Neurotransmitters - Woodridge High School
... the brain and nervous system. Glutamate is an excitatory transmitter: when it is released it increases the chance that the neuron will fire. This enhances the electrical flow among brain cells required for normal function and plays an important role during early brain development. It may also assist ...
... the brain and nervous system. Glutamate is an excitatory transmitter: when it is released it increases the chance that the neuron will fire. This enhances the electrical flow among brain cells required for normal function and plays an important role during early brain development. It may also assist ...
01 - Fort Bend ISD
... Fill in the blanks in the Concept Map with the names of the different types of neurons. ...
... Fill in the blanks in the Concept Map with the names of the different types of neurons. ...
What is the Nervous System?
... 2. Motor Neurons - project axons out from the central nervous system to control muscles ...
... 2. Motor Neurons - project axons out from the central nervous system to control muscles ...
Document
... --communication occurs in one direction: presynaptic membrane to postsynaptic membrane ...
... --communication occurs in one direction: presynaptic membrane to postsynaptic membrane ...
Chapter 2 - bobcat
... – Interneuron– billions and billions– complexity lies in this internal communication system – Motor neurons ...
... – Interneuron– billions and billions– complexity lies in this internal communication system – Motor neurons ...
title of video - Discovery Education
... A neuron is a specialized cell for the transmission of information to other nerve cells, muscles or glands. ...
... A neuron is a specialized cell for the transmission of information to other nerve cells, muscles or glands. ...
The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions
... Neurotransmitter must be released, diffuse across the synapse, and bind to receptors Synaptic delay – time needed to do this (0.3-5.0 ms) Synaptic delay is the rate-limiting step of neural ...
... Neurotransmitter must be released, diffuse across the synapse, and bind to receptors Synaptic delay – time needed to do this (0.3-5.0 ms) Synaptic delay is the rate-limiting step of neural ...
Study Guide 1
... the following parts: 1) cerebral cortex; 2) thalamus; 3) brainstem; 4) cerebellum; 5) spinal cord. 6. What is a nucleus (as the term applies to gross anatomical structure)? What is a ganglion? 7. What are the cranial nerves? What are the spinal nerves? 8. What is the difference between a sensory ner ...
... the following parts: 1) cerebral cortex; 2) thalamus; 3) brainstem; 4) cerebellum; 5) spinal cord. 6. What is a nucleus (as the term applies to gross anatomical structure)? What is a ganglion? 7. What are the cranial nerves? What are the spinal nerves? 8. What is the difference between a sensory ner ...
Spinal Cord/ Reflex Action mainly
... inactivated by enzymes &reabsorbed by presynaptic neuron – makes new neurotranmitter chemical to clear receptor sites for next impulse ...
... inactivated by enzymes &reabsorbed by presynaptic neuron – makes new neurotranmitter chemical to clear receptor sites for next impulse ...
Neuron Notes Neuron- Cells that carry messages throughout the
... 4. myelin sheath: (lipids) insulating membrane around axon. There are small gaps in the myelin sheath along an axon called _nodes_____ Schwann Cells – individual cells of the myelin sheath 5. Axon Terminal- the ending of the nerve cell where the synapse is located. Nerve Impulses • Messages carried ...
... 4. myelin sheath: (lipids) insulating membrane around axon. There are small gaps in the myelin sheath along an axon called _nodes_____ Schwann Cells – individual cells of the myelin sheath 5. Axon Terminal- the ending of the nerve cell where the synapse is located. Nerve Impulses • Messages carried ...
Synapses & Neurotransmitters
... postsynaptic neurons, found at chemical synapses • Transmission across the synaptic cleft • Is a chemical event (not electrical) • Involves release, diffusion, and binding of neurotransmitters • Provides unidirectional communication between neurons ...
... postsynaptic neurons, found at chemical synapses • Transmission across the synaptic cleft • Is a chemical event (not electrical) • Involves release, diffusion, and binding of neurotransmitters • Provides unidirectional communication between neurons ...
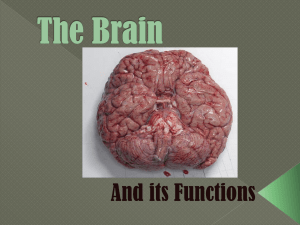
The Brain
... neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body and are covered with synapses. These receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma Cell Body - where the signals from the dendrites are joined and passed on. The cell body does not play an active rol ...
... neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body and are covered with synapses. These receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma Cell Body - where the signals from the dendrites are joined and passed on. The cell body does not play an active rol ...
Fiche UE 5BN08 Ouverture en Neurosciences
... psychoactive drugs, that have behavioral consequences. Drugs tolerance, sensitization and dependency will be analyzed in light of the most recent molecular and cellular data, particularly on the functional plasticity mechanisms that are associated in the CNS to these phenomena. ...
... psychoactive drugs, that have behavioral consequences. Drugs tolerance, sensitization and dependency will be analyzed in light of the most recent molecular and cellular data, particularly on the functional plasticity mechanisms that are associated in the CNS to these phenomena. ...
Chapter 14 - The Nervous System: Organization
... cell body • Axon Terminals - Neurotransmitters are manufactured in the cell body but released from axon terminals. The neurotransmitters stimulate other neurons. ...
... cell body • Axon Terminals - Neurotransmitters are manufactured in the cell body but released from axon terminals. The neurotransmitters stimulate other neurons. ...
Chapter 3
... Chemical Events at the Synapse • Neurons synthesize neurotransmitters and other chemicals from substances provided by the diet. • Smaller neurotransmitters are synthesized in the presynaptic terminal and held there for release. – Example: acetylcholine • Larger neurotransmitters are synthesized in ...
... Chemical Events at the Synapse • Neurons synthesize neurotransmitters and other chemicals from substances provided by the diet. • Smaller neurotransmitters are synthesized in the presynaptic terminal and held there for release. – Example: acetylcholine • Larger neurotransmitters are synthesized in ...
DevelopmentII
... in the brain • Human brain consists of 1011 neurons that form a network with 1014 connections • The number and specificity of synaptic connection needs to be precisely controlled • Changes of synaptic connections and synaptic strength are the basis of information processing and memory formation ...
... in the brain • Human brain consists of 1011 neurons that form a network with 1014 connections • The number and specificity of synaptic connection needs to be precisely controlled • Changes of synaptic connections and synaptic strength are the basis of information processing and memory formation ...
Synapse Formation in the Peripheral and Central Nervous System
... and synaptic function lead to disease states • Loss of synapses in Alzheimer’s disease • In epilepsy excessive synapse formation and synaptic misfunction are observed • Genes associated with mental retardation and schizophrenia have synaptic functions • Paralysis after spinal cord injuries ...
... and synaptic function lead to disease states • Loss of synapses in Alzheimer’s disease • In epilepsy excessive synapse formation and synaptic misfunction are observed • Genes associated with mental retardation and schizophrenia have synaptic functions • Paralysis after spinal cord injuries ...
research Nerve Cells, Axons, Dendrites, and Synapses: The
... This article first appeared in Center for Neuroskills’ Inside View newsletter. It is reprinted in part with permission. ...
... This article first appeared in Center for Neuroskills’ Inside View newsletter. It is reprinted in part with permission. ...
CH4
... The monoamine transmitters share a common structure and form a family of neurotransmitters Catecholamines include dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (NE), and epinephrine (EPI) Indolamines include serotonin (5-HT) ...
... The monoamine transmitters share a common structure and form a family of neurotransmitters Catecholamines include dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (NE), and epinephrine (EPI) Indolamines include serotonin (5-HT) ...
Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of
... 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will not affect the intensity of an action potential. This indicates that a neuron's reaction is A) inhibited by the myelin sheath. B) delayed by the refractory period. C) an all-or-none response. D) dependent on neurotransmi ...
... 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will not affect the intensity of an action potential. This indicates that a neuron's reaction is A) inhibited by the myelin sheath. B) delayed by the refractory period. C) an all-or-none response. D) dependent on neurotransmi ...
Nervous System
... covered by Schwann cells. Since these cells are made from lipids, they are insulators. This causes the electrical signal to jump over the Schwann cells increase the speed of the signal. This is known as salutatory conduction. ...
... covered by Schwann cells. Since these cells are made from lipids, they are insulators. This causes the electrical signal to jump over the Schwann cells increase the speed of the signal. This is known as salutatory conduction. ...