SChapter 12
... -Continuous propagation-Saltatory propagation▫Axon diameter affects propagation speed. -Type A fibers -Type B fibers -Type C fibers Synaptic Activity ▪Electric events of messages moving from one place to another are called nerve impulses. ▪General Properties of Synapses ▫Electrical synapse -Extremel ...
... -Continuous propagation-Saltatory propagation▫Axon diameter affects propagation speed. -Type A fibers -Type B fibers -Type C fibers Synaptic Activity ▪Electric events of messages moving from one place to another are called nerve impulses. ▪General Properties of Synapses ▫Electrical synapse -Extremel ...
File
... and axon. What are the functions of each component? Answer: Cell body- control center (nucleus & cytoplasm). Axons- extends from cell body & produces nerve terminals. Dendrite- receives messages from other neurons. ...
... and axon. What are the functions of each component? Answer: Cell body- control center (nucleus & cytoplasm). Axons- extends from cell body & produces nerve terminals. Dendrite- receives messages from other neurons. ...
9.2 - 4ubiology
... Electrochemical message is created by the movement of ions across the nerve cell membrane The resting nerve membrane has a electrical potential difference (potential) of -70 mV due to an unequal concentration of positive ions across the membrane ...
... Electrochemical message is created by the movement of ions across the nerve cell membrane The resting nerve membrane has a electrical potential difference (potential) of -70 mV due to an unequal concentration of positive ions across the membrane ...
Neuron Anatomy Activity - Ask a Biologist
... The parts of the neuron have been labeled. Your challenge is to write the correct name for each part and explain what it does. If you need some help, visit the web article listed below. ...
... The parts of the neuron have been labeled. Your challenge is to write the correct name for each part and explain what it does. If you need some help, visit the web article listed below. ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
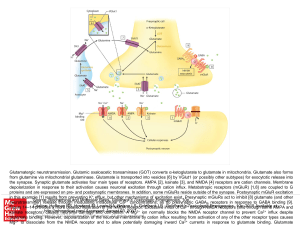
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
Lecture 5
... a. also from hypothalamus, pituitary, and other organs b. are often neurosecretory hormones c. also endorphins and enkephalins - bind to same receptors as opiates - endogenous opioids ...
... a. also from hypothalamus, pituitary, and other organs b. are often neurosecretory hormones c. also endorphins and enkephalins - bind to same receptors as opiates - endogenous opioids ...
An Herbalist`s View of the Nervous System
... Nicotinic receptor Nociceptors Reuptake Secondary messenger Tolerance Vagus nerve ...
... Nicotinic receptor Nociceptors Reuptake Secondary messenger Tolerance Vagus nerve ...
Unit 2 Review
... 7. Another name for a neural impulse is an ______________________________. 8. Explain how neural communication is both an electrical and chemical process. ...
... 7. Another name for a neural impulse is an ______________________________. 8. Explain how neural communication is both an electrical and chemical process. ...
Slide 1
... NMDA, GABA A, 5HT3 and nicotinic Ach receptors •G- protein receptors When transmitter or agonist binds – either activate or inhibit second messenger systems 1. Adenylate cyclase/cyclic adenosine monophosphate (CAMP) 2. Phospholipase C/Inositol triphosphate / Diacyglycerol DA, NA, 5-HT (except 5H ...
... NMDA, GABA A, 5HT3 and nicotinic Ach receptors •G- protein receptors When transmitter or agonist binds – either activate or inhibit second messenger systems 1. Adenylate cyclase/cyclic adenosine monophosphate (CAMP) 2. Phospholipase C/Inositol triphosphate / Diacyglycerol DA, NA, 5-HT (except 5H ...
CHAPTER 12 AND 13 OUTLINE
... • • Temporal summation – presynaptic neurons transmit impulses in rapid-fire order • • Spatial summation – postsynaptic neuron is stimulated by a large number of terminals at the same time • • IPSPs can also summate with EPSPs, canceling each other out Neurotransmitters • • Chemicals used for neuron ...
... • • Temporal summation – presynaptic neurons transmit impulses in rapid-fire order • • Spatial summation – postsynaptic neuron is stimulated by a large number of terminals at the same time • • IPSPs can also summate with EPSPs, canceling each other out Neurotransmitters • • Chemicals used for neuron ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... •Neurotransmitters are synthesized and packaged into vesicles within the varicosities. •Presynaptic receptors can modulate release. Facilitate or inhibit it. •Substances are co-released along with transmitters. ...
... •Neurotransmitters are synthesized and packaged into vesicles within the varicosities. •Presynaptic receptors can modulate release. Facilitate or inhibit it. •Substances are co-released along with transmitters. ...
Nervous System - Cloudfront.net
... integrate input (nonmyelinated). Motor neurons take information from the CNS to muscles or glands. ...
... integrate input (nonmyelinated). Motor neurons take information from the CNS to muscles or glands. ...
Pipecleaner Neuron Guide - spectrUM Discovery Area
... • Dendrite–dendrites receive information from other neurons. The dendrites of one neuron may have between 8,000 and 150,000 contacts with other neurons. • Myelin sheath–myelin is a special type of cell that wraps around axons to insulate the information that is being sent and helps deliver it fast ...
... • Dendrite–dendrites receive information from other neurons. The dendrites of one neuron may have between 8,000 and 150,000 contacts with other neurons. • Myelin sheath–myelin is a special type of cell that wraps around axons to insulate the information that is being sent and helps deliver it fast ...
Lecture 3
... • This reduces the number of receptors, increases receptor turnover and degradation ...
... • This reduces the number of receptors, increases receptor turnover and degradation ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... The Neurons and the Neurotransmitters: Communication between Neurons • Axon terminals are separated from the receiving neurons by fluid-filled gaps: synaptic gap (or cleft). • Synapse – junction where axon terminal of sending neuron communicates with receiving neuron ...
... The Neurons and the Neurotransmitters: Communication between Neurons • Axon terminals are separated from the receiving neurons by fluid-filled gaps: synaptic gap (or cleft). • Synapse – junction where axon terminal of sending neuron communicates with receiving neuron ...
Chapter 4
... Neurotransmitters stored in axon terminal in vesicles Action potential arrives at axon terminals – Causes Calcium (Ca++) influx – Results in vesicles moving to wall of axon terminal and releasing neurotransmitter ...
... Neurotransmitters stored in axon terminal in vesicles Action potential arrives at axon terminals – Causes Calcium (Ca++) influx – Results in vesicles moving to wall of axon terminal and releasing neurotransmitter ...
Drugs and the Brain
... connects the 2 different neurons so the message can be received. This is called binding. There are different types of neurotransmitters including serotonin, dopamine, and epinephrine. ...
... connects the 2 different neurons so the message can be received. This is called binding. There are different types of neurotransmitters including serotonin, dopamine, and epinephrine. ...
Biology 30 NERVOUS SYSTEM
... All or None Response – if the threshold level is not reached, the action potential will not occur at all. If the threshold is reached or exceeded a full action potential will result. ...
... All or None Response – if the threshold level is not reached, the action potential will not occur at all. If the threshold is reached or exceeded a full action potential will result. ...
MS Word Version
... Page 14. Fast Versus Slow Synaptic Action: Indirectly-acting Neurotransmitters • All of the neurotransmitters at effector organs of the peripheral autonomic nervous system act indirectly. • Norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and serotonin, another central nervous system neurotransmitter, all produce sta ...
... Page 14. Fast Versus Slow Synaptic Action: Indirectly-acting Neurotransmitters • All of the neurotransmitters at effector organs of the peripheral autonomic nervous system act indirectly. • Norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and serotonin, another central nervous system neurotransmitter, all produce sta ...
Document
... 2. During an action potential, Na channels open, causing Na ions to move into the axon. ...
... 2. During an action potential, Na channels open, causing Na ions to move into the axon. ...
Chapter 12 Synapses and Neurotransmitters
... • degradation by enzymes (cont.) – acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in synaptic cleft degrades ACh into acetate and choline // choline reabsorbed by synaptic knob – Catecholines also degradation by enzymes » monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzyme // enzyme located in synaptic knob // after release from synaptic ...
... • degradation by enzymes (cont.) – acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in synaptic cleft degrades ACh into acetate and choline // choline reabsorbed by synaptic knob – Catecholines also degradation by enzymes » monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzyme // enzyme located in synaptic knob // after release from synaptic ...
Stewart - University of Colorado
... Substance P (SP) is a neuropeptide. It is synthesized by neurons and used as a neurotransmitter, neuromodulator, and neurohormone. SP has the structure: ...
... Substance P (SP) is a neuropeptide. It is synthesized by neurons and used as a neurotransmitter, neuromodulator, and neurohormone. SP has the structure: ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... Page 14. Fast Versus Slow Synaptic Action: Indirectly-acting Neurotransmitters • All of the neurotransmitters at effector organs of the peripheral autonomic nervous system act indirectly. • Norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and serotonin, another central nervous system neurotransmitter, all produce sta ...
... Page 14. Fast Versus Slow Synaptic Action: Indirectly-acting Neurotransmitters • All of the neurotransmitters at effector organs of the peripheral autonomic nervous system act indirectly. • Norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and serotonin, another central nervous system neurotransmitter, all produce sta ...