Receptors and Neurotransmitters
... . This neurotransmitter is involved in the control of skeletal muscle action in the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), stimulating skeletal muscle contraction at neuromuscular junctions. It can excite or inhibit ANS synapses. Most of the postganglionic fibers of th ...
... . This neurotransmitter is involved in the control of skeletal muscle action in the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), stimulating skeletal muscle contraction at neuromuscular junctions. It can excite or inhibit ANS synapses. Most of the postganglionic fibers of th ...
Nervous System Objectives
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
How do neurotransmitters generate electrochemical signals in
... Include glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glycine, and aspartate. Of these, the first two are most important. Glutamatergic neurons: the principle excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and spinal cord; associated with learning and memory. GABA-secreting neurons: the principle inhi ...
... Include glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), glycine, and aspartate. Of these, the first two are most important. Glutamatergic neurons: the principle excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and spinal cord; associated with learning and memory. GABA-secreting neurons: the principle inhi ...
Summary of the Known Major Neurotransmitters
... receptor sites, stimulating skeletal muscles and causing the heart to beat more rapidly. 2. Drugs can mimic or block the effects of a neurotransmitter by fitting into receptor sites and preventing the neurotransmitter from acting. For example, the drug curare produces almost instant paralysis by blo ...
... receptor sites, stimulating skeletal muscles and causing the heart to beat more rapidly. 2. Drugs can mimic or block the effects of a neurotransmitter by fitting into receptor sites and preventing the neurotransmitter from acting. For example, the drug curare produces almost instant paralysis by blo ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous System – Homework – Part I
... 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following rel ...
... 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following rel ...
48 - Groupfusion.net
... 4) The vesicles release neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft 5)The neurotransmitter binds to the receptor portion of ligand-gated ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, opening the channels. In the synapse illustrated here, both Na+ and K+ can diffuse through the channels 6) The neurotransmi ...
... 4) The vesicles release neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft 5)The neurotransmitter binds to the receptor portion of ligand-gated ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, opening the channels. In the synapse illustrated here, both Na+ and K+ can diffuse through the channels 6) The neurotransmi ...
Sample Questions for Evaluation #1 – General
... 12. A synapse is a(n): a) neural cable containing many axons. b) chemical messenger that triggers muscle contractions. c) automatic response to sensory input. d) junction between a sending neuron and a receiving neuron. 13. Reuptake refers to the: a) release of hormones into the bloodstream. b) reab ...
... 12. A synapse is a(n): a) neural cable containing many axons. b) chemical messenger that triggers muscle contractions. c) automatic response to sensory input. d) junction between a sending neuron and a receiving neuron. 13. Reuptake refers to the: a) release of hormones into the bloodstream. b) reab ...
KS4_nervous_models_Pupil_Sheets
... complex network of neurons. In order for impulses to get from one place to another they have to be able to pass from neuron to neuron. The gaps between neurons are called synapses ...
... complex network of neurons. In order for impulses to get from one place to another they have to be able to pass from neuron to neuron. The gaps between neurons are called synapses ...
Key Stage 4 – Nervous models Pupil worksheet
... complex network of neurons. In order for impulses to get from one place to another they have to be able to pass from neuron to neuron. The gaps between neurons are called synapses ...
... complex network of neurons. In order for impulses to get from one place to another they have to be able to pass from neuron to neuron. The gaps between neurons are called synapses ...
big
... Neurotransmitter stored in vesicles in axon of presynaptic cell is released into synaptic cleft as a result of depolarization (action potential). Neurotransmitter diffuses across cleft, binds to receptors, and causes a postsynaptic effect Neurotransmitter is taken back into the presynaptic cell (“re ...
... Neurotransmitter stored in vesicles in axon of presynaptic cell is released into synaptic cleft as a result of depolarization (action potential). Neurotransmitter diffuses across cleft, binds to receptors, and causes a postsynaptic effect Neurotransmitter is taken back into the presynaptic cell (“re ...
File
... At this point, please go back to your diagram summaries and revise them. You should be able to use correct terminology and have a better understanding of what is going on. ...
... At this point, please go back to your diagram summaries and revise them. You should be able to use correct terminology and have a better understanding of what is going on. ...
Neurotransmission
... specialized cells, which coordinate the actions of an individual by sending signals from one part of the body to the other. ...
... specialized cells, which coordinate the actions of an individual by sending signals from one part of the body to the other. ...
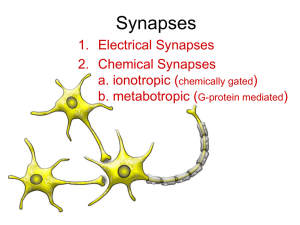
Synapses
... enzymes at the synapse? • What is the function of reuptake transporters at the presynaptic membrane? • Therapeutic and Recreational Drug Effects A. monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) B. Prozac (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) C. Cocaine ( dopamine reuptake inhibitor) ...
... enzymes at the synapse? • What is the function of reuptake transporters at the presynaptic membrane? • Therapeutic and Recreational Drug Effects A. monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) B. Prozac (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) C. Cocaine ( dopamine reuptake inhibitor) ...
Synaptic Transmission
... work against sending a message and can be inhibitory. When they bind to the post-synaptic neuron, they let potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...
... work against sending a message and can be inhibitory. When they bind to the post-synaptic neuron, they let potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...
excitatory neurotransmitter
... axon to the axon terminals. At the axon terminals, the message is converted to its chemical form to cross the synapse. The chemical form of a neural message is known as a neurotransmitter. When the neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminals, they cross the synapse to the next neuron in t ...
... axon to the axon terminals. At the axon terminals, the message is converted to its chemical form to cross the synapse. The chemical form of a neural message is known as a neurotransmitter. When the neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminals, they cross the synapse to the next neuron in t ...
Topic 5
... – Vesicles fuse with SNARE pins to presynaptic terminal – Neurotransmitter spills into synaptic cleft via exocytosis – Neurotransmitter binds to postsynaptic receptor proteins – Biochemical “electrical” message elicited in postsynaptic cell – Removal/retrieval of neurotransmitter from synaptic cleft ...
... – Vesicles fuse with SNARE pins to presynaptic terminal – Neurotransmitter spills into synaptic cleft via exocytosis – Neurotransmitter binds to postsynaptic receptor proteins – Biochemical “electrical” message elicited in postsynaptic cell – Removal/retrieval of neurotransmitter from synaptic cleft ...
Functions in Alertness and SLEEP WAKE Cycles
... Difference in time courses of synaptic interactions ○ This allows the possibility of designing drugs that target specific neuronal subsystems - Neuropeptides ○ Large molecules that are stored/released from same neurons as small neurotransmitters ○ Are metabolically expensive => are effective even ...
... Difference in time courses of synaptic interactions ○ This allows the possibility of designing drugs that target specific neuronal subsystems - Neuropeptides ○ Large molecules that are stored/released from same neurons as small neurotransmitters ○ Are metabolically expensive => are effective even ...
overview of neural f..
... • conditioning produces LTP-like changes in brain. • drugs that block LTP block learning. ...
... • conditioning produces LTP-like changes in brain. • drugs that block LTP block learning. ...
neurology1ned2013 31.5 KB - d
... Nerves can end at muscle tissue to deliver a stimulus to contract muscle. This enables locomotion or movement. Neurons communicate via neurotransmitters (NTs)~chemical signals. 2 types of potentials: excitatory and inhibitory. They are classified based on stimuli. Excitatory neurotransmitters more l ...
... Nerves can end at muscle tissue to deliver a stimulus to contract muscle. This enables locomotion or movement. Neurons communicate via neurotransmitters (NTs)~chemical signals. 2 types of potentials: excitatory and inhibitory. They are classified based on stimuli. Excitatory neurotransmitters more l ...
Module Two
... They communicate to other neurons by binding to receptors on neighboring neurons -The communication between neurons is chemical ...
... They communicate to other neurons by binding to receptors on neighboring neurons -The communication between neurons is chemical ...
Synapses - Franklin College
... enzymes at the synapse? • What is the function of reuptake transporters at the presynaptic membrane? • Therapeutic and Recreational Drug Effects A. monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) B. Prozac (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) C. Cocaine ( dopamine reuptake inhibitor) ...
... enzymes at the synapse? • What is the function of reuptake transporters at the presynaptic membrane? • Therapeutic and Recreational Drug Effects A. monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) B. Prozac (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) C. Cocaine ( dopamine reuptake inhibitor) ...
No Slide Title
... reflex may not be produced, however if several small pinches are rapidly applied they trigger a reflex. This is called temporal summation. ...
... reflex may not be produced, however if several small pinches are rapidly applied they trigger a reflex. This is called temporal summation. ...
File
... 2. Depolarization – an active transport process that requires ATP and protein channels. Depolarization occurs when Na+ moves into the cell, causing the charge on the axonal membrane to become negative, thus initiating an action potential. 3. Repolarization – Na+ channels close, K+ moves back into th ...
... 2. Depolarization – an active transport process that requires ATP and protein channels. Depolarization occurs when Na+ moves into the cell, causing the charge on the axonal membrane to become negative, thus initiating an action potential. 3. Repolarization – Na+ channels close, K+ moves back into th ...
THE BRAIN - Dublin City Schools
... A fatty substance that covers axons. The more myelin an axon has, the faster nerve impulses can travel. – After puberty, the amount of myelin in the brain increases dramatically, making the brain much more efficient. ...
... A fatty substance that covers axons. The more myelin an axon has, the faster nerve impulses can travel. – After puberty, the amount of myelin in the brain increases dramatically, making the brain much more efficient. ...