The Renaissance - History by Mills
... culture of antiquity (the time period before the Middle Ages) “rebirth” of Greek and Roman classics Applies to art, politics, and science Praises individual achievement ...
... culture of antiquity (the time period before the Middle Ages) “rebirth” of Greek and Roman classics Applies to art, politics, and science Praises individual achievement ...
The Renaissance, 1300-1600 Essential Question 2
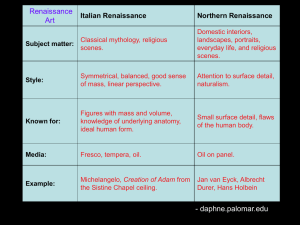
... Art as expression humanist topics & themes a. Greek/Roman Mythology b. Individual portraits c. Landscapes /Nature / Science New techniques developed a. Perspective & shading (3-D) b. More humanist subjects/styles c. use of oils Architecture a. Copies building design of Greeks/Romans (geometric shape ...
... Art as expression humanist topics & themes a. Greek/Roman Mythology b. Individual portraits c. Landscapes /Nature / Science New techniques developed a. Perspective & shading (3-D) b. More humanist subjects/styles c. use of oils Architecture a. Copies building design of Greeks/Romans (geometric shape ...
The Renaissance
... Leonardo is said to have painted in the church of Orsanmichele. But his skills and interests took him all over Florence. No matter where Leonardo was, he constantly searched for knowledge. He kept detailed notes and complex drawings on hundreds of subjects. Many of these drawings anticipated inventi ...
... Leonardo is said to have painted in the church of Orsanmichele. But his skills and interests took him all over Florence. No matter where Leonardo was, he constantly searched for knowledge. He kept detailed notes and complex drawings on hundreds of subjects. Many of these drawings anticipated inventi ...
renaissance and italy - sccoesocialstudiesresources
... Beauty was believed to afford at least some glimpse of a transcendental existence. ...
... Beauty was believed to afford at least some glimpse of a transcendental existence. ...
the renaissance - Rowan County Schools
... A basic concern with the material world instead of the spiritual world. “Worldly” Attention on improving life in the here and now, but did not abandon religion. More focus on education, business, wealth More leisure time, art patronage, etc… ...
... A basic concern with the material world instead of the spiritual world. “Worldly” Attention on improving life in the here and now, but did not abandon religion. More focus on education, business, wealth More leisure time, art patronage, etc… ...
Renaissance Unit Study Guide - Garnet Valley School District
... How and why can the Renaissance Era be seen as a time of great change, and the beginning of our Modern Age? Notes: Renaissance Era includes: (You do not need to discuss all) o Renaissance Ideas o Renaissance Art o Renaissance Literature o The Age of Exploration o The Scientific Revolution o The Re ...
... How and why can the Renaissance Era be seen as a time of great change, and the beginning of our Modern Age? Notes: Renaissance Era includes: (You do not need to discuss all) o Renaissance Ideas o Renaissance Art o Renaissance Literature o The Age of Exploration o The Scientific Revolution o The Re ...
Renaissance Unit Study Guide - Garnet Valley School District
... How and why can the Renaissance Era be seen as a time of great change, and the beginning of our Modern Age? Notes: Renaissance Era includes: (You do not need to discuss all) o Renaissance Ideas o Renaissance Art o Renaissance Literature o The Age of Exploration o The Scientific Revolution o The Refo ...
... How and why can the Renaissance Era be seen as a time of great change, and the beginning of our Modern Age? Notes: Renaissance Era includes: (You do not need to discuss all) o Renaissance Ideas o Renaissance Art o Renaissance Literature o The Age of Exploration o The Scientific Revolution o The Refo ...
Unit 5 – Renaissance, Reformation, Exploration Using the maps on
... Charles VIII occupied ________________________ in the south. Who did the northern Italian states ask for help? For the next 30 years, France and Spain fight in Italy. The sacking of _____________________ ends the wars and leaves Spain a dominant force in Italy It also brings about the end of the ___ ...
... Charles VIII occupied ________________________ in the south. Who did the northern Italian states ask for help? For the next 30 years, France and Spain fight in Italy. The sacking of _____________________ ends the wars and leaves Spain a dominant force in Italy It also brings about the end of the ___ ...
Chapter 9_ Lesson 1_2_Renaissance
... •Humanism was a key intellectual (learning) movement of the Renaissance •Goal of humanism is to educate well-rounded citizen. •Study of the classics (Ancient Greeks/ Romans • Humanities education: history, public speaking, grammar, logic, poetry, math, astronomy, and music (liberal arts today!) • R ...
... •Humanism was a key intellectual (learning) movement of the Renaissance •Goal of humanism is to educate well-rounded citizen. •Study of the classics (Ancient Greeks/ Romans • Humanities education: history, public speaking, grammar, logic, poetry, math, astronomy, and music (liberal arts today!) • R ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... The Renaissance is the name given to the time period of history between 1300 and 1600. The word “renaissance is a French word meaning “new birth.” Probably the greatest achievement of the Renaissance came in education and the arts. The Renaissance began in Italy. Italy’s location in the Mediterranea ...
... The Renaissance is the name given to the time period of history between 1300 and 1600. The word “renaissance is a French word meaning “new birth.” Probably the greatest achievement of the Renaissance came in education and the arts. The Renaissance began in Italy. Italy’s location in the Mediterranea ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... The Renaissance is the name given to the time period of history between 1300 and 1600. The word “renaissance is a French word meaning “new birth.” Probably the greatest achievement of the Renaissance came in education and the arts. The Renaissance began in Italy. Italy’s location in the Mediterranea ...
... The Renaissance is the name given to the time period of history between 1300 and 1600. The word “renaissance is a French word meaning “new birth.” Probably the greatest achievement of the Renaissance came in education and the arts. The Renaissance began in Italy. Italy’s location in the Mediterranea ...
Renaissance Worksheet
... emphasized non-religious concerns? Identify three Greco-Roman beliefs that humanists adopted. A. B. C. What four factors helped promote the diffusion of Renaissance art and humanist ideas northward from Italy to other European countries? A. B. C. D. Humanism inspired new forms of writing/literature. ...
... emphasized non-religious concerns? Identify three Greco-Roman beliefs that humanists adopted. A. B. C. What four factors helped promote the diffusion of Renaissance art and humanist ideas northward from Italy to other European countries? A. B. C. D. Humanism inspired new forms of writing/literature. ...
Chapter 11 Objects List PDF
... Contrast the Renaissance attitude toward life with the Medieval outlook. I.B. Contrast humanism and its effects with a Biblical view of man. I.C.1 List the causes of the Renaissance revival of learning. I.C.2 Describe the humanistic learning of the Renaissance II Introduction 1. Explain why the Rena ...
... Contrast the Renaissance attitude toward life with the Medieval outlook. I.B. Contrast humanism and its effects with a Biblical view of man. I.C.1 List the causes of the Renaissance revival of learning. I.C.2 Describe the humanistic learning of the Renaissance II Introduction 1. Explain why the Rena ...
File
... Harsh weather at this time also made conditions tough. Crops were ruined. These events led to a great famine between 1315-1322. Many people died as a result and it became a demographic disaster. During this time period many other horrible events took place such as torrential rain in 1310 and failed ...
... Harsh weather at this time also made conditions tough. Crops were ruined. These events led to a great famine between 1315-1322. Many people died as a result and it became a demographic disaster. During this time period many other horrible events took place such as torrential rain in 1310 and failed ...
The Renaissance
... • Focus of education shifted to the humanities: grammar, rhetoric, history, poetry, and moral philosophy • Tried to produce people more engaged in civic life • Attention shifted to Jesus’s life and the early martyred saints • Increased emphasis on materialism, leading to the beginning of capitalism ...
... • Focus of education shifted to the humanities: grammar, rhetoric, history, poetry, and moral philosophy • Tried to produce people more engaged in civic life • Attention shifted to Jesus’s life and the early martyred saints • Increased emphasis on materialism, leading to the beginning of capitalism ...
Chapter 13 Vocab - Everglades High School
... Section 1 • humanism – the Renaissance intellectual movement that studied classical cultures to increase understanding of their own times • humanities – subjects such as grammar, poetry, rhetoric, and history • Florence – an Italian city-state that produced many gifted artists, scholars, scientists, ...
... Section 1 • humanism – the Renaissance intellectual movement that studied classical cultures to increase understanding of their own times • humanities – subjects such as grammar, poetry, rhetoric, and history • Florence – an Italian city-state that produced many gifted artists, scholars, scientists, ...
On Pleasure - SCHOOLinSITES
... The Renaissance in the north began in the last quarter of the fifteenth century ...
... The Renaissance in the north began in the last quarter of the fifteenth century ...
WHAP Student Copy Science Technology and a New Way of Thinking
... A. HumanismRenaissance ideaSense of tremendous capacities and potential of every human being replaced the concept of the frail creature in need of God’s grace: humanity became worthy of study in its own ________ B. Dante (1265-1321) wrote his Divine Comedy in Italian (vernacular) rather than in La ...
... A. HumanismRenaissance ideaSense of tremendous capacities and potential of every human being replaced the concept of the frail creature in need of God’s grace: humanity became worthy of study in its own ________ B. Dante (1265-1321) wrote his Divine Comedy in Italian (vernacular) rather than in La ...
Renaissance - jstachowiak
... Origins The Renaissance first began in Italy. People developed new attitudes about themselves and the world around them. Signaled the beginning of modern times. Italian preservation of ancient Rome encouraged advancements in artistic and architectural realms. ...
... Origins The Renaissance first began in Italy. People developed new attitudes about themselves and the world around them. Signaled the beginning of modern times. Italian preservation of ancient Rome encouraged advancements in artistic and architectural realms. ...
File - Ms. Sanfilippo`s Class
... Renaissance architects also added their own ideas to classical building styles. During the Renaissance, wealthy families built private townhouses known as palazzi (pahl-AH-tzee), which is Italian for “palaces.” Many had shops on the ground floor and homes above. Most palazzi were built around a priv ...
... Renaissance architects also added their own ideas to classical building styles. During the Renaissance, wealthy families built private townhouses known as palazzi (pahl-AH-tzee), which is Italian for “palaces.” Many had shops on the ground floor and homes above. Most palazzi were built around a priv ...
Renaissance means rebirth because during the
... 13. How did Machiavelli think a prince should rule his people? He believed a wise leader cannot and should not keep his word when keeping it is not to his advantage. 14. How did artists in northern Europe embody features of Renaissance art? They realistically portrayed the tiniest details in works o ...
... 13. How did Machiavelli think a prince should rule his people? He believed a wise leader cannot and should not keep his word when keeping it is not to his advantage. 14. How did artists in northern Europe embody features of Renaissance art? They realistically portrayed the tiniest details in works o ...
File
... What results is a lot of fighting and wars and consequently not much time for literature, arts, and education ...
... What results is a lot of fighting and wars and consequently not much time for literature, arts, and education ...
Renaissance in Scotland

The Renaissance in Scotland was a cultural, intellectual and artistic movement in Scotland, from the late fifteenth century to the beginning of the seventeenth century. It is associated with the pan-European Renaissance that is usually regarded as beginning in Italy in the late fourteenth century and reaching northern Europe as a Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century. It involved an attempt to revive the principles of the classical era, including humanism, a spirit of scholarly enquiry, scepticism, and concepts of balance and proportion. Since the twentieth century the uniqueness and unity of the Renaissance has been challenged by historians, but significant changes in Scotland can be seen to have taken place in education, intellectual life, literature, art, architecture, music and politics.The court was central to the patronage and dissemination of Renaissance works and ideas. It was also central to the staging of lavish display that portrayed the political and religious role of the monarchy. The Renaissance led to the adoption of ideas of imperial monarchy, encouraging the Scottish crown to join the new monarchies by asserting imperial jurisdiction and distinction. The growing emphasis on education in the Middle Ages became part of a humanist and then Protestant programme to extend and reform learning. It resulted in the expansion of the school system and the foundation of six university colleges by the end of the sixteenth century. Relatively large numbers of Scottish scholars studied on the continent or in England and some, such as Hector Boece, John Mair, Andrew Melville and George Buchanan, returned to Scotland to play a major part in developing Scottish intellectual life. Vernacular works in Scots began to emerge in the fifteenth century, while Latin remained a major literary language. With the patronage of James V and James VI, writers included William Stewart, John Bellenden, David Lyndsay, William Fowler and Alexander Montgomerie.In the sixteenth century, Scottish kings, particularly James V, built palaces in a Renaissance style, beginning at Linlithgow. The trend soon spread to members of the aristocracy. Painting was strongly influenced by Flemish art, with works commissioned from the continent and Flemings serving as court artists. While church art suffered iconoclasm and a loss of patronage as a result of the Reformation, house decoration and portraiture became significant for the wealthy, with George Jamesone emerging as the first major named artist in the early seventeenth century. Music also incorporated wider European influences although the Reformation caused a move from complex polyphonic church music to the simpler singing of metrical psalms. Combined with the Union of Crowns in 1603, the Reformation also removed the church and the court as sources of patronage, changing the direction of artistic creation and limiting its scope. In the early seventeenth century the major elements of the Renaissance began to give way to Stoicism, Mannerism and the Baroque.