File
... and the America’s. Portugal began to explore the west coast of Africa during the mid- 1400’s. They established the first Europe-Asian water trade route. Vasco da Gama was the first explorer to make it from Portugal to India. He began his voyage in 1497 and reached India in 1498. Ferdinand Magellan b ...
... and the America’s. Portugal began to explore the west coast of Africa during the mid- 1400’s. They established the first Europe-Asian water trade route. Vasco da Gama was the first explorer to make it from Portugal to India. He began his voyage in 1497 and reached India in 1498. Ferdinand Magellan b ...
Ways of the World Chapter 17 Study Guide
... 12. The United States began its history as the leftover dregs of the New World and the Spanish colonies occupied the wealthiest areas and were regarded as the more promising region. Nevertheless, as the United States grew in power what happened to Latin America? ...
... 12. The United States began its history as the leftover dregs of the New World and the Spanish colonies occupied the wealthiest areas and were regarded as the more promising region. Nevertheless, as the United States grew in power what happened to Latin America? ...
Pacing guide
... Reforms, Revolution, and War (1800-1900) – Ch. 9 Unit 5: The Road to War (1914 – 1945) {32 days} A. Nationalism in Europe (1800-1920) – Ch. 10 B. Age of Imperialism(1800-1920) – Ch. 11 C. World War I (1914-1918) – Ch. 12 Unit 6: Interwar Years and World War II (1919-1945) {25 days} A. The Interwar Y ...
... Reforms, Revolution, and War (1800-1900) – Ch. 9 Unit 5: The Road to War (1914 – 1945) {32 days} A. Nationalism in Europe (1800-1920) – Ch. 10 B. Age of Imperialism(1800-1920) – Ch. 11 C. World War I (1914-1918) – Ch. 12 Unit 6: Interwar Years and World War II (1919-1945) {25 days} A. The Interwar Y ...
Period 5 1750-1900 Industrial Revolution Greatest change in world
... Japan decides to westernize with the Meiji Restoration Rapid state sponsored Industrialization Railways, western education, samurais abolished Differing response compared to China Japan becomes an imperial power at the end of this time period Imperialism in Africa Prior time period, Europeans stayed ...
... Japan decides to westernize with the Meiji Restoration Rapid state sponsored Industrialization Railways, western education, samurais abolished Differing response compared to China Japan becomes an imperial power at the end of this time period Imperialism in Africa Prior time period, Europeans stayed ...
Study Guide
... Chapter 28 –The Islamic Empires Three powerful Islamic empires emerged in India and southwest Asia after the fifteenth century. Beginning with the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Turks in 1453, Turkish warriors and charismatic leaders established first the Ottoman Empire, then the Safavid dyna ...
... Chapter 28 –The Islamic Empires Three powerful Islamic empires emerged in India and southwest Asia after the fifteenth century. Beginning with the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Turks in 1453, Turkish warriors and charismatic leaders established first the Ottoman Empire, then the Safavid dyna ...
Word - State of New Jersey
... The diverse religious, cultural, and geographic factors that influenced the ability of the Muslim government to rule The split into Sunni and Shi’ite factions The importance of Muslim civilization in mediating long-distance commercial, cultural, intellectual, and food crop exchange across Eura ...
... The diverse religious, cultural, and geographic factors that influenced the ability of the Muslim government to rule The split into Sunni and Shi’ite factions The importance of Muslim civilization in mediating long-distance commercial, cultural, intellectual, and food crop exchange across Eura ...
6.3.8.C. Expanding Zones of Exchange and Interaction to 1400 CE
... • The diverse religious, cultural, and geographic factors that influenced the ability of the Muslim government to rule • The split into Sunni and Shi’ite factions • The importance of Muslim civilization in mediating long-distance commercial, cultural, intellectual, and food crop exchange across Eura ...
... • The diverse religious, cultural, and geographic factors that influenced the ability of the Muslim government to rule • The split into Sunni and Shi’ite factions • The importance of Muslim civilization in mediating long-distance commercial, cultural, intellectual, and food crop exchange across Eura ...
Curriculum – Scope and Sequence/STAAR
... WH.1.C identify major causes and describe the major effects of the following important turning points in world history from 600 to 1450: the spread of Christianity, the decline of Rome and the formation of medieval Europe; the development of Islamic caliphates and their impact on Asia, Africa, and E ...
... WH.1.C identify major causes and describe the major effects of the following important turning points in world history from 600 to 1450: the spread of Christianity, the decline of Rome and the formation of medieval Europe; the development of Islamic caliphates and their impact on Asia, Africa, and E ...
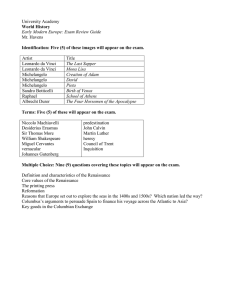
Renaissance Practice Exam*Introduction and the Arts
... Reasons that Europe set out to explore the seas in the 1400s and 1500s? Which nation led the way? Columbus’s arguments to persuade Spain to finance his voyage across the Atlantic to Asia? Key goods in the Columbian Exchange ...
... Reasons that Europe set out to explore the seas in the 1400s and 1500s? Which nation led the way? Columbus’s arguments to persuade Spain to finance his voyage across the Atlantic to Asia? Key goods in the Columbian Exchange ...
Study Guide with Answers - Effingham County Schools
... in mines and on plantations because they were more immune to the European diseases than the indigenous people; many on the natives had died and left a labor shortage 22.What were three reasons why the Columbian Exchange was important? Spread diseases which killed about 80% of the indigenous populati ...
... in mines and on plantations because they were more immune to the European diseases than the indigenous people; many on the natives had died and left a labor shortage 22.What were three reasons why the Columbian Exchange was important? Spread diseases which killed about 80% of the indigenous populati ...
WorldsInMotion
... possessions before Muslims could gain influence Econ. & Religious – undercut or bypass Muslim world Racial – through contact with other peoples, Europeans formulated ideas of racial superiority – combined ideas of cultural, scientific, religious, economic, and physical superiority ...
... possessions before Muslims could gain influence Econ. & Religious – undercut or bypass Muslim world Racial – through contact with other peoples, Europeans formulated ideas of racial superiority – combined ideas of cultural, scientific, religious, economic, and physical superiority ...
AP World History Class Schedule 11/28
... Food for Thought While Reading the Introduction What can you learn from the intro story about empire building and maintenance in this time period? What claims allowed the Russian tsars (also spelled czar) to establish their power? What claims led the new Russian kingdom to expand into Asia? Ru ...
... Food for Thought While Reading the Introduction What can you learn from the intro story about empire building and maintenance in this time period? What claims allowed the Russian tsars (also spelled czar) to establish their power? What claims led the new Russian kingdom to expand into Asia? Ru ...
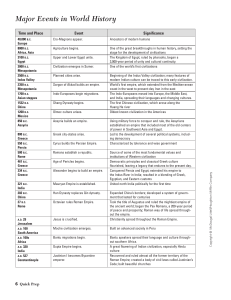
Major Events in World History
... Beginning of the Indus Valley civilization; many features of modern Indian culture can be traced to this early civilization. World’s first empire, which extended from the Mediterranean coast in the west to present-day Iran in the east The Indo-Europeans moved into Europe, the Middle East, and India, ...
... Beginning of the Indus Valley civilization; many features of modern Indian culture can be traced to this early civilization. World’s first empire, which extended from the Mediterranean coast in the west to present-day Iran in the east The Indo-Europeans moved into Europe, the Middle East, and India, ...
People Who Have Made A Difference
... Today we continue to use many techniques begun during this time. One technique was chiaroscuro, (remember The Tale of Despereaux), which was a technique where shades appeared in the picture and it helped things in paintings such as clothes become more in-depth and more realistic. Another technique w ...
... Today we continue to use many techniques begun during this time. One technique was chiaroscuro, (remember The Tale of Despereaux), which was a technique where shades appeared in the picture and it helped things in paintings such as clothes become more in-depth and more realistic. Another technique w ...
Guided Notes
... This belief became the heart of the new beliefs he developed, and these beliefs became known as _________________________. Luther starts a Reformation In 1517 Luther denounced Tetzel, and soon the news spread all over Europe. posted on a local church door, ____________________________, or statements ...
... This belief became the heart of the new beliefs he developed, and these beliefs became known as _________________________. Luther starts a Reformation In 1517 Luther denounced Tetzel, and soon the news spread all over Europe. posted on a local church door, ____________________________, or statements ...
4th Six WeeksC
... influence; monarchs of these nations centralized their authority in a quest for absolute power. New ideas about science, human society and government began to sweep across Europe. The Enlightenment reinvigorated ideas, like democracy and individual rights. These ideas were the foundation of the revo ...
... influence; monarchs of these nations centralized their authority in a quest for absolute power. New ideas about science, human society and government began to sweep across Europe. The Enlightenment reinvigorated ideas, like democracy and individual rights. These ideas were the foundation of the revo ...
Unit 2, Section 1 Test
... 9. Although the Spanish had fewer soldiers than the Aztecs, they were able to conquer the Aztec civilization. This was possible because the Spanish had horses, cannons, and guns. More importantly, the Native Americans did not have immunity to the diseases, which the Spanish brought with them. 10. Ne ...
... 9. Although the Spanish had fewer soldiers than the Aztecs, they were able to conquer the Aztec civilization. This was possible because the Spanish had horses, cannons, and guns. More importantly, the Native Americans did not have immunity to the diseases, which the Spanish brought with them. 10. Ne ...
Syllabus for Mr. Klotzkin`s World History Class World History 5
... innovative educational methods that include replying to primary and secondary document based questions, using advanced technology to create multi-media projects, participating in cooperative learning, listening to guest speakers, partaking in educational trips, and making extensive inter-disciplinar ...
... innovative educational methods that include replying to primary and secondary document based questions, using advanced technology to create multi-media projects, participating in cooperative learning, listening to guest speakers, partaking in educational trips, and making extensive inter-disciplinar ...
Absolute Monarchies-Setting the Stage for - Steven-J
... Small kingdoms merge into big kingdoms/End of Feudalism ...
... Small kingdoms merge into big kingdoms/End of Feudalism ...
1/2 Historical Tripos Part I Paper 21 Empires and World History from
... Empires and World History from the Fifteenth Century to the First World War Course Guide 2016-2017 Course description This course addresses one of the most important historical questions of our time: how did the modern world come to be? In order to answer this, the course spans the long run of globa ...
... Empires and World History from the Fifteenth Century to the First World War Course Guide 2016-2017 Course description This course addresses one of the most important historical questions of our time: how did the modern world come to be? In order to answer this, the course spans the long run of globa ...
Byzantine Empire and Orthodox World
... Europe and Asia was Muslim. After the death of Muhammad, the founder of Islam in 632, Muslim armies and merchants spread the Islamic religion eastward to India and westward across northern Africa into Spain. ...
... Europe and Asia was Muslim. After the death of Muhammad, the founder of Islam in 632, Muslim armies and merchants spread the Islamic religion eastward to India and westward across northern Africa into Spain. ...
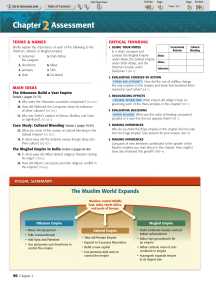
Chapter2Assessment
... Conquest of new territories contributed to the growth of the Muslim empires you read about in this chapter. How might it have also hindered this growth? (REP 4) ...
... Conquest of new territories contributed to the growth of the Muslim empires you read about in this chapter. How might it have also hindered this growth? (REP 4) ...
AP World History Class Notes Ch 22 Cross
... • Religion. Islamic law and culture were common to societies from north and west Africa to southeast Asia and the Philippines. Travel for Muslim pilgrims and scholars was common under Mongol rule. Christian missionaries also traveled to East Asia, but less frequently. • Cultural diffusion. These rou ...
... • Religion. Islamic law and culture were common to societies from north and west Africa to southeast Asia and the Philippines. Travel for Muslim pilgrims and scholars was common under Mongol rule. Christian missionaries also traveled to East Asia, but less frequently. • Cultural diffusion. These rou ...
Early modern period

In history, the early modern period of modern history follows the late Middle Ages of the post-classical era. Although the chronological limits of the period are open to debate, the timeframe spans the period after the late portion of the post-classical age (c. 1500), known as the Middle Ages, through the beginning of the Age of Revolutions (c. 1800) and is variously demarcated by historians as beginning with the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, with the Renaissance period, and with the Age of Discovery (especially with the voyages of Christopher Columbus beginning in 1492, but also with the discovery of the sea route to the East in 1498), and ending around the French Revolution in 1789.Historians in recent decades have argued that from a worldwide standpoint, the most important feature of the early modern period was its globalizing character. The period witnessed the exploration and colonization of the Americas and the rise of sustained contacts between previously isolated parts of the globe. The historical powers became involved in global trade. This world trading of goods, plants, animals, and food crops saw exchange in the Old World and the New World. The Columbian exchange greatly affected the human environment.Economies and institutions began to appear, becoming more sophisticated and globally articulated over the course of the early modern period. This process began in the medieval North Italian city-states, particularly Genoa, Venice, and Milan. The early modern period also saw the rise and beginning of the dominance of the economic theory of mercantilism. It also saw the European colonization of the Americas, Asia, and Africa during the 15th to 19th centuries, which spread Christianity around the world.The early modern trends in various regions of the world represented a shift away from medieval modes of organization, politically and other-times economically. The period in Europe witnessed the decline of feudalism and includes the Reformation, the disastrous Thirty Years' War, the Commercial Revolution, the European colonization of the Americas, and the Golden Age of Piracy.Ruling China at the beginning of the early modern period, the Ming Dynasty was “one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history”. By the 16th century the Ming economy was stimulated by trade with the Portuguese, the Spanish, and the Dutch. The Azuchi-Momoyama period in Japan saw the Nanban trade after the arrival of the first European Portuguese.Other notable trends of the early modern period include the development of experimental science, the speedup of travel through improvements in mapping and ship design, increasingly rapid technological progress, secularized civic politics and the emergence of nation states. Historians typically date the end of the early modern period when the French Revolution of the 1790s began the ""modern"" period.