Receptive Fields of Second-order Neurons in the Olfactory Bulb of
... by which the olfactory system encodes and processes information from odorant stimuli have been proposed (Moulton and Beidler, 1967; Beets, 1970; Davies, 1971; Shepherd, 1972; Moulton, 1976). Several of these theories assume the existence of a spatially organized projection of receptor neurons onto t ...
... by which the olfactory system encodes and processes information from odorant stimuli have been proposed (Moulton and Beidler, 1967; Beets, 1970; Davies, 1971; Shepherd, 1972; Moulton, 1976). Several of these theories assume the existence of a spatially organized projection of receptor neurons onto t ...
Duration Sensitivity to Other Response Properties of the Rat
... (IC) were tested for sensitivity to sound duration. About one-half (54%) of the units sampled showed some form of duration selectivity. The majority of these (76%) were long-pass neurons that responded to sounds exceeding some duration threshold (range: 5– 60 ms). Bandpass neurons, which only respon ...
... (IC) were tested for sensitivity to sound duration. About one-half (54%) of the units sampled showed some form of duration selectivity. The majority of these (76%) were long-pass neurons that responded to sounds exceeding some duration threshold (range: 5– 60 ms). Bandpass neurons, which only respon ...
Connections underlying the synthesis of cognition,
... There is a commonly held view that the frontal cortex in humans holds a privileged position within the nervous system with regard to thought and reason. This view stems, in part, from the classic neurological literature which has provided evidence that the frontal cortex, and its anterior (prefronta ...
... There is a commonly held view that the frontal cortex in humans holds a privileged position within the nervous system with regard to thought and reason. This view stems, in part, from the classic neurological literature which has provided evidence that the frontal cortex, and its anterior (prefronta ...
Disruption of experience-dependent synaptic modifications in striate
... GABA, receptor antagonist bicuculline and found that the deprived eye inputs were retained in area 17. Finally, both Frtgnac et al. (1988) and Greuel et al. (1988) found in acute preparations that synaptic effectiveness could be changed by pairing retinal stimulation with the ionophoretic applicatio ...
... GABA, receptor antagonist bicuculline and found that the deprived eye inputs were retained in area 17. Finally, both Frtgnac et al. (1988) and Greuel et al. (1988) found in acute preparations that synaptic effectiveness could be changed by pairing retinal stimulation with the ionophoretic applicatio ...
Basal Ganglia objectives - NBio401
... -Be able to explain how, in addition to the pathways affecting limb movements, there are other loops between the basal ganglia and cerebral cortex that perform analogous functions for oculomotor, executive, and emotional systems. - Be able to describe the type of learning in which the basal ganglia ...
... -Be able to explain how, in addition to the pathways affecting limb movements, there are other loops between the basal ganglia and cerebral cortex that perform analogous functions for oculomotor, executive, and emotional systems. - Be able to describe the type of learning in which the basal ganglia ...
Sound processing by local neural populations in the
... until recently, this has been technically impossible to do in vivo, because electrophysiological recording techniques cannot densely probe neurons at this spatial resolution, while optical techniques to monitor neural physiology have been limited to use at the surface of the tissue. Recently, this h ...
... until recently, this has been technically impossible to do in vivo, because electrophysiological recording techniques cannot densely probe neurons at this spatial resolution, while optical techniques to monitor neural physiology have been limited to use at the surface of the tissue. Recently, this h ...
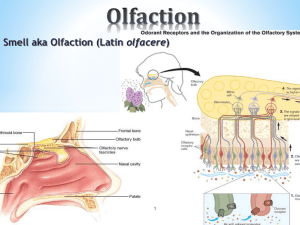
olfaction
... Some project into the limbic system and hypothalamus (emotional and memory evoked responses). Olfactory sensations are the only sensations that reach the cerebral cortex without first synapsing in the thalamus. The primary olfactory area has axons that extend to the orbit frontal area (frontal ...
... Some project into the limbic system and hypothalamus (emotional and memory evoked responses). Olfactory sensations are the only sensations that reach the cerebral cortex without first synapsing in the thalamus. The primary olfactory area has axons that extend to the orbit frontal area (frontal ...
Contact guidance of CNS neurites on grooved quartz: influence of
... (Harrison, 1914) yet surprisingly little is known about the cellular events of contact sensing and their transduction into directional growth, especially in neuronal growth cones. The aim of the present study was to describe the directional effects of substratum contours on the morphology of develop ...
... (Harrison, 1914) yet surprisingly little is known about the cellular events of contact sensing and their transduction into directional growth, especially in neuronal growth cones. The aim of the present study was to describe the directional effects of substratum contours on the morphology of develop ...
Refinement of feedforward projections, neuronal density, and
... in turn, will be important for the elimination of synapses. Thus, this mechanism could explain how visual experience leads to refinement of connections in the visual cortex. A fundamental question in neuroscience is whether different visual areas mature with similar or different timecourses. In orde ...
... in turn, will be important for the elimination of synapses. Thus, this mechanism could explain how visual experience leads to refinement of connections in the visual cortex. A fundamental question in neuroscience is whether different visual areas mature with similar or different timecourses. In orde ...
Read Here
... School and Dartmouth Giesel School of Medicine. Triple-transgenic animals were generated by breeding Tac1::IRES-cre (Harris et al., 2014) mice to either double-transgenic Pet1::Flpe (Jensen et al., 2008), RC:: FPDi (Ray et al., 2011) mice, Pet1::Flpe, RC::FrePe (Brust et al., 2014) mice, or Pet1::Fl ...
... School and Dartmouth Giesel School of Medicine. Triple-transgenic animals were generated by breeding Tac1::IRES-cre (Harris et al., 2014) mice to either double-transgenic Pet1::Flpe (Jensen et al., 2008), RC:: FPDi (Ray et al., 2011) mice, Pet1::Flpe, RC::FrePe (Brust et al., 2014) mice, or Pet1::Fl ...
Subcortical loops through the basal ganglia
... superior colliculus to the thalamus suggests that there are at least three functionally segregated systems, one originating from the superficial layers and two from the deep layers. The loops can be distinguished primarily according to their thalamic targets, and then according to how these thalamic ...
... superior colliculus to the thalamus suggests that there are at least three functionally segregated systems, one originating from the superficial layers and two from the deep layers. The loops can be distinguished primarily according to their thalamic targets, and then according to how these thalamic ...
Lateral prefrontal cortex: architectonic and functional organization
... al. 1955), two areas are shown on the mid-lateral prefrontal cortex: area 9 and area 46 (figure 2a,b). Area 46 is shown on the middle frontal gyrus, whereas area 9 is shown both on the superior frontal gyrus and on the middle frontal gyrus. In all the maps of the human frontal cortex, area 46 is sep ...
... al. 1955), two areas are shown on the mid-lateral prefrontal cortex: area 9 and area 46 (figure 2a,b). Area 46 is shown on the middle frontal gyrus, whereas area 9 is shown both on the superior frontal gyrus and on the middle frontal gyrus. In all the maps of the human frontal cortex, area 46 is sep ...
Passive Properties of Swimmeret Motor Neurons
... the structures of the filled neurons. Motor neurons could be distinguished from those sensory neurons that also have axons in N1 by their central cell bodies; all known sensory neurons except the two NSSRs have peripheral cell bodies. One other neuron with an axon in N1, the segmental giant interneu ...
... the structures of the filled neurons. Motor neurons could be distinguished from those sensory neurons that also have axons in N1 by their central cell bodies; all known sensory neurons except the two NSSRs have peripheral cell bodies. One other neuron with an axon in N1, the segmental giant interneu ...
Specificity and Plasticity of Thalamocortical Connections in Sema6A
... During brain development, the emergence of distinct areas in the cerebral cortex involves an interplay between patterning of the cortical sheet in the early embryo and later influences of incoming connections made from other brain areas, namely the thalamus. Connectivity between the thalamus and the ...
... During brain development, the emergence of distinct areas in the cerebral cortex involves an interplay between patterning of the cortical sheet in the early embryo and later influences of incoming connections made from other brain areas, namely the thalamus. Connectivity between the thalamus and the ...
THE VISUAL CLAUSTRUM OF THE CAT I. Structure and Connections`
... preparations, is of large, angular, and densely staining somata. Near the edges of the claustrum, these tend to be elongated parallel to the edge, but elsewhere, there is no orderly alignment of cells like that characteristic of cerebral cortex. In Golgi preparations, two common cell types and a thi ...
... preparations, is of large, angular, and densely staining somata. Near the edges of the claustrum, these tend to be elongated parallel to the edge, but elsewhere, there is no orderly alignment of cells like that characteristic of cerebral cortex. In Golgi preparations, two common cell types and a thi ...
Spatial distribution and characterization of non
... basal locations but maintain an apical contact during mitoses [7,11,14]. These subapical progenitors are mainly characterized by undergoing multiple and fast rounds of division. The non-apical progenitor populations have been widely studied in the mammalian brain, and there is some evidence that the ...
... basal locations but maintain an apical contact during mitoses [7,11,14]. These subapical progenitors are mainly characterized by undergoing multiple and fast rounds of division. The non-apical progenitor populations have been widely studied in the mammalian brain, and there is some evidence that the ...
Information Processing in the Rostral Solitary Nucleus: Modulation
... chorda tympani (CT) inputs (J. B. Travers & Smith, 1979). Although there is considerable variability in both firing frequency and breadth of tuning within populations of peripheral afferents and central rNST neurons, there is a clear tendency for taste responses to become both faster and more broadl ...
... chorda tympani (CT) inputs (J. B. Travers & Smith, 1979). Although there is considerable variability in both firing frequency and breadth of tuning within populations of peripheral afferents and central rNST neurons, there is a clear tendency for taste responses to become both faster and more broadl ...
Structure and Central Connections Of PERIPHERAL OLFACTORY
... and duct cells of Bowman’s glands, the major source of mucus in the olfactory epithelium. The third cell type is the poorly understood microvillar cell located at the surface of the epithelium. Microvillar cells, which look similar to the so-called brush cells found throughout the upper and lower a ...
... and duct cells of Bowman’s glands, the major source of mucus in the olfactory epithelium. The third cell type is the poorly understood microvillar cell located at the surface of the epithelium. Microvillar cells, which look similar to the so-called brush cells found throughout the upper and lower a ...
Neuron 2013 Bartolini
... on their connectivity, which is roughly linked to their laminar location in the cortex (Jones, 1984) (Figure 1). Subcortical projection pyramidal cells are the main neurons in layers V and VI. They target the thalamus (layer VI) and other telencephalic and subcerebral regions, such as the striatum, ...
... on their connectivity, which is roughly linked to their laminar location in the cortex (Jones, 1984) (Figure 1). Subcortical projection pyramidal cells are the main neurons in layers V and VI. They target the thalamus (layer VI) and other telencephalic and subcerebral regions, such as the striatum, ...
Chapter 16 - MBFys Home Page
... to many spinal cord segments; indeed, some project to targets along the entire length of the cord. Moreover, many of these local circuit neurons also have axonal branches that cross the midline in the commissure of the spinal cord to innervate lower motor neurons in the medial part of the contralate ...
... to many spinal cord segments; indeed, some project to targets along the entire length of the cord. Moreover, many of these local circuit neurons also have axonal branches that cross the midline in the commissure of the spinal cord to innervate lower motor neurons in the medial part of the contralate ...
This article was originally published in the
... anatomical connections linking the cingulate cortex with brain areas closely associated with each of these functions. The centrality of motivational and emotional processing to cingulate function is highlighted by its strong reciprocal connections to the reward centers of the brain, including the or ...
... anatomical connections linking the cingulate cortex with brain areas closely associated with each of these functions. The centrality of motivational and emotional processing to cingulate function is highlighted by its strong reciprocal connections to the reward centers of the brain, including the or ...
Organization of Visual Inputs to the Inferior Temporal and Posterior
... alone suggests some relationship between the dorsal/ventral and magno/parvo schemes. However, many of the anatomical and functional details of this relationship remain to be worked out. Previous anatomical studies have revealed many of the inputs to the posterior parietal and inferior temporal corte ...
... alone suggests some relationship between the dorsal/ventral and magno/parvo schemes. However, many of the anatomical and functional details of this relationship remain to be worked out. Previous anatomical studies have revealed many of the inputs to the posterior parietal and inferior temporal corte ...
Cognon Neural Model Software Verification and
... Systems of Neuromorphic Adaptive Plastic Scalable Electronics (SyNAPSE) is a Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) program with the goal to develop electronic neuromorphic machine technology that scales to biological levels. The ultimate aim is to build an electronic microprocessor syste ...
... Systems of Neuromorphic Adaptive Plastic Scalable Electronics (SyNAPSE) is a Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) program with the goal to develop electronic neuromorphic machine technology that scales to biological levels. The ultimate aim is to build an electronic microprocessor syste ...
Dynamics and Synchronization of Motifs of Neuronal Populations in the Presence
... concept of receptive field pervades our knowledge about the visual system. Following the flow direction of the neuronal activity elicited by the visual stimulus, neurons from any level show traces of the receptive fields: photoreceptors, retinal ganglion, lateral geniculate nucleus, primary visual c ...
... concept of receptive field pervades our knowledge about the visual system. Following the flow direction of the neuronal activity elicited by the visual stimulus, neurons from any level show traces of the receptive fields: photoreceptors, retinal ganglion, lateral geniculate nucleus, primary visual c ...
Weak orientation and direction selectivity in lateral geniculate
... recording using the methods described in Van Hooser et al. (2003) and Heimel et al. (2005). In brief, animals were initially anesthetized with a mixture of ketamine and acepromazine maleate (90 mg/ml ketamine, 0.91 mg/ml acepromazine maleate, and 0.5 ml/kg initial dose im). A femoral vein was cannul ...
... recording using the methods described in Van Hooser et al. (2003) and Heimel et al. (2005). In brief, animals were initially anesthetized with a mixture of ketamine and acepromazine maleate (90 mg/ml ketamine, 0.91 mg/ml acepromazine maleate, and 0.5 ml/kg initial dose im). A femoral vein was cannul ...