Insular cortex – review
... important from the aspect of social interactions as well. That is because we recognize the same subjective feeling states we once experienced in others. It is a basis in applying empathy towards others and building strong intersocial connections inside a group 5. Social awareness end empathy are jus ...
... important from the aspect of social interactions as well. That is because we recognize the same subjective feeling states we once experienced in others. It is a basis in applying empathy towards others and building strong intersocial connections inside a group 5. Social awareness end empathy are jus ...
The hippocampo-cortical loop: Spatio
... goal, however, revealed that it peaked just before the end of the 2 s delay. Since the rat is immobile at that time, no motor commands or changes in its location can account for such a transitory firing peak. This firing pattern suggests instead that excess firing at the goal is linked with reward e ...
... goal, however, revealed that it peaked just before the end of the 2 s delay. Since the rat is immobile at that time, no motor commands or changes in its location can account for such a transitory firing peak. This firing pattern suggests instead that excess firing at the goal is linked with reward e ...
the cognitive neuroscience of motivation and learning
... A number of factors seem to impact the tradeoff between goal-directed and habitual behavior in devaluation studies. Notably, knowledge about goal identity appears to support behavior early in training, which is often devaluation sensitive, but behaviors often become devaluation insensitive following ...
... A number of factors seem to impact the tradeoff between goal-directed and habitual behavior in devaluation studies. Notably, knowledge about goal identity appears to support behavior early in training, which is often devaluation sensitive, but behaviors often become devaluation insensitive following ...
Homework Market
... a room, a caged white rat was brought in and placed far enough away so that the boy would not be frightened. At this point, Peter was given candy to eat. On each successive day, the cage was moved closer, after which, Peter was given candy. Eventually, he showed no fear of the rat, even without any ...
... a room, a caged white rat was brought in and placed far enough away so that the boy would not be frightened. At this point, Peter was given candy to eat. On each successive day, the cage was moved closer, after which, Peter was given candy. Eventually, he showed no fear of the rat, even without any ...
Appetitive associative learning recruits a distinct
... water except when otherwise noted. The colony room was maintained at 21 °C on a 12-h light/dark cycle (lights on 06:00) and all behavioral testing was conducted during the light phase of the cycle. Rats were given 1 week to acclimate to the colony room during which time they were handled and weighed ...
... water except when otherwise noted. The colony room was maintained at 21 °C on a 12-h light/dark cycle (lights on 06:00) and all behavioral testing was conducted during the light phase of the cycle. Rats were given 1 week to acclimate to the colony room during which time they were handled and weighed ...
Molekuláris bionika és Infobionika Szakok tananyagának komplex
... PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members ...
... PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members ...
A neural basis for a false memory
... Moreover, implanted memory is not an artifact of unintended reward or punishment because NBstm as used in our studies is motivationally neutral (Miasnikov, Chen, Gross, Poytress, & Weinberger, 2008a). Rather, the nucleus basalis appears to be ‘‘downstream’’ of motivational systems and may constitute ...
... Moreover, implanted memory is not an artifact of unintended reward or punishment because NBstm as used in our studies is motivationally neutral (Miasnikov, Chen, Gross, Poytress, & Weinberger, 2008a). Rather, the nucleus basalis appears to be ‘‘downstream’’ of motivational systems and may constitute ...
Auditory cortex
... In this theory left-hemisphere language organization is not result of domain-specific development, but results from domain general bias of the left hemisphere for decoding rapidly changing sounds (such as those contained in speech). ...
... In this theory left-hemisphere language organization is not result of domain-specific development, but results from domain general bias of the left hemisphere for decoding rapidly changing sounds (such as those contained in speech). ...
Chapter 4 monkey
... which mediate both attentional and decision-making processes if the task requires an eye movement response. The roles of area FEF and the principal sulcus (PS) in decision making have been investigated in a task in which randomly moving dots indicated to the monkey which of the two targets was to be ...
... which mediate both attentional and decision-making processes if the task requires an eye movement response. The roles of area FEF and the principal sulcus (PS) in decision making have been investigated in a task in which randomly moving dots indicated to the monkey which of the two targets was to be ...
Functional and Dysfunctional Aspects of the Cerebral Cortex
... to take care of large receptive fields, reaching the conscious level, and others of small receptive fields for local function at the brainstem level [44]. The strength of information processing performed by a cortical circuit depends on the number of interneuronal connections or synapses. Morphologica ...
... to take care of large receptive fields, reaching the conscious level, and others of small receptive fields for local function at the brainstem level [44]. The strength of information processing performed by a cortical circuit depends on the number of interneuronal connections or synapses. Morphologica ...
Human medial frontal cortex mediates unconscious inhibition of
... of the response activated by the first stimulus and allow responses associated with new stimuli (Jaskowski, in press; Jaskowski and Przekoracka-Krawczyk, 2005; Lleras and Enns, 2006). While this debate is also tangential to our main purpose of simply studying whether SEF and SMA are associated with ...
... of the response activated by the first stimulus and allow responses associated with new stimuli (Jaskowski, in press; Jaskowski and Przekoracka-Krawczyk, 2005; Lleras and Enns, 2006). While this debate is also tangential to our main purpose of simply studying whether SEF and SMA are associated with ...
Responses to Rare Visual Target and Distractor Stimuli Using Event
... Previous studies have found that the P300 or P3 event-related potential (ERP) component is useful in the diagnosis and treatment of many disorders that influence CNS function. However, the anatomic locations of brain regions involved in this response are not precisely known. In the present event-rel ...
... Previous studies have found that the P300 or P3 event-related potential (ERP) component is useful in the diagnosis and treatment of many disorders that influence CNS function. However, the anatomic locations of brain regions involved in this response are not precisely known. In the present event-rel ...
Mayberg HS, Lozano AM. (2009). Targeted electrode
... frontal hyperactivity have also been reported (35, 36). Localization of abnormalities within the frontal lobe includes regions of the dorsolateral and ventral-lateral prefrontal cortex (specifically Brodmann area 9 [BA9], BA46, BA10, and BA47) as well as orbital frontal and ventromedial frontal cort ...
... frontal hyperactivity have also been reported (35, 36). Localization of abnormalities within the frontal lobe includes regions of the dorsolateral and ventral-lateral prefrontal cortex (specifically Brodmann area 9 [BA9], BA46, BA10, and BA47) as well as orbital frontal and ventromedial frontal cort ...
31 - UCL
... and output areas, laminar origins and targets of connections), visuotopic organization (e.g., mirror-image or non-mirror-image map of hemifield, bounding areas, pattern of map discontinuities, degree of retinotopy), and physiological properties (e.g., excitatory receptive field size, direction selec ...
... and output areas, laminar origins and targets of connections), visuotopic organization (e.g., mirror-image or non-mirror-image map of hemifield, bounding areas, pattern of map discontinuities, degree of retinotopy), and physiological properties (e.g., excitatory receptive field size, direction selec ...
Biology 358 — Neuroanatomy First Exam
... This tract is comprised of crossed fibers that terminate primarily within the cervical cord. The UMN synapses primarily on interneurons, and is believed to produced coordinated movements of the eye and head as parts of optic reflexes. Tectospinal ...
... This tract is comprised of crossed fibers that terminate primarily within the cervical cord. The UMN synapses primarily on interneurons, and is believed to produced coordinated movements of the eye and head as parts of optic reflexes. Tectospinal ...
Voltage-Sensitive Dye Imaging: Technique review and Models
... vivo recordings obtained with VSDI in several animal studies. In a second part, we make the underlying limitations of this method explicit: what does the VSD signal measure? A question that is not completely answered in the literature. Finally, this review shows the benefit of brain activity modelin ...
... vivo recordings obtained with VSDI in several animal studies. In a second part, we make the underlying limitations of this method explicit: what does the VSD signal measure? A question that is not completely answered in the literature. Finally, this review shows the benefit of brain activity modelin ...
Prediction in Human Decision Making
... because of the established evidences on existing many common aspects between them [15-26]. The development of biologically inspired models could have many advantages in studying cognitive functions of the brain as they do not have the same limitations as the study of real subjects do. One of the imp ...
... because of the established evidences on existing many common aspects between them [15-26]. The development of biologically inspired models could have many advantages in studying cognitive functions of the brain as they do not have the same limitations as the study of real subjects do. One of the imp ...
J Neurophysiol - University of Connecticut
... highly asymmetric STRFs, evidence of frequency sweep selectivity, but the population showed no directional bias. Binaural preferences differed in their relative proportions, most notably an increased prevalence of excitatory contralateral-only cells in cortex (40%) versus thalamus (23%), indicating ...
... highly asymmetric STRFs, evidence of frequency sweep selectivity, but the population showed no directional bias. Binaural preferences differed in their relative proportions, most notably an increased prevalence of excitatory contralateral-only cells in cortex (40%) versus thalamus (23%), indicating ...
Supervised learning - TKK Automation Technology Laboratory
... • Depending on the method, the learning system will build an internal model based on the training input-output pairs, that then produces reasonable results for unseen inputs too • Usually used for minimization of error signals for problems that have static input-output mappings • Training can be use ...
... • Depending on the method, the learning system will build an internal model based on the training input-output pairs, that then produces reasonable results for unseen inputs too • Usually used for minimization of error signals for problems that have static input-output mappings • Training can be use ...
Chapter 10 - Brands Delmar
... The Spinal Nerves (cont’d.) • Named and numbered according to region and level of spinal cord – Cervical: 8 pairs – Thoracic: 12 pairs – Lumbar: 5 pairs – Sacral: 5 pairs – Coccygeal: 1 pair ...
... The Spinal Nerves (cont’d.) • Named and numbered according to region and level of spinal cord – Cervical: 8 pairs – Thoracic: 12 pairs – Lumbar: 5 pairs – Sacral: 5 pairs – Coccygeal: 1 pair ...
50 Emotional States and Feelings
... These observations provided the basis for the important conclusion that the hypothalamus is not only a motor nucleus for the autonomic nervous system. Rather, it is a coordinating center that integrates various inputs to ensure a well-organized, coherent, and appropriate set of autonomic and somatic ...
... These observations provided the basis for the important conclusion that the hypothalamus is not only a motor nucleus for the autonomic nervous system. Rather, it is a coordinating center that integrates various inputs to ensure a well-organized, coherent, and appropriate set of autonomic and somatic ...
Chapter 14: Brain Control of Movement
... • Loss of inhibition with loss of neurons in caudate, putamen, globus pallidus Copyright © 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
... • Loss of inhibition with loss of neurons in caudate, putamen, globus pallidus Copyright © 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
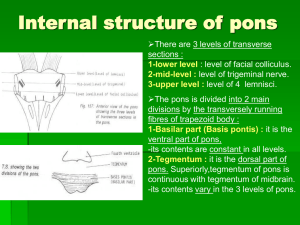
07-pons + midbrain2009-03-24 08:441.9 MB
... by stroke,tumour or multiple sclerosis causes : 1-epsilateral cranial nerve dysfunction + contralateral spastic hemiparesis. 2-hyperreflexia & an extensor plantar response (upper motor neurone lesion). 3-contalateral hemisensory loss. 4-ipsilateral incoordination (ataxia). 5-it can affect eye moveme ...
... by stroke,tumour or multiple sclerosis causes : 1-epsilateral cranial nerve dysfunction + contralateral spastic hemiparesis. 2-hyperreflexia & an extensor plantar response (upper motor neurone lesion). 3-contalateral hemisensory loss. 4-ipsilateral incoordination (ataxia). 5-it can affect eye moveme ...
Horvitz, J.C. Stimulus-response and response
... sory event are cells in the lateral habenula which send inhibitory projections to both VTA and SN DA cells [34,59,92], and which respond to the presentation of non-reward-related visual target stimuli (interspersed with reward-related target trials) approximately 40 ms prior to the onset of the DA i ...
... sory event are cells in the lateral habenula which send inhibitory projections to both VTA and SN DA cells [34,59,92], and which respond to the presentation of non-reward-related visual target stimuli (interspersed with reward-related target trials) approximately 40 ms prior to the onset of the DA i ...
Three-dimensional reconstruction of the lentiform nucleus from
... a human cadaver. Cheap and easily available programs were used during the reconstruction procedure. ...
... a human cadaver. Cheap and easily available programs were used during the reconstruction procedure. ...