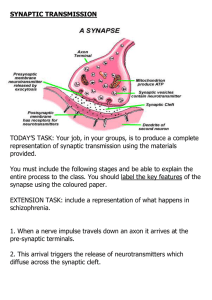
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... immediately by the post-synaptic neuron, otherwise it will either be re-absorbed by the synaptic terminals from which it was released OR it will be chemically broken down by enzymes in the synaptic cleft thus making it inactive. 4. If successfully transmitted, the nerve impulse is then carried along ...
... immediately by the post-synaptic neuron, otherwise it will either be re-absorbed by the synaptic terminals from which it was released OR it will be chemically broken down by enzymes in the synaptic cleft thus making it inactive. 4. If successfully transmitted, the nerve impulse is then carried along ...
Neurotransmitters
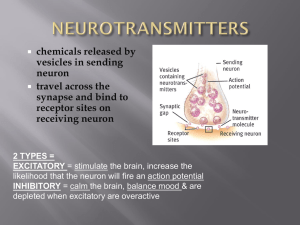
... Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals which relay, amplify, and modulate signals between a neuron and another cell. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles that cluster beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they ...
... Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals which relay, amplify, and modulate signals between a neuron and another cell. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles that cluster beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they ...
4-5_Chem_postsyn_KolozsvariB
... each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control o ...
... each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control o ...
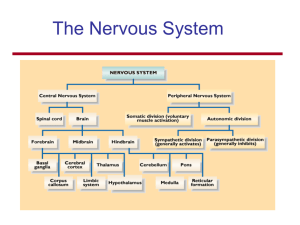
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
... BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
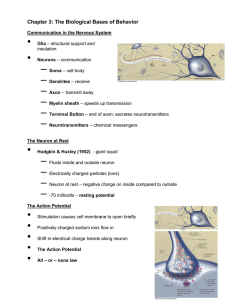
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Twin studies – compare resemblance of identical (monozygotic) and fraternal (dizygotic) twins on a trait Adoption studies – examine resemblance between adopted children and their biological and adoptive parents ...
... Twin studies – compare resemblance of identical (monozygotic) and fraternal (dizygotic) twins on a trait Adoption studies – examine resemblance between adopted children and their biological and adoptive parents ...
neurotransmitter
... the body. • NTs can be either excitatory or inhibitory • Each neuron generally synthesizes and releases a single type of neurotransmitter • The major neurotransmitters are indicated on the next slide. ...
... the body. • NTs can be either excitatory or inhibitory • Each neuron generally synthesizes and releases a single type of neurotransmitter • The major neurotransmitters are indicated on the next slide. ...
Neurotransmitters
... • Sometimes there is a decrease in the number of receptors for a neurotransmitter on the postsynaptic neuron due to long-term exposure to the neurotransmitter. This is called downregulation. • Neurotransmitters can be classified into 4 major groups: 1. Amino acids (eg, glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric ...
... • Sometimes there is a decrease in the number of receptors for a neurotransmitter on the postsynaptic neuron due to long-term exposure to the neurotransmitter. This is called downregulation. • Neurotransmitters can be classified into 4 major groups: 1. Amino acids (eg, glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric ...
9.3 Synaptic Transmission
... presynaptic neuron it causes synaptic vesicles to move to the presynaptic membrane. ...
... presynaptic neuron it causes synaptic vesicles to move to the presynaptic membrane. ...