Corticofugal Modulation of Initial Sound
... trials were recorded as control data. Starting from the 51st trial, a single electrical pulse was delivered to the primary auditory cortex 500 ms before the onset of the first tone burst. After 250 trials, the ES stopped but the tone bursts were continuously delivered until the ES-evoked changes in ...
... trials were recorded as control data. Starting from the 51st trial, a single electrical pulse was delivered to the primary auditory cortex 500 ms before the onset of the first tone burst. After 250 trials, the ES stopped but the tone bursts were continuously delivered until the ES-evoked changes in ...
PHS 398 (Rev. 9/04), Biographical Sketch Format Page
... the spinal cord-computer interface (SCCI) to extract the volitional motor signals from the proximal spinal cord that is still intact above the site of injury in the spinal cord and use the population activity of the axons in the motor tracts rather than single spikes. Spinal cord approach has at lea ...
... the spinal cord-computer interface (SCCI) to extract the volitional motor signals from the proximal spinal cord that is still intact above the site of injury in the spinal cord and use the population activity of the axons in the motor tracts rather than single spikes. Spinal cord approach has at lea ...
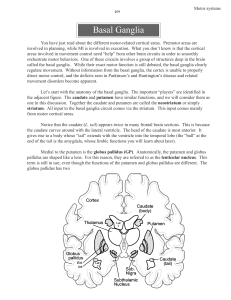
BASAL GANGLIA: A "pit stop" that integrates the movement
... submitted to EPOS by third parties in the form of scientific presentations. References to any names, marks, products, or services of third parties or hypertext links to thirdparty sites or information are provided solely as a convenience to you and do not in any way constitute or imply ECR's endorse ...
... submitted to EPOS by third parties in the form of scientific presentations. References to any names, marks, products, or services of third parties or hypertext links to thirdparty sites or information are provided solely as a convenience to you and do not in any way constitute or imply ECR's endorse ...
PDF
... 500, 800 and 1000 pps. The time interval between presentation of two consecutive trains was 1–2 s. Electrical pulses were generated through a calibrated output of an isolation unit (WPI), allowing fine adjustments of stimulation intensities. Initially, the recorded units were tested with single-puls ...
... 500, 800 and 1000 pps. The time interval between presentation of two consecutive trains was 1–2 s. Electrical pulses were generated through a calibrated output of an isolation unit (WPI), allowing fine adjustments of stimulation intensities. Initially, the recorded units were tested with single-puls ...
Kandel chs. 17, 18 - Weizmann Institute of Science
... one or another kind of stimulus and encode information about the stimulus, such as its location and intensity. The receptors in turn excite sensory neurons that form connections with discrete sets of neurons in the spinal cord. The information from each receptor is then analyzed in the brain stem, ...
... one or another kind of stimulus and encode information about the stimulus, such as its location and intensity. The receptors in turn excite sensory neurons that form connections with discrete sets of neurons in the spinal cord. The information from each receptor is then analyzed in the brain stem, ...
The Thalamic Projections of the Spinothalamic Tract
... and that they reached different thalamic domains including lateral, posterior, and intralaminar nuclei [e.g., 1,3,8]. Gingold and coworkers [35] studied terminal STT-like structures in the thalamus of squirrel monkeys after spinal injections of wheat germ agglutinin-horseradish peroxidase (WGAHRP). T ...
... and that they reached different thalamic domains including lateral, posterior, and intralaminar nuclei [e.g., 1,3,8]. Gingold and coworkers [35] studied terminal STT-like structures in the thalamus of squirrel monkeys after spinal injections of wheat germ agglutinin-horseradish peroxidase (WGAHRP). T ...
Tangential Networks of Precocious Neurons and Early Axonal
... munoreactivity were seen in the rostral thalamus, where GAP43-positive cells and fibers were more abundant: only a few MAP2immunopositive cells were detected in the DTh at CS 17. The more mature intermediate zone of the VTh was composed partly of MAP2-positive cells and fibers. In the rostral basal ...
... munoreactivity were seen in the rostral thalamus, where GAP43-positive cells and fibers were more abundant: only a few MAP2immunopositive cells were detected in the DTh at CS 17. The more mature intermediate zone of the VTh was composed partly of MAP2-positive cells and fibers. In the rostral basal ...
Functional and comparative assessments of the octopus learning
... cases (39). None of these induction mechanisms appear to involve NMDA-like receptors, because the induction was not affected by APV or MK-801 (Hochner et al., 2003) (39). This issue remains to be clarified in a more detailed study. However, if these findings hold, they are most significant, because ...
... cases (39). None of these induction mechanisms appear to involve NMDA-like receptors, because the induction was not affected by APV or MK-801 (Hochner et al., 2003) (39). This issue remains to be clarified in a more detailed study. However, if these findings hold, they are most significant, because ...
Plasticity of Sensory and Motor Maps in Adult Mammals
... monkeysafter different experimental manipulations. A. The location of area 3b on a dorsolateral view of an owl monkeybrain. Because of the lack of a central fissure, most of the representation of the body is in the cortex exposed on the surface of the anterior parietal cortex. The foot and body are ...
... monkeysafter different experimental manipulations. A. The location of area 3b on a dorsolateral view of an owl monkeybrain. Because of the lack of a central fissure, most of the representation of the body is in the cortex exposed on the surface of the anterior parietal cortex. The foot and body are ...
Stimulus-Dependent Synchronization of Neuronal Responses in the
... evoked by the same stimulus are expected to contain such synchronous episodes much more frequently than responses evoked by different stimuli. To test this prediction, we investigated response synchronization in the middle temporal area (area V5 or MT) of alert fixating macaque monkeys. This area is ...
... evoked by the same stimulus are expected to contain such synchronous episodes much more frequently than responses evoked by different stimuli. To test this prediction, we investigated response synchronization in the middle temporal area (area V5 or MT) of alert fixating macaque monkeys. This area is ...
This article was originally published in the
... of error, but no error actually occurs. These trials are characterized as having high conflict, defined as the tension between two or more incompatible competing motor responses. For example, in a Stroop task, subjects must mediate between the habitual tendency to read the word and the instructed ta ...
... of error, but no error actually occurs. These trials are characterized as having high conflict, defined as the tension between two or more incompatible competing motor responses. For example, in a Stroop task, subjects must mediate between the habitual tendency to read the word and the instructed ta ...
Conditional Stimulus Informativeness Governs Conditioned Stimulus
... compared to the other groups, which was reflected in the significant C /T ⫻ Session Block interaction, F(14, 280) ⫽ 5.43 and 4.77, respectively. In addition, the groups trained with the lowest ratio did not respond as often as the other groups. The value of T had no overall effect on the differen ...
... compared to the other groups, which was reflected in the significant C /T ⫻ Session Block interaction, F(14, 280) ⫽ 5.43 and 4.77, respectively. In addition, the groups trained with the lowest ratio did not respond as often as the other groups. The value of T had no overall effect on the differen ...
Principles and Applications of Pavlovian Conditioning
... rats show. Pavlovian conditioning undoubtedly contributes to the enhancement of the predatory attack by causing the animal to approach and contact the stimuli characteristic of the prey. Brown and Jenkins (1968) conducted the first sign-tracking, or autoshaping, experiment. They placed pigeons in an ...
... rats show. Pavlovian conditioning undoubtedly contributes to the enhancement of the predatory attack by causing the animal to approach and contact the stimuli characteristic of the prey. Brown and Jenkins (1968) conducted the first sign-tracking, or autoshaping, experiment. They placed pigeons in an ...
Oriented Axon Projections in Primary Visual Cortex of the Monkey
... it appears that patterned input from the lateral geniculate nucleus to layer 4 provides the basis for orientation selectivity (Hubel and Wiesel, 1962; Ferster and Miller, 2000), neurons in layer 4C of primate V1 are insensitive to stimulus orientation. Instead, sharp orientation tuning is found in l ...
... it appears that patterned input from the lateral geniculate nucleus to layer 4 provides the basis for orientation selectivity (Hubel and Wiesel, 1962; Ferster and Miller, 2000), neurons in layer 4C of primate V1 are insensitive to stimulus orientation. Instead, sharp orientation tuning is found in l ...
MCQ
... a. pretectal nuclei b. optic tract c. optic radiation d. brachium of superior colliculus e. optic chiasm f. third cranial nerve c 43. The motor nucleus and the chief sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve are located in the: a. lower pons b. middle pons c. upper pons d. lower midbrain e. lower medu ...
... a. pretectal nuclei b. optic tract c. optic radiation d. brachium of superior colliculus e. optic chiasm f. third cranial nerve c 43. The motor nucleus and the chief sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve are located in the: a. lower pons b. middle pons c. upper pons d. lower midbrain e. lower medu ...
Rhythmic Spontaneous Activity in the Piriform Cortex
... Figure 2. Characteristics of the spontaneous rhythmic activity in the piriform network. (A) Autocorrelogram and mean frequency (horizontal line) of multiunit activity in layer III. The inset shows how duration was measured at the point where the mean frequency line crossed the central peak. The 2 d ...
... Figure 2. Characteristics of the spontaneous rhythmic activity in the piriform network. (A) Autocorrelogram and mean frequency (horizontal line) of multiunit activity in layer III. The inset shows how duration was measured at the point where the mean frequency line crossed the central peak. The 2 d ...
Motor systems Basal ganglia
... GP(internal). The cells in GP(internal) that project to VA/VL also use GABA. So, the cortical signal excites striatal neurons, which results in MORE inhibition from striatum to GP(internal). More inhibition of GP(internal) means LESS inhibition of motor thalamus (VA/VL). Since the motor thalamus rec ...
... GP(internal). The cells in GP(internal) that project to VA/VL also use GABA. So, the cortical signal excites striatal neurons, which results in MORE inhibition from striatum to GP(internal). More inhibition of GP(internal) means LESS inhibition of motor thalamus (VA/VL). Since the motor thalamus rec ...
Neuronal DNA Content Variation (DCV) With Regional
... The brain and virtually all somatic cells have been generally assumed to contain identical amounts of genomic DNA. The major exception to this assumption are lymphocytes that produce immunoglobulins or T-cell receptors, in part through DNA recombination processes (Schatz and Spanopoulou, 2005). The ...
... The brain and virtually all somatic cells have been generally assumed to contain identical amounts of genomic DNA. The major exception to this assumption are lymphocytes that produce immunoglobulins or T-cell receptors, in part through DNA recombination processes (Schatz and Spanopoulou, 2005). The ...
smell
... • consists of 3 types of cells; a) Olfactory receptor cells; • Bipolar neurons which have: 1. A short thick dendrite with an expanded end called an olfactory rod. Each rod has 10-20 cilia 2. Axons → pierce the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone and enter the olfactory bulbs. • Each olfactory muco ...
... • consists of 3 types of cells; a) Olfactory receptor cells; • Bipolar neurons which have: 1. A short thick dendrite with an expanded end called an olfactory rod. Each rod has 10-20 cilia 2. Axons → pierce the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone and enter the olfactory bulbs. • Each olfactory muco ...
Assessing the Function of Motor Cortex: Single
... a wider repertoire of motor behaviors, the computations of joint torques, muscle forces, and muscle activations are rendered tractable. As a result of this tractability, hypotheses about the correlations between cell activity and variables related to biomechanical force generation can be tested at a ...
... a wider repertoire of motor behaviors, the computations of joint torques, muscle forces, and muscle activations are rendered tractable. As a result of this tractability, hypotheses about the correlations between cell activity and variables related to biomechanical force generation can be tested at a ...
Interkinetic and Migratory Behavior of a Cohort of Neocortical
... the cortex and, after their migrations are completed, as they become redistributed within the cortex (Figs. 1, 2). The Q fraction at E14 is 0.37 (Takahashi et al., 1994). Thus, it is to be expected that only 37% of the cohort labeled by this protocol will exit the cell cycle. To label a larger conti ...
... the cortex and, after their migrations are completed, as they become redistributed within the cortex (Figs. 1, 2). The Q fraction at E14 is 0.37 (Takahashi et al., 1994). Thus, it is to be expected that only 37% of the cohort labeled by this protocol will exit the cell cycle. To label a larger conti ...
The Circuitry of V1 and V2 - UCSD Cognitive Science
... hard to define. The cortex is a fairly uniform tissue adapted, like the skin, for many uses but for no one specific purpose. Neurons in V1 and V2 are not feature detectors, although they can detect features. We shy away from functional assignations and simply describe receptive field properties, recogn ...
... hard to define. The cortex is a fairly uniform tissue adapted, like the skin, for many uses but for no one specific purpose. Neurons in V1 and V2 are not feature detectors, although they can detect features. We shy away from functional assignations and simply describe receptive field properties, recogn ...
Branched thalamic afferents - the Sherman Lab
... been applied to these and to other motor control systems, with a variety of different precise meanings attached to the terms. There have been many studies of efference copies1 in a number of different systems, often with a particular focus on visual or limb movements or cerebellar pathways (e.g. Kan ...
... been applied to these and to other motor control systems, with a variety of different precise meanings attached to the terms. There have been many studies of efference copies1 in a number of different systems, often with a particular focus on visual or limb movements or cerebellar pathways (e.g. Kan ...
Chapter 16 - MBFys Home Page
... hemicord. This arrangement ensures that groups of axial muscles on both sides of the body act in concert to maintain and adjust posture. In contrast, local circuit neurons in the lateral region of the intermediate zone have shorter axons that typically extend fewer than five segments and are predomi ...
... hemicord. This arrangement ensures that groups of axial muscles on both sides of the body act in concert to maintain and adjust posture. In contrast, local circuit neurons in the lateral region of the intermediate zone have shorter axons that typically extend fewer than five segments and are predomi ...
Neural computations associated with goal
... alternative theory of stimulus value computation that takes advantage of the fact that most stimuli are complex bundles of more basic attributes (e.g., foods can be described by a list of perceptual pro ...
... alternative theory of stimulus value computation that takes advantage of the fact that most stimuli are complex bundles of more basic attributes (e.g., foods can be described by a list of perceptual pro ...