Physiology of Proprioception in Balance
... Interoception: By which one perceives pain, hunger…etc and the movement of internal organs. E.g.: peristalsis which is the typical movement of the esophagus, stomach, and intestine. ...
... Interoception: By which one perceives pain, hunger…etc and the movement of internal organs. E.g.: peristalsis which is the typical movement of the esophagus, stomach, and intestine. ...
Basal Ganglia and Associated Pathways
... In addition to the projection neurons (spiny neurons), the striatum also contains large interneurons called aspiny neurons. These neurons are excitatory and use acetylcholine as the neurotransmitter. They seem to preferentially excite projection neurons in the striatum which are part of the indirect ...
... In addition to the projection neurons (spiny neurons), the striatum also contains large interneurons called aspiny neurons. These neurons are excitatory and use acetylcholine as the neurotransmitter. They seem to preferentially excite projection neurons in the striatum which are part of the indirect ...
An Optogenetic Approach to Understanding the Neural Circuits of Fear
... simple features is used) require the medial geniculate (MGm) and the posterior intralaminar thalamic nuclei (PIN) (28 –31) (but see Campeau and Davis [30] and Boatman and Kim [32]), whereas fear conditioning to more complex CSs recruits both thalamic and auditory cortical pathways (31,33). Neurons i ...
... simple features is used) require the medial geniculate (MGm) and the posterior intralaminar thalamic nuclei (PIN) (28 –31) (but see Campeau and Davis [30] and Boatman and Kim [32]), whereas fear conditioning to more complex CSs recruits both thalamic and auditory cortical pathways (31,33). Neurons i ...
neuronal coding of prediction errors
... generalize the mechanisms underlying erroneous behavior, differences between outcome and prediction are referred to as errors in the prediction of outcome. As this example shows, prediction errors lead to the acquisition or modification of behavioral responses until the outcome can be reliably antic ...
... generalize the mechanisms underlying erroneous behavior, differences between outcome and prediction are referred to as errors in the prediction of outcome. As this example shows, prediction errors lead to the acquisition or modification of behavioral responses until the outcome can be reliably antic ...
The avian `prefrontal cortex` and cognition - Ruhr-Universität
... mammals and birds is the lack of a laminated cortex within the avian telencephalon. The mammalian cortex, including neo-, archi- and paleocortical components, together with the claustrum and lateral parts of the amygdala, constitutes the forebrain pallium [2]. Pallium, striatum and pallidum make up ...
... mammals and birds is the lack of a laminated cortex within the avian telencephalon. The mammalian cortex, including neo-, archi- and paleocortical components, together with the claustrum and lateral parts of the amygdala, constitutes the forebrain pallium [2]. Pallium, striatum and pallidum make up ...
Lecture notes for October 9, 2015 FINAL
... Communication to and from the brain involves tracts Ascending tracts are sensory o Deliver information to the brain Descending tracts are motor o Deliver information to the periphery Naming the tracts o If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract deliv ...
... Communication to and from the brain involves tracts Ascending tracts are sensory o Deliver information to the brain Descending tracts are motor o Deliver information to the periphery Naming the tracts o If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract deliv ...
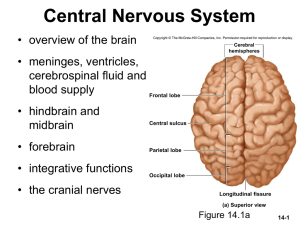
Chapter 12 PowerPoint - Hillsborough Community College
... Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Different Roles for Amygdala Central Nucleus and Substantia
... identical for experiments 3 (n ⫽ 48) and 4 (n ⫽ 43), except that lesions and cannulas were directed to the SI/nBM. SI/nBM lesions were made using stereotaxic coordinates 0.8 mm posterior to bregma and 2.3 and 3.3 mm from the midline, with infusions at depths of ⫺7.8 and ⫺8.1 mm, respectively. For ea ...
... identical for experiments 3 (n ⫽ 48) and 4 (n ⫽ 43), except that lesions and cannulas were directed to the SI/nBM. SI/nBM lesions were made using stereotaxic coordinates 0.8 mm posterior to bregma and 2.3 and 3.3 mm from the midline, with infusions at depths of ⫺7.8 and ⫺8.1 mm, respectively. For ea ...
505kb pdf - Brain Sciences Center
... recorded. Let us place the x axis of a rectangular lattice along the penetration line, with the lattice origin (0, 0) at a neuron i (i ⫽ 1, 2, . . ., n). The coordinate x thus indicates the position of a given neuron recorded in the penetration with respect to the particular neuron i at the origin o ...
... recorded. Let us place the x axis of a rectangular lattice along the penetration line, with the lattice origin (0, 0) at a neuron i (i ⫽ 1, 2, . . ., n). The coordinate x thus indicates the position of a given neuron recorded in the penetration with respect to the particular neuron i at the origin o ...
Neural ensemble dynamics underlying a long
... requires the basal and lateral amygdala (BLA)1–3 but not hippocampal4 activity. Previous studies found BLA neurons with potentiated responses to a CS, such as an auditory tone, after associative conditioning with an aversive US1–3. This prompted a Hebbian model in which ‘fear cells’ with co-active i ...
... requires the basal and lateral amygdala (BLA)1–3 but not hippocampal4 activity. Previous studies found BLA neurons with potentiated responses to a CS, such as an auditory tone, after associative conditioning with an aversive US1–3. This prompted a Hebbian model in which ‘fear cells’ with co-active i ...
CNS Slide Show
... the “gateway to the cerebral cortex” – nearly all input to the cerebrum passes by way of synapses in the thalamic nuclei, filters information on its way to cerebral cortex – plays key role in motor control by relaying signals from cerebellum to cerebrum and providing feedback loops between the cereb ...
... the “gateway to the cerebral cortex” – nearly all input to the cerebrum passes by way of synapses in the thalamic nuclei, filters information on its way to cerebral cortex – plays key role in motor control by relaying signals from cerebellum to cerebrum and providing feedback loops between the cereb ...
Wirth et al., 2009, Neuron
... learning of novel object-place-response associations. Recordings were made throughout the full anterior-posterior extent of the hippocampus, and based on MRI reconstructions, they appeared to include neurons from all hippocampal subdivisions (Figure 1D). We did not attempt to select cells based on t ...
... learning of novel object-place-response associations. Recordings were made throughout the full anterior-posterior extent of the hippocampus, and based on MRI reconstructions, they appeared to include neurons from all hippocampal subdivisions (Figure 1D). We did not attempt to select cells based on t ...
Corticostriatal neurons in auditory cortex drive decisions during
... The neural pathways by which information about the acoustic world reaches the auditory cortex are well characterized, but how auditory representations are transformed into motor commands is not known. Here we use a perceptual decision-making task in rats to study this transformation. We demonstrate ...
... The neural pathways by which information about the acoustic world reaches the auditory cortex are well characterized, but how auditory representations are transformed into motor commands is not known. Here we use a perceptual decision-making task in rats to study this transformation. We demonstrate ...
Spatial Representation and Navigation in a Bio
... direction coding in artificial place and direction sensitive neurons. During agentenvironment interactions correlations between visually– and self-motion–driven cells are discovered by means of unsupervised Hebbian learning. Such a learning process results in a robust space representation consisting ...
... direction coding in artificial place and direction sensitive neurons. During agentenvironment interactions correlations between visually– and self-motion–driven cells are discovered by means of unsupervised Hebbian learning. Such a learning process results in a robust space representation consisting ...
Neural network
... • When the network is used, it identifies the input pattern and tries to output the associated output pattern. • The power of neural networks comes to life when a pattern that has no output associated with it, is given as an input. • In this case, the network gives the output that corresponds to a t ...
... • When the network is used, it identifies the input pattern and tries to output the associated output pattern. • The power of neural networks comes to life when a pattern that has no output associated with it, is given as an input. • In this case, the network gives the output that corresponds to a t ...
1 - optometrie.ch
... Upon attempted left lateral gaze, the right eye adducts In considering lateral gaze, it is important to understand that there is a difference among lesions of the abducens NERVE, the abducens NUCLEUS and the Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (MLF). The abducens nucleus has two populations of neurons. O ...
... Upon attempted left lateral gaze, the right eye adducts In considering lateral gaze, it is important to understand that there is a difference among lesions of the abducens NERVE, the abducens NUCLEUS and the Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (MLF). The abducens nucleus has two populations of neurons. O ...
CEREBRAL CORTEX - Global Anatomy Home Page
... characterized by the complexity of symptoms. Pure sensory or motor deficits of a specific nature are rarely seen following cortical damage but, rather, sensory and motor problems tend to be combined with “higher order” dysfunctions involving thought processes, speech, emotions, or memory. This proba ...
... characterized by the complexity of symptoms. Pure sensory or motor deficits of a specific nature are rarely seen following cortical damage but, rather, sensory and motor problems tend to be combined with “higher order” dysfunctions involving thought processes, speech, emotions, or memory. This proba ...
EXTINCTION LEARNING - Ruhr
... Associative Pavlovian fear conditioning and fear extinction are widely used paradigms to gain insights into substrates and mechanisms supporting learning and memory processes. They are powerful models because of striking parallels between rodents and humans and their high relevance for unraveling ne ...
... Associative Pavlovian fear conditioning and fear extinction are widely used paradigms to gain insights into substrates and mechanisms supporting learning and memory processes. They are powerful models because of striking parallels between rodents and humans and their high relevance for unraveling ne ...
The Cerebrum
... • Somatic Sensory Association Area » Receives and interprets information from skin, musculoskeletal system, vicera (organs), and taste buds » Works with primary sensory cortex ...
... • Somatic Sensory Association Area » Receives and interprets information from skin, musculoskeletal system, vicera (organs), and taste buds » Works with primary sensory cortex ...
The Basal Ganglia and Chunking of Action Repertoires
... is also slowly acquired as a result of repeated pairing between stimulus and response. Both in humans and in other animals, habit learning can be dissociated from forms of explicit learning, mediated by hippocampal–medial temporal cortical systems, and from affect-related learning associated with li ...
... is also slowly acquired as a result of repeated pairing between stimulus and response. Both in humans and in other animals, habit learning can be dissociated from forms of explicit learning, mediated by hippocampal–medial temporal cortical systems, and from affect-related learning associated with li ...
Somatosensory Systems: Pain and Temperature - Dr
... Begin learning these pathways by associating the modality with the pathway name. The Basic Plan for Somatosensory Information to Consciousness The systems that transmit somatosensory information to the level of consciousness follow a basic plan. (see Figure 1) Adequate stimuli evoke generator potent ...
... Begin learning these pathways by associating the modality with the pathway name. The Basic Plan for Somatosensory Information to Consciousness The systems that transmit somatosensory information to the level of consciousness follow a basic plan. (see Figure 1) Adequate stimuli evoke generator potent ...
Document
... CNS are via 3 peduncles: Efferent connections pass through the rostral peduncle and afferent pathways enter the cerebellum via the middle and caudal peduncles. The cerebellum regulates and smoothes motor activity initiated by the UMN system. It also acts to maintain equilibrium and appropriate body ...
... CNS are via 3 peduncles: Efferent connections pass through the rostral peduncle and afferent pathways enter the cerebellum via the middle and caudal peduncles. The cerebellum regulates and smoothes motor activity initiated by the UMN system. It also acts to maintain equilibrium and appropriate body ...
Abstract
... development is essential not only to gain insight into its normal functioning, but also to progress in the compre hension of neurological and psychiatric disease. Indeed, there is increasing evidence that defects occurring during embryonic development lead to impaired functioning of the cerebral c ...
... development is essential not only to gain insight into its normal functioning, but also to progress in the compre hension of neurological and psychiatric disease. Indeed, there is increasing evidence that defects occurring during embryonic development lead to impaired functioning of the cerebral c ...
Cranial Nerves
... • The cranial nerve routes for sensory and motor circuits have different neuroanatomical connections. Sensory pathways are composed of 3 major neurons: the primary, the secondary, and the tertiary (see Figure 2). The cell bodies of primary neurons are usually located outside the CNS in sensory gangl ...
... • The cranial nerve routes for sensory and motor circuits have different neuroanatomical connections. Sensory pathways are composed of 3 major neurons: the primary, the secondary, and the tertiary (see Figure 2). The cell bodies of primary neurons are usually located outside the CNS in sensory gangl ...
Presentation - Neuropathology
... bradykinesia, rigidity, postural instability, and a postural/action tremor rather than the classic pill-rolling tremor seen in Parkinson's disease. These symptoms are usually poorly responsive to long-term levodopa therapy. In MSA-C, typical findings are gait and limb ataxia, cerebellar dysarthria, ...
... bradykinesia, rigidity, postural instability, and a postural/action tremor rather than the classic pill-rolling tremor seen in Parkinson's disease. These symptoms are usually poorly responsive to long-term levodopa therapy. In MSA-C, typical findings are gait and limb ataxia, cerebellar dysarthria, ...