Alaskan Husky encephalopathy - UC Davis School of Veterinary
... general, neuronal loss was seen as zones of gliotic neuropil containing a diminished complement of neurons and such changes were a regular finding in all animals. In active lesions, the surrounding neuropil was sometimes only minimally gliotic, imparting the impression of neuronal ‘drop out’. In mor ...
... general, neuronal loss was seen as zones of gliotic neuropil containing a diminished complement of neurons and such changes were a regular finding in all animals. In active lesions, the surrounding neuropil was sometimes only minimally gliotic, imparting the impression of neuronal ‘drop out’. In mor ...
MirrorBot Report 6
... will design have to help us to better understand complex biological processes. As a consequence, we will have sometimes to make some compromises. Some mechanisms can be defined hardwired to accelerate the computation of some peripheral functions or the implementation can be restricted to the functio ...
... will design have to help us to better understand complex biological processes. As a consequence, we will have sometimes to make some compromises. Some mechanisms can be defined hardwired to accelerate the computation of some peripheral functions or the implementation can be restricted to the functio ...
ACQ_and_the_Basal_Ganglia
... • Different actor-critic architectures have been proposed for learning different value functions: – V(s) = State values (most common) – V(a) = Action values – Q(s,a) = State, action pair values ...
... • Different actor-critic architectures have been proposed for learning different value functions: – V(s) = State values (most common) – V(a) = Action values – Q(s,a) = State, action pair values ...
PDF
... type, Ntf3−/−, Sip1fl/fl;NexCre and Sip1Ntf3 DKO. The decrease in Ctip2 cells in Sip1 mutants is not restored in Sip1-Ntf3 DKOs. Similarly, the increase in Satb2+ cells is also not restored. (B) Brn2, another UL marker, and (C) Sox5, a layer VI marker, also confirm that the Sip1-Ntf3 DKO does not re ...
... type, Ntf3−/−, Sip1fl/fl;NexCre and Sip1Ntf3 DKO. The decrease in Ctip2 cells in Sip1 mutants is not restored in Sip1-Ntf3 DKOs. Similarly, the increase in Satb2+ cells is also not restored. (B) Brn2, another UL marker, and (C) Sox5, a layer VI marker, also confirm that the Sip1-Ntf3 DKO does not re ...
21-Spinal Cord Tracts I
... The spinocerebellar system consists of a sequence of only two neurons Two tracts: Posterior & Anterior Located near the dorsolateral and ventrolateral surfaces of the cord Contain axons of the second order neurons Carry information derived from muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs and tectile recept ...
... The spinocerebellar system consists of a sequence of only two neurons Two tracts: Posterior & Anterior Located near the dorsolateral and ventrolateral surfaces of the cord Contain axons of the second order neurons Carry information derived from muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs and tectile recept ...
Properties of ventromedial hypothalamic neurons with axons
... Surgery was performed under light urethane anesthesia (1.2 g/ kg body weight, given intraperitoneally in 0.5 g/ml solution). The animal was tracheotomized and put in a stereotaxic frame in a prone position, with the incisor bar put 5 mm above the center of the ear bars. Craniotomy was made in the pa ...
... Surgery was performed under light urethane anesthesia (1.2 g/ kg body weight, given intraperitoneally in 0.5 g/ml solution). The animal was tracheotomized and put in a stereotaxic frame in a prone position, with the incisor bar put 5 mm above the center of the ear bars. Craniotomy was made in the pa ...
Functional Neuroanatomy for Posture and Gait Control
... hypertonus-related reticulospinal neurons (b; n = 76). When carbachol (long-acting cholinomimetic agents) was injected into the pontine reticular formation muscle tone of decerebrate cats was abolished. Reticulospinal neurons of which firing frequency was increased to more than 10 Hz during carbacho ...
... hypertonus-related reticulospinal neurons (b; n = 76). When carbachol (long-acting cholinomimetic agents) was injected into the pontine reticular formation muscle tone of decerebrate cats was abolished. Reticulospinal neurons of which firing frequency was increased to more than 10 Hz during carbacho ...
Neural Compensations After Lesion of the Cerebral
... example, Whishaw (2000) has shown in an elegant series of studies that rats with small motor cortex lesions are initially severely impaired in skilled forelimb reaching tasks but over a 15-day period they show significant improvement (see also Rowntree & Kolb, 1997). Animals with larger lesions show ...
... example, Whishaw (2000) has shown in an elegant series of studies that rats with small motor cortex lesions are initially severely impaired in skilled forelimb reaching tasks but over a 15-day period they show significant improvement (see also Rowntree & Kolb, 1997). Animals with larger lesions show ...
The Neuromodulatory Basis of Emotion
... attention has been given to the catecholamines (norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin). The study of the effects of these neuroactive substances gave rise to the "catecholamine hypothesis of affective disorders" (19) that presented general (brain-wide) catecholamine (NE) depletion as a characterist ...
... attention has been given to the catecholamines (norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin). The study of the effects of these neuroactive substances gave rise to the "catecholamine hypothesis of affective disorders" (19) that presented general (brain-wide) catecholamine (NE) depletion as a characterist ...
Functional Connections of the Visual Cortex Studied by Cross
... has been achieved in two ways. Visual stimulation is one commonly used method . Neurons under investigation are activated by repeated visual stimulation. The neurally related CCG representing the true synaptic interactions between the neurons is determined by subtracting the stimulusrelated CCG whic ...
... has been achieved in two ways. Visual stimulation is one commonly used method . Neurons under investigation are activated by repeated visual stimulation. The neurally related CCG representing the true synaptic interactions between the neurons is determined by subtracting the stimulusrelated CCG whic ...
CASE 47
... The basal ganglia, located near the thalamus in the diencephalon, are composed of five pairs of nuclei: the caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. The basal ganglia receive synaptic input from motor cortex (as well as from sensory association and prefro ...
... The basal ganglia, located near the thalamus in the diencephalon, are composed of five pairs of nuclei: the caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. The basal ganglia receive synaptic input from motor cortex (as well as from sensory association and prefro ...
Trigeminal, Gustatory, and Visceral Sensory Systems
... Identify the following nuclei: main trigeminal nucleus; trigeminal motor nucleus (located medial to the sensory nucleus and separated from it by fibers of the trigeminal nerve); pontine nuclei. Identify the following fiber tracts: MLF; medial lemniscus; lateral lemniscus; middle cerebellar peduncle; ...
... Identify the following nuclei: main trigeminal nucleus; trigeminal motor nucleus (located medial to the sensory nucleus and separated from it by fibers of the trigeminal nerve); pontine nuclei. Identify the following fiber tracts: MLF; medial lemniscus; lateral lemniscus; middle cerebellar peduncle; ...
Document
... mealtimes. She grabs food from the plates of those sitting near her and tries to cram the food into her mouth. Because this behavior of stealing food is very undesirable, a plan is developed whereby every time the patient steals food from other plates, she is immediately taken to a room without food ...
... mealtimes. She grabs food from the plates of those sitting near her and tries to cram the food into her mouth. Because this behavior of stealing food is very undesirable, a plan is developed whereby every time the patient steals food from other plates, she is immediately taken to a room without food ...
The Basal Ganglia Anatomy, Physiology, etc. Overview
... • GPi is the principal basal ganglia output for control of limb movement. • Neurons in GPi fire tonically at 60 spikes/sec to 80 spikes/sec at rest. • The discharge of many GPi neurons is related to direction of limb movement. • GPi activity is not correlated with other physical parameters of movem ...
... • GPi is the principal basal ganglia output for control of limb movement. • Neurons in GPi fire tonically at 60 spikes/sec to 80 spikes/sec at rest. • The discharge of many GPi neurons is related to direction of limb movement. • GPi activity is not correlated with other physical parameters of movem ...
Auditory Brain Development in Children with Hearing Loss – Part Two
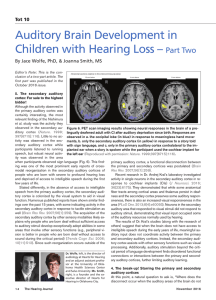
... observed in the secondary au Figure 6. PET scan imaging results showing neural responses in the brain of a pre- ditory cortex (Nature. 1999; lingually deafened adult with CI after auditory deprivation since birth. Responses are 397[6715]:116). Little to no ac observed in a. the occipital lobe (in ...
... observed in the secondary au Figure 6. PET scan imaging results showing neural responses in the brain of a pre- ditory cortex (Nature. 1999; lingually deafened adult with CI after auditory deprivation since birth. Responses are 397[6715]:116). Little to no ac observed in a. the occipital lobe (in ...
Neuroscience, 4e
... Figure 9.3 Receptive fields and two-point discrimination threshold (Part 1) ...
... Figure 9.3 Receptive fields and two-point discrimination threshold (Part 1) ...
Supplementary Materials ANTICIPATION PHASE Neutral vs. gain
... To investigate areas of decreased activity during reward anticipation, we also examined the reverse contrast (neutral cues contrasted with gain cues). This yielded predictable activations in areas related to the default mode network (DMN) [40], including bilateral middle frontal gyrus, superior fron ...
... To investigate areas of decreased activity during reward anticipation, we also examined the reverse contrast (neutral cues contrasted with gain cues). This yielded predictable activations in areas related to the default mode network (DMN) [40], including bilateral middle frontal gyrus, superior fron ...
Ch_6_Learning_PP
... training. If trials are spaced too close together or too far apart, it may take many trials to get the response strength. If trials are spaced evenly, then it will take less training to get desired effect. ...
... training. If trials are spaced too close together or too far apart, it may take many trials to get the response strength. If trials are spaced evenly, then it will take less training to get desired effect. ...
Is There a Cell-Biological Alphabet for Simple Forms of Learning?
... response, the US is a strong shock to the tail that produces a powerful set of defensive responses; the CS is a weak stimulus to the siphon that produces a feeble response. After repeated pairing of the CS and US, the CS becomes more effective and elicits a strong gill- and siphon-withdrawal reflex. ...
... response, the US is a strong shock to the tail that produces a powerful set of defensive responses; the CS is a weak stimulus to the siphon that produces a feeble response. After repeated pairing of the CS and US, the CS becomes more effective and elicits a strong gill- and siphon-withdrawal reflex. ...
differentiation of neuronal types and synapses in myelinating
... dishes and coverslips individually handled with plastic-coated forceps. Ten ml of impregnating solution, the full capacity of a Columbia dish, appeared adequate for two coverslip cultures. Gold-toning appeared to be improved by exposing the cultures to the gold chloride and oxalic acid solutions for ...
... dishes and coverslips individually handled with plastic-coated forceps. Ten ml of impregnating solution, the full capacity of a Columbia dish, appeared adequate for two coverslip cultures. Gold-toning appeared to be improved by exposing the cultures to the gold chloride and oxalic acid solutions for ...
Homeostatic plasticity mechanisms in mouse V1
... that the regulation of neuronal firing is achieved by multiple mechanisms acting at a range of levels, from the molecular to the rewiring of neural circuits. Whether these constitute a homeostat, strictly speaking, is a matter for discussion, but all have the desired effect of restoring firing rates ...
... that the regulation of neuronal firing is achieved by multiple mechanisms acting at a range of levels, from the molecular to the rewiring of neural circuits. Whether these constitute a homeostat, strictly speaking, is a matter for discussion, but all have the desired effect of restoring firing rates ...
Протокол
... Symptoms produced by lesions of the anterolateral system vary according to the level of the neuraxis involved. Lesions outside the nervous system frequently stimulate adjacent free nerve endings, thereby producing the subjective sensation of pain. This symptom is most important in calling attention ...
... Symptoms produced by lesions of the anterolateral system vary according to the level of the neuraxis involved. Lesions outside the nervous system frequently stimulate adjacent free nerve endings, thereby producing the subjective sensation of pain. This symptom is most important in calling attention ...
Mapping Pavlovian Conditioning Effects on the Brain: Blocking
... using a marker of metabolic capacity, cytochrome oxidase (Poremba et al. 1997). The regions with cytochrome oxidase differences were limited to areas of the auditory system receiving US somatosensory inputs, such as the dorsal cochlear nucleus, the inferior colliculus, and the secondary auditory cor ...
... using a marker of metabolic capacity, cytochrome oxidase (Poremba et al. 1997). The regions with cytochrome oxidase differences were limited to areas of the auditory system receiving US somatosensory inputs, such as the dorsal cochlear nucleus, the inferior colliculus, and the secondary auditory cor ...