Cerebellar Loops with Motor Cortex and Prefrontal Cortex of a
... We used transneuronal transport of neurotropic viruses to examine the topographic organization of circuits linking the cerebellar cortex with the arm area of the primary motor cortex (M1) and with area 46 in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of monkeys. Retrograde transneuronal transport of the CVS-11 ...
... We used transneuronal transport of neurotropic viruses to examine the topographic organization of circuits linking the cerebellar cortex with the arm area of the primary motor cortex (M1) and with area 46 in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of monkeys. Retrograde transneuronal transport of the CVS-11 ...
Neuronal subtype specification in the cerebral cortex
... to include a combination of morphology, electrophysiological properties and patterns of gene expression1,10. Nevertheless, the most basic schema is based on hodology, which has proved useful during the initial investigation of neuronal subtype development (BOX 2). How are these various projection ne ...
... to include a combination of morphology, electrophysiological properties and patterns of gene expression1,10. Nevertheless, the most basic schema is based on hodology, which has proved useful during the initial investigation of neuronal subtype development (BOX 2). How are these various projection ne ...
The multisensory roles for auditory cortex in primate vocal
... E-mail address: [email protected] ...
... E-mail address: [email protected] ...
Gating of Sensory Input by Spontaneous Cortical Activity
... The cc measure. To quantify the fine temporal relationship between a neuron and population activity, we assessed the asymmetry of the spiketriggered MUA using a previously described measure, cc, defined as the mean spike time of spike-triggered MUA within a 100 ms time window, which is equivalent ...
... The cc measure. To quantify the fine temporal relationship between a neuron and population activity, we assessed the asymmetry of the spiketriggered MUA using a previously described measure, cc, defined as the mean spike time of spike-triggered MUA within a 100 ms time window, which is equivalent ...
BRAIN - ESPN.com
... Repetitive mild traumatic brain injury can trigger the development of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), a progressive neurodegeneration characterized by the widespread deposition of hyperphosphorylated tau (p-tau) as neurofibrillary tangles (Corsellis and Brierley, 1959; Corsellis et al., 1973 ...
... Repetitive mild traumatic brain injury can trigger the development of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), a progressive neurodegeneration characterized by the widespread deposition of hyperphosphorylated tau (p-tau) as neurofibrillary tangles (Corsellis and Brierley, 1959; Corsellis et al., 1973 ...
A multi-level account of selective attention
... all that was retained from the unattended auditory stream. Not long after Broadbent’s seminal book, Moray (1959) demonstrated that selection was not always implemented by an early filtering mechanism, as he noted that about one-third of subjects detected their own name when it was inserted in the un ...
... all that was retained from the unattended auditory stream. Not long after Broadbent’s seminal book, Moray (1959) demonstrated that selection was not always implemented by an early filtering mechanism, as he noted that about one-third of subjects detected their own name when it was inserted in the un ...
Ventral Premotor and Inferior Parietal Cortices
... on a metal plate (3 3 3 cm) fixed to the table at a distance of 34 cm from the center of the starting point. A container (identical to the one used in the motor task) was fixed at a distance of 14 cm to the left or to the right of the target. The container was present only when grasp-toplace trials w ...
... on a metal plate (3 3 3 cm) fixed to the table at a distance of 34 cm from the center of the starting point. A container (identical to the one used in the motor task) was fixed at a distance of 14 cm to the left or to the right of the target. The container was present only when grasp-toplace trials w ...
Neuronal Clusters in the Primate Motor Cortex during Interception of
... interception point, and the target acceleration were randomized for each trial, thus requiring the animal to adjust its movement according to the visual input on a trial-by-trial basis. The two animals adopted different strategies, similar to those identified previously in human subjects. Single-cel ...
... interception point, and the target acceleration were randomized for each trial, thus requiring the animal to adjust its movement according to the visual input on a trial-by-trial basis. The two animals adopted different strategies, similar to those identified previously in human subjects. Single-cel ...
Sensory Afferent Neurotransmission in Caudal Nucleus Tractus
... types of calcium channels are present in the baroreceptor and other sensory neuron soma. A small component of the total calcium current is contributed by a low threshold T-type channel Caj (Andresen and Kunze, 1994). High threshold calcium current is present in unidentified sensory soma (Andresen an ...
... types of calcium channels are present in the baroreceptor and other sensory neuron soma. A small component of the total calcium current is contributed by a low threshold T-type channel Caj (Andresen and Kunze, 1994). High threshold calcium current is present in unidentified sensory soma (Andresen an ...
On phenomenal character and Petri dishes
... Petri dish. The second is that those who suggest that a Petri dish is too small are confusing v itself with the physical context that makes v possible. I consider these in turn. It is an empirical question how much of the brain is involved in a given experience. It will, I suspect, be a significant ...
... Petri dish. The second is that those who suggest that a Petri dish is too small are confusing v itself with the physical context that makes v possible. I consider these in turn. It is an empirical question how much of the brain is involved in a given experience. It will, I suspect, be a significant ...
Differential functional connectivity of rostral
... with AIC, putamen, caudate and ventral pallidum. There was a decrease in this connectivity in AP and AR, with AP showing greater reduction than AR. These findings provide support for the role of rACC in integrating interoceptive, emotional and cognitive functions via interactions with insula and str ...
... with AIC, putamen, caudate and ventral pallidum. There was a decrease in this connectivity in AP and AR, with AP showing greater reduction than AR. These findings provide support for the role of rACC in integrating interoceptive, emotional and cognitive functions via interactions with insula and str ...
High-Level Visual Processing: Cognitive Influences
... visual processing thus selects behaviorally meaningful attributes of the visual environment (Figure 28–1). ...
... visual processing thus selects behaviorally meaningful attributes of the visual environment (Figure 28–1). ...
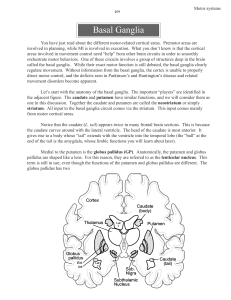
Role of the Basal Ganglia in the Control of Purposive - lsr
... globus pallidus, substantia nigra, and subthalamic nucleus (STN).1 The globus pallidus is further divided into the external segment (GPe) and the internal segment (GPi); the substantia nigra is divided into the pars reticulata (SNr) and pars compacta (SNc). The CD and PUT are the two input stations, ...
... globus pallidus, substantia nigra, and subthalamic nucleus (STN).1 The globus pallidus is further divided into the external segment (GPe) and the internal segment (GPi); the substantia nigra is divided into the pars reticulata (SNr) and pars compacta (SNc). The CD and PUT are the two input stations, ...
Single-trial decoding of intended eye movement goals from lateral
... target locations and calculating MI for 1,000 different shuffles. We labeled neurons as having significant target location information within an epoch if the MI was greater than 99% of the null values for that epoch. Neurons with significant MI during the baseline epoch were excluded from further ne ...
... target locations and calculating MI for 1,000 different shuffles. We labeled neurons as having significant target location information within an epoch if the MI was greater than 99% of the null values for that epoch. Neurons with significant MI during the baseline epoch were excluded from further ne ...
HYPOTHALAMUS
... Plate 29 shows the relationship of troph-hormone producing cells to fenestrated capillaries in the anterior pituitary. The magno- and parvocellular cell groups producing the hypothalamic hormones receive a variety of stimuli from different parts of the brain, primarily within the hypothalamus, but ...
... Plate 29 shows the relationship of troph-hormone producing cells to fenestrated capillaries in the anterior pituitary. The magno- and parvocellular cell groups producing the hypothalamic hormones receive a variety of stimuli from different parts of the brain, primarily within the hypothalamus, but ...
Chapter 2 - Monsignor Farrell High School
... Psychology, Fourth Edition, AP Edition Saundra K. Ciccarelli • J. Noland White © 2015, 2012, 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Psychology, Fourth Edition, AP Edition Saundra K. Ciccarelli • J. Noland White © 2015, 2012, 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
J. Neurophysiol. - Nonlinear Dynamics Group
... neuron can provide a clue that helps to identify its layer localization. INTRODUCTION ...
... neuron can provide a clue that helps to identify its layer localization. INTRODUCTION ...
Motor systems Basal ganglia
... You have just read about the different motor-related cortical areas. Premotor areas are involved in planning, while MI is involved in execution. What you don’t know is that the cortical areas involved in movement control need “help” from other brain circuits in order to smoothly orchestrate motor be ...
... You have just read about the different motor-related cortical areas. Premotor areas are involved in planning, while MI is involved in execution. What you don’t know is that the cortical areas involved in movement control need “help” from other brain circuits in order to smoothly orchestrate motor be ...
Chapter 4 The role of the sensory
... might be served by distributed interactive neuronal systems, organized in functional networks, rather than in local and autonomous modules (Uttal, 2003). Beside a certain degree of specialization, several brain areas are physically characterized by functional connections with many other parts of the ...
... might be served by distributed interactive neuronal systems, organized in functional networks, rather than in local and autonomous modules (Uttal, 2003). Beside a certain degree of specialization, several brain areas are physically characterized by functional connections with many other parts of the ...
Dendritic Spine Density Varies Between Unisensory
... soma, a peak reached in the middle cortical layers, and a subsequent drop-off in distal dendrites (Valverde 1967). Spine density varies not only within individual dendritic trees but also across cortical areas. A recent study (Elston 2000) demonstrated that spine density on basal dendrites of layer ...
... soma, a peak reached in the middle cortical layers, and a subsequent drop-off in distal dendrites (Valverde 1967). Spine density varies not only within individual dendritic trees but also across cortical areas. A recent study (Elston 2000) demonstrated that spine density on basal dendrites of layer ...
CNS Distribution of Members of the Two-Pore
... Two-pore-domain potassium (K ⫹) channels are substrates for resting K ⫹ currents in neurons. They are major targets for endogenous modulators, as well as for clinically important compounds such as volatile anesthetics. In the current study, we report on the CNS distribution in the rat and mouse of m ...
... Two-pore-domain potassium (K ⫹) channels are substrates for resting K ⫹ currents in neurons. They are major targets for endogenous modulators, as well as for clinically important compounds such as volatile anesthetics. In the current study, we report on the CNS distribution in the rat and mouse of m ...
The role of the medial prefrontal cortex in learning and reward Ph.D
... 1994). Behavior of humans and animals is often goal directed and can be flexibly modulated by motivation. Flexible representations are created in experimental animals during instrumental conditioning. Pavlovian CSs may modulate instrumental performance, this is the Pavlovian-instrumental transfer (P ...
... 1994). Behavior of humans and animals is often goal directed and can be flexibly modulated by motivation. Flexible representations are created in experimental animals during instrumental conditioning. Pavlovian CSs may modulate instrumental performance, this is the Pavlovian-instrumental transfer (P ...
Large-scale spatiotemporal spike patterning consistent with
... from groups of neurons near the recording site, it has never been shown whether action potentials from individual neurons demonstrate spatiotemporal patterning consistent with wave propagation. This is important because it is still debated as to what aggregate signals such as LFPs and VSD signify ph ...
... from groups of neurons near the recording site, it has never been shown whether action potentials from individual neurons demonstrate spatiotemporal patterning consistent with wave propagation. This is important because it is still debated as to what aggregate signals such as LFPs and VSD signify ph ...
Clustered Organization of Neurons with Similar Extra
... columnar in the traditional sense; i.e., the response property is not conserved within a cortical column throughout all layers. The clustering of neurons with different ERF was further demonstrated quantitatively by measuring the absolute difference in S (|⌬S|) between any two recorded cells as a fu ...
... columnar in the traditional sense; i.e., the response property is not conserved within a cortical column throughout all layers. The clustering of neurons with different ERF was further demonstrated quantitatively by measuring the absolute difference in S (|⌬S|) between any two recorded cells as a fu ...
Study Objectives
... 4. Identify and briefly describe experimental approaches used to examine cerebral lateralization in humans. 5. Describe Sperry's and Gazzaniga's work with split-brain patients. What did their results reveal about the functions of the two cerebral hemispheres? 6. Define aphasia and list at least thr ...
... 4. Identify and briefly describe experimental approaches used to examine cerebral lateralization in humans. 5. Describe Sperry's and Gazzaniga's work with split-brain patients. What did their results reveal about the functions of the two cerebral hemispheres? 6. Define aphasia and list at least thr ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.