Diencephalon and Hypothalamus
... oxytocin). 2) Indirectly by secretion of releasing factors into the local hypophyseal portal venous plexus (a vascular plexus that carries these releasing factors from the base of the hypothalamus The hypothalamus thus controls anterior pituitary hormone synthesis and release via the transport of th ...
... oxytocin). 2) Indirectly by secretion of releasing factors into the local hypophyseal portal venous plexus (a vascular plexus that carries these releasing factors from the base of the hypothalamus The hypothalamus thus controls anterior pituitary hormone synthesis and release via the transport of th ...
Role of Feedforward and Feedback Projections in Figure
... While stimulating with such a figure-ground texture and recording neural spike activity in the primary visual cortex, two stages of neural processing after stimulus onset can be discerned. One dominated by the early (<100 msec) response transient, another occurring at relatively longer latencies (> ...
... While stimulating with such a figure-ground texture and recording neural spike activity in the primary visual cortex, two stages of neural processing after stimulus onset can be discerned. One dominated by the early (<100 msec) response transient, another occurring at relatively longer latencies (> ...
Spatial organization of thalamocortical and corticothalamic
... observed not only in the barrel centers in layer IV but also in the regions deep to individual barrels in lower layer V and layer VI. Some cells in this deeper aspect of the cortex project axons to the thalamus and send recurrent collaterals to terminate on neurons in layer IV; also, the apical dend ...
... observed not only in the barrel centers in layer IV but also in the regions deep to individual barrels in lower layer V and layer VI. Some cells in this deeper aspect of the cortex project axons to the thalamus and send recurrent collaterals to terminate on neurons in layer IV; also, the apical dend ...
Ch19 Lecture
... Neural Basis of Fear Extinction: A CS-noUS Neural Circuit Extinction training reconfigures the fear circuit (black arrows) so that the CS activates intercalated clusters that inhibit neurons in the central amygdala. To accomplish this, extinction training strengthens synaptic connections linking th ...
... Neural Basis of Fear Extinction: A CS-noUS Neural Circuit Extinction training reconfigures the fear circuit (black arrows) so that the CS activates intercalated clusters that inhibit neurons in the central amygdala. To accomplish this, extinction training strengthens synaptic connections linking th ...
Rule-Selection and Action-Selection have a Shared
... individuals and as a species. It is widely thought to depend on a hierarchy of cognitive and motor processes (Norman and Shallice 1980) that are often associated with the frontal lobes. In this hierarchy, actions are subordinate to the rules that govern them, and they may therefore have a distinct n ...
... individuals and as a species. It is widely thought to depend on a hierarchy of cognitive and motor processes (Norman and Shallice 1980) that are often associated with the frontal lobes. In this hierarchy, actions are subordinate to the rules that govern them, and they may therefore have a distinct n ...
“Parcelation of the White Matter Using DTI: Insights into the
... cognition including social, attentional and emotional well functioning and has been the focus of intense research in certain psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, autism, Tourette’s syndrome, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), dyslexia, depression, genetic disorders (i.e., Down’ ...
... cognition including social, attentional and emotional well functioning and has been the focus of intense research in certain psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, autism, Tourette’s syndrome, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), dyslexia, depression, genetic disorders (i.e., Down’ ...
Task-related “cortical” bursting depends critically
... (i.e., when birds were not singing) were similar to those in intact birds (Fig. 3 A, B Bottom, D and E; data from birds with lesions of Area X are plotted in two different colors, denoting hearing vs. deaf birds, but hereafter are described together as data from lesion birds, as results were similar ...
... (i.e., when birds were not singing) were similar to those in intact birds (Fig. 3 A, B Bottom, D and E; data from birds with lesions of Area X are plotted in two different colors, denoting hearing vs. deaf birds, but hereafter are described together as data from lesion birds, as results were similar ...
asgn2d -- CEREBRAL CORTEX:
... The map of the body is the way the brain codes location on the body. Touch on the foot makes neurons (nerve cells) at the top end of the somatosensory area respond. Touch to the face activates neurons at the bottom end of the somatosensory area. Touch on each finger activates cells in neighboring pa ...
... The map of the body is the way the brain codes location on the body. Touch on the foot makes neurons (nerve cells) at the top end of the somatosensory area respond. Touch to the face activates neurons at the bottom end of the somatosensory area. Touch on each finger activates cells in neighboring pa ...
STDP produces robust oscillatory architectures that exhibit precise
... window τ is 20 ms. For depression, the learning rate value λ is 0.3105 and the window τ is 10 ms. F. Evolution of oscillatory nodes Although groups of neurons firing together rhythmically can occur because of intrinsic firing patterns of excitatory principal cells or common input from a pacemaker, i ...
... window τ is 20 ms. For depression, the learning rate value λ is 0.3105 and the window τ is 10 ms. F. Evolution of oscillatory nodes Although groups of neurons firing together rhythmically can occur because of intrinsic firing patterns of excitatory principal cells or common input from a pacemaker, i ...
Vertical Organization of r=Aminobutyric Acid
... Figure 2. Photomicrographs of a [3H]GABA injection and retrograde cell labeling in motor cortex of a monkey pretreated with amino-oxyacetic acid. The injection of [3H]GABA is in layers I to IIIA (A). Many labeled cells are found around the injection and, at some distance, in layer V. Bar = 200 pm. / ...
... Figure 2. Photomicrographs of a [3H]GABA injection and retrograde cell labeling in motor cortex of a monkey pretreated with amino-oxyacetic acid. The injection of [3H]GABA is in layers I to IIIA (A). Many labeled cells are found around the injection and, at some distance, in layer V. Bar = 200 pm. / ...
The Timing of Response Onset and Offset in Macaque
... stimuli: spots, annuli, and gratings. (1) Spots: P was a disk of maximum or minimum luminance (for ON or OFF cells, respectively) presented on a gray background and confined to the central region of the RF determined from the reverse-correlation map. A was the disk of opposite contrast to P. (2) Ann ...
... stimuli: spots, annuli, and gratings. (1) Spots: P was a disk of maximum or minimum luminance (for ON or OFF cells, respectively) presented on a gray background and confined to the central region of the RF determined from the reverse-correlation map. A was the disk of opposite contrast to P. (2) Ann ...
The Roles of Dopamine - ETH E
... collicular neurons) of the saccadic movement required to bring the target to the fovea. If it is assumed that the animal must execute a saccade to a visually presented stimulus before it can adequately assess its predictive value, the latency of dopamine response would be too short to signal reward. ...
... collicular neurons) of the saccadic movement required to bring the target to the fovea. If it is assumed that the animal must execute a saccade to a visually presented stimulus before it can adequately assess its predictive value, the latency of dopamine response would be too short to signal reward. ...
Cochlea and Auditory Pathways
... Hearing begins with pressure waves impacting the tympanic membrane, causing it to vibrate. The vibration is transmitted from malleus to incus to stapes. The stapes rocks in & out, causing the membrane of the oval window to produce pressure waves within perilymph of the scala vestibuli. Pressure is t ...
... Hearing begins with pressure waves impacting the tympanic membrane, causing it to vibrate. The vibration is transmitted from malleus to incus to stapes. The stapes rocks in & out, causing the membrane of the oval window to produce pressure waves within perilymph of the scala vestibuli. Pressure is t ...
Variance and invariance of neuronal long
... representations of stimulus features by neuronal populations [14,15]. Especially in the latter case, however, it is debated whether stable population coding results from invariant stimulus selectivities of individual neurons or from noisy and potentially drifting single-cell responses that are ‘aver ...
... representations of stimulus features by neuronal populations [14,15]. Especially in the latter case, however, it is debated whether stable population coding results from invariant stimulus selectivities of individual neurons or from noisy and potentially drifting single-cell responses that are ‘aver ...
Visual pathway class..
... receptive fields than V1, so they can integrate multiple cues in the image. MT neurons can detect global motion of the object. ...
... receptive fields than V1, so they can integrate multiple cues in the image. MT neurons can detect global motion of the object. ...
Vertebrate brains and evolutionary connectomics: on the origins of
... wings compared with non-avian anterior appendages in tetrapods, may initially appear to constitute marked novelties. However, they are both anterior pentadactyl appendages, with morphologically differing end results, but with clearly similar and homologous skeletal components, muscles, developmental ...
... wings compared with non-avian anterior appendages in tetrapods, may initially appear to constitute marked novelties. However, they are both anterior pentadactyl appendages, with morphologically differing end results, but with clearly similar and homologous skeletal components, muscles, developmental ...
- D-Scholarship@Pitt
... unfolded cerebral hemisphere simulation17 that exposed cortex within the sulci. The results of the studies are extremely valuable, in that they demonstrated projections from a number of occipital visual areas with superficial SC injections and frontal and parietal visuomotor areas with deeper SC inj ...
... unfolded cerebral hemisphere simulation17 that exposed cortex within the sulci. The results of the studies are extremely valuable, in that they demonstrated projections from a number of occipital visual areas with superficial SC injections and frontal and parietal visuomotor areas with deeper SC inj ...
- Wiley Online Library
... control, ingestion, elimination, reproduction, etc.), as discovered in studies of chronic decerebrate and decorticate animals at the end of the 1800 s (e.g., see Ref. 6). Modern experiments that revealed approach/avoidance columns in the PAG with correlative, opposing cardiorespiratory actions,7 pro ...
... control, ingestion, elimination, reproduction, etc.), as discovered in studies of chronic decerebrate and decorticate animals at the end of the 1800 s (e.g., see Ref. 6). Modern experiments that revealed approach/avoidance columns in the PAG with correlative, opposing cardiorespiratory actions,7 pro ...
30 Hearing - Semantic Scholar
... Because of the systematic variation in mechanical properties along the basilar membrane, stimulation with a pure tone evokes a complex and elegant movement of the membrane. At any instant the partition displays a pattern of up-and-down motion along its length, with the amplitude greatest at a partic ...
... Because of the systematic variation in mechanical properties along the basilar membrane, stimulation with a pure tone evokes a complex and elegant movement of the membrane. At any instant the partition displays a pattern of up-and-down motion along its length, with the amplitude greatest at a partic ...
... In this study we found that in electrophysiologically identified EC layer V principal cells17, bath application of the cholinergic agent carbachol (CCh) (5 mM, n ¼ 38; 10 mM, n ¼ 49) blocked the slow afterhyperpolarization that follows a train of action potentials and, in most cases (84% and 98% in ...
Physiology and mathematical modeling of the auditory system
... and many connections are just beginning to form (e.g. between brainstem nuclei, thalamic nuclei, and auditory cortex). As for other sensory systems, stimulation during this time is essential for normal development. When hearing is impaired in early life, the morphology and function of auditory neuro ...
... and many connections are just beginning to form (e.g. between brainstem nuclei, thalamic nuclei, and auditory cortex). As for other sensory systems, stimulation during this time is essential for normal development. When hearing is impaired in early life, the morphology and function of auditory neuro ...
Rapid Critical Period Induction by Tonic Inhibition in Visual Cortex
... Diazepam (DZ) or vehicle solution was infused daily before and/or during 4 d of MD in GAD65 knock-out mice. Extracellular singleunit recordings from the binocular zone of visual cortex were performed at the end of deprivation. We found that a minimum treatment of 2 d near the beginning of MD was suf ...
... Diazepam (DZ) or vehicle solution was infused daily before and/or during 4 d of MD in GAD65 knock-out mice. Extracellular singleunit recordings from the binocular zone of visual cortex were performed at the end of deprivation. We found that a minimum treatment of 2 d near the beginning of MD was suf ...
View: Chapter Text (PDF with new
... ventrolaterally in the brainstem (previously these somatic efferent nuclei were labeled “special visceral efferent”). Individual cranial nuclei will be described in more detail per brain stem region. RETICULAR FORMATION OVERVIEW. In addition to distinct regions formed by gray matter nuclei and white ...
... ventrolaterally in the brainstem (previously these somatic efferent nuclei were labeled “special visceral efferent”). Individual cranial nuclei will be described in more detail per brain stem region. RETICULAR FORMATION OVERVIEW. In addition to distinct regions formed by gray matter nuclei and white ...
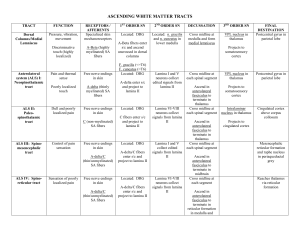
ASCENDING WHITE MATTER TRACTS
... Spinal border cells send axons that corss at each segment and ascend to upper pons where they cross again to reach CB via superior CB peduncle Ends up ipsilateral ...
... Spinal border cells send axons that corss at each segment and ascend to upper pons where they cross again to reach CB via superior CB peduncle Ends up ipsilateral ...
Heterotopic Transcallosal Projections Are Present throughout the
... Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience | www.frontiersin.org ...
... Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience | www.frontiersin.org ...