No Slide Title
... The Past: Abnormal Behavior and the Psychoanalytic Tradition Freudian Theory – Overview and Development Structure and Function of the Mind Id (pleasure principle; illogical, emotional, irrational) Ego (reality principle; logical and rational) Superego (moral principles; keeps Id and Ego in ...
... The Past: Abnormal Behavior and the Psychoanalytic Tradition Freudian Theory – Overview and Development Structure and Function of the Mind Id (pleasure principle; illogical, emotional, irrational) Ego (reality principle; logical and rational) Superego (moral principles; keeps Id and Ego in ...
Chapter 13 additional PPT
... Analogue behavioral observation - Situations are created in which the problem behavior is likely to occur Accuracy of behavior can be improved by having two or more observers independently code the same behaviors ...
... Analogue behavioral observation - Situations are created in which the problem behavior is likely to occur Accuracy of behavior can be improved by having two or more observers independently code the same behaviors ...
General
... times-the shock always occurred during the tone In another group of rats the tone and shock were paired 20 times just as in the other group, but this group received an additional 20 shocks that were not pair with the tone Only the first group developed a conditioned fear response to the tone T ...
... times-the shock always occurred during the tone In another group of rats the tone and shock were paired 20 times just as in the other group, but this group received an additional 20 shocks that were not pair with the tone Only the first group developed a conditioned fear response to the tone T ...
Chapter 6
... Advertisers will often use famous people and celebrities to endorse their products in commercials. For example, they assume if people like a person such as Britney Spears, then they will be more likely to buy a product such as Pepsi. Unconditioned Stimulus ...
... Advertisers will often use famous people and celebrities to endorse their products in commercials. For example, they assume if people like a person such as Britney Spears, then they will be more likely to buy a product such as Pepsi. Unconditioned Stimulus ...
1 - Wofford
... 9. Explain Timberlake and Allison’s response-deprivation hypothesis. 10. Explain the concept of a behavioral bliss point. How can it be measured? 11. Explain how reinforcement schedules are constraints on the normal allocation of behavior. 12. What is behavioral regulation theory? 13. Explain Staddo ...
... 9. Explain Timberlake and Allison’s response-deprivation hypothesis. 10. Explain the concept of a behavioral bliss point. How can it be measured? 11. Explain how reinforcement schedules are constraints on the normal allocation of behavior. 12. What is behavioral regulation theory? 13. Explain Staddo ...
Ch 9 Escape
... at other times proper conduct keeps us out of trouble. Oftentimes we behave prudently, not because of any positive reinforcements derived from our proper actions but to avoid punishment that might ensue if we did not. The class of stimuli that operates to control behavior in ways described above is ...
... at other times proper conduct keeps us out of trouble. Oftentimes we behave prudently, not because of any positive reinforcements derived from our proper actions but to avoid punishment that might ensue if we did not. The class of stimuli that operates to control behavior in ways described above is ...
Ch 3 Conditioning and Extinction
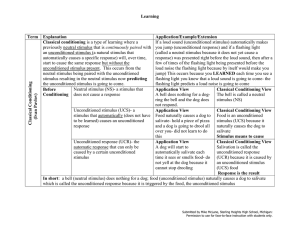
... process is involved in the child's fear of the doctor or dentist. The man in the white coat (CS) drills his teeth or sticks him with a needle, both painful stimuli. Later, the sight of the doctor or the sound of the drill puts him into a state of terror. A classical experiment on the conditioning of ...
... process is involved in the child's fear of the doctor or dentist. The man in the white coat (CS) drills his teeth or sticks him with a needle, both painful stimuli. Later, the sight of the doctor or the sound of the drill puts him into a state of terror. A classical experiment on the conditioning of ...
Chapter 8: Learning
... Stimulus Generalization and Discrimination a. Stimulus Generalization • When a conditioned response occurs in response to a stimulus similar to the conditioned stimulus • Probably explains how some phobias develop ...
... Stimulus Generalization and Discrimination a. Stimulus Generalization • When a conditioned response occurs in response to a stimulus similar to the conditioned stimulus • Probably explains how some phobias develop ...
No Slide Title
... Increase in bad behavior? (Several studies have measured a positive correlation between number of spankings and number of antisocial behaviors. Correlation doesn’t prove cause, but the relationship should make you think about whether or not spanking is a good discipline technique. Spanking may work ...
... Increase in bad behavior? (Several studies have measured a positive correlation between number of spankings and number of antisocial behaviors. Correlation doesn’t prove cause, but the relationship should make you think about whether or not spanking is a good discipline technique. Spanking may work ...
Unit 6 Notes - Reading Community Schools
... socks, batting box routine, etc. • At work- Boss passing out praise, bonuses, little competitions, etc. Notice someone doing things right, and reinforce it). • At home- Potty training, putting kids to bed, etc. • For self improvement- getting your spouses to do things you want, conditioning yourself ...
... socks, batting box routine, etc. • At work- Boss passing out praise, bonuses, little competitions, etc. Notice someone doing things right, and reinforce it). • At home- Potty training, putting kids to bed, etc. • For self improvement- getting your spouses to do things you want, conditioning yourself ...
Chapter 11: Theories of learning Learning activity suggested answers
... The UCS is ‘sights and sounds of a big pokie win’ and the UCR is a ‘huge buzz’ or euphoria. Through classical conditioning, the ‘sight and sound of a big pokie win’ (UCS) become associated with ...
... The UCS is ‘sights and sounds of a big pokie win’ and the UCR is a ‘huge buzz’ or euphoria. Through classical conditioning, the ‘sight and sound of a big pokie win’ (UCS) become associated with ...
Contemporary Perspectives on Abnormal Behavior
... system with the back of the head, where the spinal cord meets the brain, and work forward (see Figure 2.4). The lower part of the brain, or hindbrain, consists of the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. The medulla plays roles in such vital life-support functions as heart rate, respiration, and blood pre ...
... system with the back of the head, where the spinal cord meets the brain, and work forward (see Figure 2.4). The lower part of the brain, or hindbrain, consists of the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. The medulla plays roles in such vital life-support functions as heart rate, respiration, and blood pre ...
Understanding behavior to understand behavior change: a literature
... Another familiar concept in environmental education is second-order conditioning. Second-order conditioning occurs when one stimulus is paired with an unconditioned stimulus until the desired conditioned response is elicited. At that point, the second stimulus becomes paired with the first stimulus. ...
... Another familiar concept in environmental education is second-order conditioning. Second-order conditioning occurs when one stimulus is paired with an unconditioned stimulus until the desired conditioned response is elicited. At that point, the second stimulus becomes paired with the first stimulus. ...
Chapter 6
... • Attraction to other people • Positive, negative attitudes • Conditioned aversions (aversion therapy) • Anticipatory nausea and vomiting (ANV) • Allergic Reactions ...
... • Attraction to other people • Positive, negative attitudes • Conditioned aversions (aversion therapy) • Anticipatory nausea and vomiting (ANV) • Allergic Reactions ...
This is Where You Type the Slide Title
... • Occurs by watching and imitating actions of another person or by noting consequences of a person’s actions – Occurs before direct practice is allowed • Model: Someone who serves as an example ...
... • Occurs by watching and imitating actions of another person or by noting consequences of a person’s actions – Occurs before direct practice is allowed • Model: Someone who serves as an example ...
Causes of unity and disunity in Psychology and Behaviorism
... the separation of different schools (Staats, 1963). Throughout that book I have integrated things that are important regardless of where they come from and I have cited where they come from. So PB has been constructed to be a unifying framework, a behaviorism that uses and cites prior developments s ...
... the separation of different schools (Staats, 1963). Throughout that book I have integrated things that are important regardless of where they come from and I have cited where they come from. So PB has been constructed to be a unifying framework, a behaviorism that uses and cites prior developments s ...
Behavior - worldowiki
... next time.” The behavior of doing your homework might actually decrease. (Continuous reinforcement) Intermittent reinforcement is actually more powerful, particularly when you don’t know what will be reinforced (ratio) or when (interval). If you know that homework will be rewarded on Monday, you mig ...
... next time.” The behavior of doing your homework might actually decrease. (Continuous reinforcement) Intermittent reinforcement is actually more powerful, particularly when you don’t know what will be reinforced (ratio) or when (interval). If you know that homework will be rewarded on Monday, you mig ...
5. Operant Conditioning V2
... It is usually more effective to reinforce alternative desirable behaviour than it is to punish undesirable behaviour ...
... It is usually more effective to reinforce alternative desirable behaviour than it is to punish undesirable behaviour ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... So, the marketers, basically, go in for a variation, you know, and they, to bring about, they try to bring about variation in the advertisement, either in the message content or in the context or you know, in the music being used, jingle being used, the celebrity being used or the any one. So, in or ...
... So, the marketers, basically, go in for a variation, you know, and they, to bring about, they try to bring about variation in the advertisement, either in the message content or in the context or you know, in the music being used, jingle being used, the celebrity being used or the any one. So, in or ...
Brembs B. - blogarchive.brembs.blog
... training: they now press the lever less often when they are placed back in the box, because they are not hungry anymore. However, the same treatment fails to reduce lever pressing after the animals have been trained for an extended period. The behavior has now become habitual or compulsive; whenever ...
... training: they now press the lever less often when they are placed back in the box, because they are not hungry anymore. However, the same treatment fails to reduce lever pressing after the animals have been trained for an extended period. The behavior has now become habitual or compulsive; whenever ...
Chapter 5 - Safford Unified School
... 31. Which of the following is an example of negative reinforcement? A) A mother picks up her infant when he cries, which then stops his crying, thereby reducing the mother's level of annoyance. B) A father picks up his infant when she cries, thereby increasing the likelihood that she will cry to be ...
... 31. Which of the following is an example of negative reinforcement? A) A mother picks up her infant when he cries, which then stops his crying, thereby reducing the mother's level of annoyance. B) A father picks up his infant when she cries, thereby increasing the likelihood that she will cry to be ...
Learning handout - Miami Beach Senior High School
... Continuous reinforcement teaches desired behavior quickly. If a student notices that every time someone raises their hand they get extra credit then he or she will quickly raise his or her hand, but as quick as behavior is learned is as quick as it will be extinguished, or stopped. If students expec ...
... Continuous reinforcement teaches desired behavior quickly. If a student notices that every time someone raises their hand they get extra credit then he or she will quickly raise his or her hand, but as quick as behavior is learned is as quick as it will be extinguished, or stopped. If students expec ...
Chapter 8: Conditioning and Learning
... In the example shown, a horn precedes a puff of air to the eye. Eventually the horn alone will produce an eye blink. In operant conditioning, a response that is followed by a reinforcing consequence becomes more likely to occur on future occasions. In the example shown, a dog learns to sit up when i ...
... In the example shown, a horn precedes a puff of air to the eye. Eventually the horn alone will produce an eye blink. In operant conditioning, a response that is followed by a reinforcing consequence becomes more likely to occur on future occasions. In the example shown, a dog learns to sit up when i ...