Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... • Voltage change at receptor site – postsynaptic potential (PSP) – Not all-or-none – Changes the probability of the postsynaptic neuron firing • Positive voltage shift – excitatory PSP • Negative voltage shift – inhibitory PSP ...
... • Voltage change at receptor site – postsynaptic potential (PSP) – Not all-or-none – Changes the probability of the postsynaptic neuron firing • Positive voltage shift – excitatory PSP • Negative voltage shift – inhibitory PSP ...
fleming_Oct
... Excitatory paths are shown in green; inhibitory are in red. The substantia nigra’s axons inhibit the putamen. Axon loss increases excitatory communication to the globus pallidus. The result is increased inhibition from the globus pallidus to the thalamus and decreased excitation from the thalamus to ...
... Excitatory paths are shown in green; inhibitory are in red. The substantia nigra’s axons inhibit the putamen. Axon loss increases excitatory communication to the globus pallidus. The result is increased inhibition from the globus pallidus to the thalamus and decreased excitation from the thalamus to ...
Synaptic Transmission and Neurotransmitters
... – Principal excitatory NT in central nervous system – Critical for learning: it is Glutamate and the NMDA receptors that allow for long term potentiation – May play significant role in schizophrenia: disrupts regulation of DA, NE, Ach, 5HT. • Affects memory formation • Affects arousal • Affects proc ...
... – Principal excitatory NT in central nervous system – Critical for learning: it is Glutamate and the NMDA receptors that allow for long term potentiation – May play significant role in schizophrenia: disrupts regulation of DA, NE, Ach, 5HT. • Affects memory formation • Affects arousal • Affects proc ...
neurons
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
Ch. 48-49 Nervous System 9e S13
... • Bind to receptors on neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells • Broken down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells • Types of neurotransmitters: – Excitatory: speed up impulses by causing depolarization of postsynaptic membrane – Inhibitory: slow impulses by causing hyperpolarization of p ...
... • Bind to receptors on neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells • Broken down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells • Types of neurotransmitters: – Excitatory: speed up impulses by causing depolarization of postsynaptic membrane – Inhibitory: slow impulses by causing hyperpolarization of p ...
Time Zones
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
... 2. Name 2 things that can compromise neural communication (especially synaptic transmission): 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes ...
The Neuron: The Basic Unit of Communication Neuron: Basic
... Neurotransmitters The main neurotransmitters • Acetylcholine (ACh) • Norepinephrine (aka noradrenaline) • Serotonin • Dopamine • GABA (gamma aminobutyric acid) • Endorphins (covered in Chapter 12) What are the major roles of each neurotransmitters (see handout)? ...
... Neurotransmitters The main neurotransmitters • Acetylcholine (ACh) • Norepinephrine (aka noradrenaline) • Serotonin • Dopamine • GABA (gamma aminobutyric acid) • Endorphins (covered in Chapter 12) What are the major roles of each neurotransmitters (see handout)? ...
Document
... Composed of integral membrane protein Mediate direct neurotransmitter action Action is immediate, brief, simple, and highly localized Ligand binds the receptor, and ions enter the cells Excitatory receptors depolarize membranes Inhibitory receptors hyperpolarize membranes ...
... Composed of integral membrane protein Mediate direct neurotransmitter action Action is immediate, brief, simple, and highly localized Ligand binds the receptor, and ions enter the cells Excitatory receptors depolarize membranes Inhibitory receptors hyperpolarize membranes ...
Transmission at the Synapse and the
... INCREASED calcium release into the cell (thus increased release of neurotransmitter) o for example: SEROTONIN acts a presynaptic facilitator; it increases cAMP activity, which results in phosphorylation of potassium channels (which become closed in the phosphorylated state). The result is delayed re ...
... INCREASED calcium release into the cell (thus increased release of neurotransmitter) o for example: SEROTONIN acts a presynaptic facilitator; it increases cAMP activity, which results in phosphorylation of potassium channels (which become closed in the phosphorylated state). The result is delayed re ...
Neurotransmitter Test Assessment
... learning. In fact, it is believed that 70% of the fast excitatory CNS synapses utilize glutamate as a transmitter. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the activity of signal-receiving neurons and play a major role in controlling brain function. An event or process that dramatically increases the a ...
... learning. In fact, it is believed that 70% of the fast excitatory CNS synapses utilize glutamate as a transmitter. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the activity of signal-receiving neurons and play a major role in controlling brain function. An event or process that dramatically increases the a ...
Power Point
... – The action potential cannot cross the synaptic cleft • Causes neurotransmitters to be released from vesicles in the synaptic knob ...
... – The action potential cannot cross the synaptic cleft • Causes neurotransmitters to be released from vesicles in the synaptic knob ...
Nervous System Study Guide
... 8. Functions of sodium-potassium pumps during action potential. 9. When an impulse moves down the axon, a small part of the axon momentarily reserves its__________. 10. Definitions and functions of different neurotransmitters. 11. When a neuron transmitter is released from a presynaptic neuron, the ...
... 8. Functions of sodium-potassium pumps during action potential. 9. When an impulse moves down the axon, a small part of the axon momentarily reserves its__________. 10. Definitions and functions of different neurotransmitters. 11. When a neuron transmitter is released from a presynaptic neuron, the ...
Neurotransmitters
... Serotonin (excitatory and inhibitory) o Serotonin has been found to be intimately involved in emotion and mood. o Too little serotonin has been shown to lead to depression, problems with anger control, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and suicide. o Too little also leads to an increased appetite for ...
... Serotonin (excitatory and inhibitory) o Serotonin has been found to be intimately involved in emotion and mood. o Too little serotonin has been shown to lead to depression, problems with anger control, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and suicide. o Too little also leads to an increased appetite for ...
Name
... 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of neuron cell bodies found in the PNS 16. a chemical which diffuses across the synapse in order to affect a postsynaptic neuron 17. stimulus strength NOT strong enough to cause a response 18. when these “ ...
... 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of neuron cell bodies found in the PNS 16. a chemical which diffuses across the synapse in order to affect a postsynaptic neuron 17. stimulus strength NOT strong enough to cause a response 18. when these “ ...
How is the Nervous System Organized? Class Objectives:
... Acetylcholine (ACh) usually stimulates the firing of neurons and is involved in muscle action, learning, and attention and memory Why do people have Botox treatments? ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ...
... Acetylcholine (ACh) usually stimulates the firing of neurons and is involved in muscle action, learning, and attention and memory Why do people have Botox treatments? ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ...
10synapse & neurotransmitter
... • Transmission of electrical impulse [AP] by chemical means from presynaptic neuron to post-synaptic neuron takes time. It is called ‘Synaptic Delay’. It is 0.5 to 1 millisecond. ...
... • Transmission of electrical impulse [AP] by chemical means from presynaptic neuron to post-synaptic neuron takes time. It is called ‘Synaptic Delay’. It is 0.5 to 1 millisecond. ...
Concepts of Neurobiology
... Play an important role in human emotions and behavior Are the target for the mechanism of action for psychotropic medications Summary: Neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft from the axon to the dendrite. The substance is either inactivated or returned to the axon. ...
... Play an important role in human emotions and behavior Are the target for the mechanism of action for psychotropic medications Summary: Neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft from the axon to the dendrite. The substance is either inactivated or returned to the axon. ...
Neurons - Seung Lab
... • They can be distinguished in some types of neurons. • Dendrites receive synaptic inputs. • Axons make synapses on other ...
... • They can be distinguished in some types of neurons. • Dendrites receive synaptic inputs. • Axons make synapses on other ...
Acetylcholine
... Neurotransmitters are the chemicals which allow the transmission of signals from one neuron to the next across synapses. They are also found at the axon endings of motor neurons, where they stimulate the muscle fibers. And they and their close relatives are produced by some glands such as the pituit ...
... Neurotransmitters are the chemicals which allow the transmission of signals from one neuron to the next across synapses. They are also found at the axon endings of motor neurons, where they stimulate the muscle fibers. And they and their close relatives are produced by some glands such as the pituit ...
Nerve impulses and Synapses Electro
... • Countless drugs and medicines work by interfering with neuro-transmitter systems, and can have very powerful, and sometimes beneficial effects. • However, because the same neurotransmitter often have several different actions at different places in your brain or body, such drugs have numerous side ...
... • Countless drugs and medicines work by interfering with neuro-transmitter systems, and can have very powerful, and sometimes beneficial effects. • However, because the same neurotransmitter often have several different actions at different places in your brain or body, such drugs have numerous side ...
Types of neurons - Brigham Young University
... NTs diffuse across the synaptic cleft and then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and initiate some sort of response on the postsynaptic cell. ...
... NTs diffuse across the synaptic cleft and then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and initiate some sort of response on the postsynaptic cell. ...
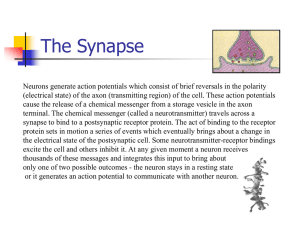
The Synapse
... Commonly used in labs around the world Fugu Poisoning: Estimates as high as 200 cases per year have been reported with mortality approaching 50% ...
... Commonly used in labs around the world Fugu Poisoning: Estimates as high as 200 cases per year have been reported with mortality approaching 50% ...
Document
... • Alcohol has multiple effects on neurons. It alters neuron membranes, ion channels, enzymes, and receptors. • It binds directly to receptors for acetylcholine, serotonin, and gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), and glutamate. • We will focus on GABA and its receptor. ...
... • Alcohol has multiple effects on neurons. It alters neuron membranes, ion channels, enzymes, and receptors. • It binds directly to receptors for acetylcholine, serotonin, and gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), and glutamate. • We will focus on GABA and its receptor. ...