, up to a point, repeated pairings of CSs and USs yield stronger CRs. The order and timing of the CS and US pairings also have an impact on strength of conditioning. Generally the most effective method is to present the CS first a ...
... acquired a new behavior. Many factors affect acquisition. For instance, up to a point, repeated pairings of CSs and USs yield stronger CRs. The order and timing of the CS and US pairings also have an impact on strength of conditioning. Generally the most effective method is to present the CS first a ...
neuroanatomy - NC State Veterinary Medicine
... spinotectal tract- move neck (head and eyes) towards movements Tegmentum The tegmentum is the ventral mesencephalon. Some definitions exclude the crus cerebri. This area is the location of several LMN nuclei associated with eye functions. In addition, there are pathways passing through this region, ...
... spinotectal tract- move neck (head and eyes) towards movements Tegmentum The tegmentum is the ventral mesencephalon. Some definitions exclude the crus cerebri. This area is the location of several LMN nuclei associated with eye functions. In addition, there are pathways passing through this region, ...
Towards understanding of the cortical network underlying
... Declarative knowledge and experiences are represented in the association cortex and are recalled by reactivation of the neural representation. Electrophysiological experiments have revealed that associations between semantically linked visual objects are formed in neural representations in the tempo ...
... Declarative knowledge and experiences are represented in the association cortex and are recalled by reactivation of the neural representation. Electrophysiological experiments have revealed that associations between semantically linked visual objects are formed in neural representations in the tempo ...
Circuits of emotion in the primate brain
... challenges of their physical and social environment. Emotional states are characterized by a specific configuration of inputs (triggering events), outputs (autonomic and somatic responses), and the neural processes that mediate their transformation. Many emotional states, especially acute states suc ...
... challenges of their physical and social environment. Emotional states are characterized by a specific configuration of inputs (triggering events), outputs (autonomic and somatic responses), and the neural processes that mediate their transformation. Many emotional states, especially acute states suc ...
Sensory Pathways and Emotional Context for Action
... cortex are more global than to lateral prefrontal cortex by virtue of their topography from anterior high-order sensory association cortices that represent each and every sensory modality (29,30) (Figure 1). Further, more than any other prefrontal region, the orbitofrontal cortex is connected with a ...
... cortex are more global than to lateral prefrontal cortex by virtue of their topography from anterior high-order sensory association cortices that represent each and every sensory modality (29,30) (Figure 1). Further, more than any other prefrontal region, the orbitofrontal cortex is connected with a ...
Is this a brain which I see before me? Modeling human neural
... cardinal features of neural ontogenesis are remarkably conserved in human models, which can be studied in a reductionist fashion. They have also revealed species-specific features, which constitute attractive lines of investigation to elucidate the mechanisms underlying the development of the human ...
... cardinal features of neural ontogenesis are remarkably conserved in human models, which can be studied in a reductionist fashion. They have also revealed species-specific features, which constitute attractive lines of investigation to elucidate the mechanisms underlying the development of the human ...
A neural reinforcement learning model for tasks with unknown time... Daniel Rasmussen () Chris Eliasmith ()
... building models capable of this type of learning is an important step in understanding the decision making processes in the brain. There have been models built that solve these types of tasks, but often they take the TD error signal (Equation 3) as given, or it is computed outside the model (Foster ...
... building models capable of this type of learning is an important step in understanding the decision making processes in the brain. There have been models built that solve these types of tasks, but often they take the TD error signal (Equation 3) as given, or it is computed outside the model (Foster ...
Is this a brain which I see before me? Modeling human neural
... cardinal features of neural ontogenesis are remarkably conserved in human models, which can be studied in a reductionist fashion. They have also revealed species-specific features, which constitute attractive lines of investigation to elucidate the mechanisms underlying the development of the human ...
... cardinal features of neural ontogenesis are remarkably conserved in human models, which can be studied in a reductionist fashion. They have also revealed species-specific features, which constitute attractive lines of investigation to elucidate the mechanisms underlying the development of the human ...
Neuronal Selectivities to Complex Object
... (e.g., Marr 1982) propose that the visual recognition of objects requires many steps of computation; thus we wish to assign different kinds of computation to different stages of the pathway. Although a functional dissociation between posterior IT and anterior IT was suggested on the basis of lesion ...
... (e.g., Marr 1982) propose that the visual recognition of objects requires many steps of computation; thus we wish to assign different kinds of computation to different stages of the pathway. Although a functional dissociation between posterior IT and anterior IT was suggested on the basis of lesion ...
Auditory Brain Development in Children With Hearing Loss– Part One
... their hearing as adults, and received a CI after a variable We have yet to develop a full understanding of exactly how range of duration of deafness (1 to 48 years). As shown in and where auditory objects are represented in the brain. DeFigure 3, a broad area of activation was seen in the auditory r ...
... their hearing as adults, and received a CI after a variable We have yet to develop a full understanding of exactly how range of duration of deafness (1 to 48 years). As shown in and where auditory objects are represented in the brain. DeFigure 3, a broad area of activation was seen in the auditory r ...
Mapping form and function in the human brain: the emerging field of
... glucose metabolism in the heterotopic band of gray matter [19–21], have long raised the possibility of normal physiological activity in the heterotopic neurons, although they are subject to the same spatial resolution limitations mentioned earlier. More recently, a number of case reports of blood ox ...
... glucose metabolism in the heterotopic band of gray matter [19–21], have long raised the possibility of normal physiological activity in the heterotopic neurons, although they are subject to the same spatial resolution limitations mentioned earlier. More recently, a number of case reports of blood ox ...
Motor and cognitive functions of the ventral premotor cortex
... reversibly inactivated. The results showed that after inactivation of F5ab (the sector where canonical neurons are located), the hand shaping that relies on the visual properties of the objects was markedly impaired. The monkeys were able to grasp the objects, but only after corrections made under t ...
... reversibly inactivated. The results showed that after inactivation of F5ab (the sector where canonical neurons are located), the hand shaping that relies on the visual properties of the objects was markedly impaired. The monkeys were able to grasp the objects, but only after corrections made under t ...
Morphology and Physiology of the Cerebellar Vestibulolateral Lobe
... Two days before an acute experiment, goldfish were deeply anesthetized in tricaine methanesulfonate (MS222; 1:2,000 wt/vol; Sigma, St. Louis, MO). Self-tapping screws were placed in the skull and stabilizing bolts were anchored with dental acrylic. To obtain orthodromic identification of Area II neu ...
... Two days before an acute experiment, goldfish were deeply anesthetized in tricaine methanesulfonate (MS222; 1:2,000 wt/vol; Sigma, St. Louis, MO). Self-tapping screws were placed in the skull and stabilizing bolts were anchored with dental acrylic. To obtain orthodromic identification of Area II neu ...
Circuits in Psychopharmacology
... this picture when studying images throughout this book to remind yourself at times what cut of the brain you are looking at, and how the cut relates to the orientation of the whole brain. One can also visualize the brain in some figures that attempt to show the structures underlying the cortex in a ...
... this picture when studying images throughout this book to remind yourself at times what cut of the brain you are looking at, and how the cut relates to the orientation of the whole brain. One can also visualize the brain in some figures that attempt to show the structures underlying the cortex in a ...
Chapter 11: Theories of learning Learning activity suggested answers
... Describe the relationship between timing and acquisition. Timing is important in acquisition because the CS and UCS must be presented/paired close together in time (contiguous and about half a second maximum ...
... Describe the relationship between timing and acquisition. Timing is important in acquisition because the CS and UCS must be presented/paired close together in time (contiguous and about half a second maximum ...
Structural changes that occur during normal aging of primate
... larger cortical neurons, the Meynert cells of visual cortex [27] come to contain little age pigment, while the Betz cells of motor cortex can become so full of pigment that their nuclei are displaced to one side of the cell body [29]. But otherwise the cell bodies of cortical neurons seem to be slig ...
... larger cortical neurons, the Meynert cells of visual cortex [27] come to contain little age pigment, while the Betz cells of motor cortex can become so full of pigment that their nuclei are displaced to one side of the cell body [29]. But otherwise the cell bodies of cortical neurons seem to be slig ...
Inhibitory interneurons in the piriform cortex
... the olfactory bulb via the lateral olfactory tract (LOT; Figure 1A). The PC is commonly divided into anterior (aPC) and posterior (pPC) regions, with the boundary at the caudal end of the LOT.16 A coronal slice taken from the aPC has the typical trilaminar structure shown schematically in Figure 1B. ...
... the olfactory bulb via the lateral olfactory tract (LOT; Figure 1A). The PC is commonly divided into anterior (aPC) and posterior (pPC) regions, with the boundary at the caudal end of the LOT.16 A coronal slice taken from the aPC has the typical trilaminar structure shown schematically in Figure 1B. ...
Cajal`s debt to Golgi
... similar results. It was only after Cajal much later, in 1888 and 1889, applied the stain in repeated impregnations, with longer immersion times and more concentrated reagents, and in infant animals in which myelination was less advanced than in adults, that others were able successfully to use it (D ...
... similar results. It was only after Cajal much later, in 1888 and 1889, applied the stain in repeated impregnations, with longer immersion times and more concentrated reagents, and in infant animals in which myelination was less advanced than in adults, that others were able successfully to use it (D ...
Perception of Motion, Depth, and Form
... cleus to the inferior temporal cortex can therefore also be identified (Figure 28-2). But are these pathways exclusive of each other? Several anatomical observations suggest that they are not. In V1 both the magnocellular and parvocellular pathways have inputs in the blobs, and local neurons make ex ...
... cleus to the inferior temporal cortex can therefore also be identified (Figure 28-2). But are these pathways exclusive of each other? Several anatomical observations suggest that they are not. In V1 both the magnocellular and parvocellular pathways have inputs in the blobs, and local neurons make ex ...