Specificity in Inhibitory Systems Associated with Prefrontal Pathways to
... to inhibitory neurons labeled for calbindin (CB) or parvalbumin (PV), which differ in mode of inhibition. Projection neurons in area 10 originated mostly in layers 2--3 and were intermingled with CB inhibitory neurons. In contrast, projections from area 32 originated predominantly in layers 5--6 amo ...
... to inhibitory neurons labeled for calbindin (CB) or parvalbumin (PV), which differ in mode of inhibition. Projection neurons in area 10 originated mostly in layers 2--3 and were intermingled with CB inhibitory neurons. In contrast, projections from area 32 originated predominantly in layers 5--6 amo ...
prenatal formation of cortical input and development of
... are virtually devoid of such input was first fully developed in a fetus injected at El33 and sacrificed at El34 (Figs. 2E, 4B, and 7, A and B). It is noteworthy that the crosssectional diameters of the projection-free cores or islands surrounded by a field of labeled prefrontal fibers measure 250 to ...
... are virtually devoid of such input was first fully developed in a fetus injected at El33 and sacrificed at El34 (Figs. 2E, 4B, and 7, A and B). It is noteworthy that the crosssectional diameters of the projection-free cores or islands surrounded by a field of labeled prefrontal fibers measure 250 to ...
paper - Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit
... The organization of computations in networks of spiking neurons in the brain is still largely unknown, in particular in view of the inherently stochastic features of their firing activity and the experimentally observed trial-to-trial variability of neural systems in the brain. In principle there ex ...
... The organization of computations in networks of spiking neurons in the brain is still largely unknown, in particular in view of the inherently stochastic features of their firing activity and the experimentally observed trial-to-trial variability of neural systems in the brain. In principle there ex ...
Reward-Related Neuronal Activity During Go - Research
... cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 83: 1864 –1876, 2000. The orbitofrontal cortex appears to be involved in the control of voluntary, goal-directed behavior by motivational outcomes. This study investigated how orbitofrontal neurons process information about rewards in a task that depends on intact orbitofron ...
... cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 83: 1864 –1876, 2000. The orbitofrontal cortex appears to be involved in the control of voluntary, goal-directed behavior by motivational outcomes. This study investigated how orbitofrontal neurons process information about rewards in a task that depends on intact orbitofron ...
Purves ch. 8 + Kandel ch. 23 - Weizmann Institute of Science
... The long axis of the corpuscle is usually oriented parallel to the stretch lines in skin; thus, Ruffini’s corpuscles are particularly sensitive to the cutaneous stretching produced by digit or limb movements. They account for about 20% of the receptors in the human hand and do not elicit any particu ...
... The long axis of the corpuscle is usually oriented parallel to the stretch lines in skin; thus, Ruffini’s corpuscles are particularly sensitive to the cutaneous stretching produced by digit or limb movements. They account for about 20% of the receptors in the human hand and do not elicit any particu ...
Regulation of synaptic functions in central nervous system by
... action by leptin signalling in energy homoeostasis regulation. A number of studies attempted to identify additional effector neurons for leptin action. Lowell and co-workers [22] recently investigated whether the ‘first-order’ effectors of leptin signaling are excitatory- or inhibitory-neurons. In t ...
... action by leptin signalling in energy homoeostasis regulation. A number of studies attempted to identify additional effector neurons for leptin action. Lowell and co-workers [22] recently investigated whether the ‘first-order’ effectors of leptin signaling are excitatory- or inhibitory-neurons. In t ...
Computing with Spiking Neuron Networks
... for simulating traditional connectionist models by SNNs, as in [96]. The basic idea is biologically well-founded: the more intensive the input, the earlier the spike transmission (e.g. in visual system). Hence a network of spiking neurons can be designed with n input neurons Ni whose firing times ar ...
... for simulating traditional connectionist models by SNNs, as in [96]. The basic idea is biologically well-founded: the more intensive the input, the earlier the spike transmission (e.g. in visual system). Hence a network of spiking neurons can be designed with n input neurons Ni whose firing times ar ...
PDF
... of the beginning of the reach. (b) The median bias of the trajectory over time. A bias of 1 signifies that the direction of the trajectory is toward the expected target direction, while a bias o ...
... of the beginning of the reach. (b) The median bias of the trajectory over time. A bias of 1 signifies that the direction of the trajectory is toward the expected target direction, while a bias o ...
Clustered Organization of Neurons with Similar Extra
... five different penetrations. The summation indices of all neurons recorded were shown (Figure 3, left panels), together with histological reconstruction of the electrode track through the cortical layers (Figure 3, right panels). Regardless of whether the penetration was tangential, oblique, or norm ...
... five different penetrations. The summation indices of all neurons recorded were shown (Figure 3, left panels), together with histological reconstruction of the electrode track through the cortical layers (Figure 3, right panels). Regardless of whether the penetration was tangential, oblique, or norm ...
A Critical Review of the Role of the Proposed VMpo Nucleus in Pain
... nervous system nuclei is usually based on cytoarchitecture, rather than on fiber architecture, although the patterns of connections of a nucleus are obviously important. A major problem is that it is unclear to what extent the calbindin-positive axons in this case terminate in the proposed nucleus a ...
... nervous system nuclei is usually based on cytoarchitecture, rather than on fiber architecture, although the patterns of connections of a nucleus are obviously important. A major problem is that it is unclear to what extent the calbindin-positive axons in this case terminate in the proposed nucleus a ...
self-organising map
... •The model of Willshaw & von der Malsburg was proposed as an effort to explain the retinotopic mapping from the retina to the visual cortex. •Two layers of neurons with each input neuron fully connected to the output neurons layer. •The output neurons have connections of two types among them: •Short ...
... •The model of Willshaw & von der Malsburg was proposed as an effort to explain the retinotopic mapping from the retina to the visual cortex. •Two layers of neurons with each input neuron fully connected to the output neurons layer. •The output neurons have connections of two types among them: •Short ...
Computation with Spikes in a Winner-Take-All Network
... Sarpeshkar, Mahowald, Douglas, & Seung, 2000; Liu, 2000, 2002). In the past decade, spiking neuron models and their electronic counterparts have gained increasing interest. Spike-based networks capture the asynchronous and time-continuous computation inherent in biological nervous systems. Neuron mo ...
... Sarpeshkar, Mahowald, Douglas, & Seung, 2000; Liu, 2000, 2002). In the past decade, spiking neuron models and their electronic counterparts have gained increasing interest. Spike-based networks capture the asynchronous and time-continuous computation inherent in biological nervous systems. Neuron mo ...
Sensory Afferent Neurotransmission in Caudal Nucleus Tractus
... receptors are generally presynaptic and inhibit transmitter release by reducing calcium conductance and/or by increasing potassium conductance (Bowery, 1989; Nicoll et al, 1990). Both GABAA and GABA B binding are found in NTS (Van Giersbergen et al, 1992) and affect BP control. GABA micro-injection ...
... receptors are generally presynaptic and inhibit transmitter release by reducing calcium conductance and/or by increasing potassium conductance (Bowery, 1989; Nicoll et al, 1990). Both GABAA and GABA B binding are found in NTS (Van Giersbergen et al, 1992) and affect BP control. GABA micro-injection ...
TESIS DOCTORAL Dynamics and Synchronization in Neuronal Models
... Since many years scientists have been studying the nervous system and its constituent elements. One of the most notable advances in the description of the structural and functional units of the nervous system came from the Spanish physician Santiago Ramón y Cajal in the late 19th century with his ne ...
... Since many years scientists have been studying the nervous system and its constituent elements. One of the most notable advances in the description of the structural and functional units of the nervous system came from the Spanish physician Santiago Ramón y Cajal in the late 19th century with his ne ...
Luczak, 2015 - University of Lethbridge
... How long are the activity packets evoked by sensory stimuli? The duration of stimulus-evoked packets can be estimated as the period from response onset to the time at which most neurons cease their stimulusdriven activity. Although small changes in firing rate induced by stimuli can sometimes be fou ...
... How long are the activity packets evoked by sensory stimuli? The duration of stimulus-evoked packets can be estimated as the period from response onset to the time at which most neurons cease their stimulusdriven activity. Although small changes in firing rate induced by stimuli can sometimes be fou ...
- Columbia University Medical Center
... are also expressed by proprioceptive sensory neurons, raising the possibility that cadherins regulate additional steps in the development of sensory-motor circuits. Introduction Many hundreds of neuronal cell types are generated during the development of the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS)—a ...
... are also expressed by proprioceptive sensory neurons, raising the possibility that cadherins regulate additional steps in the development of sensory-motor circuits. Introduction Many hundreds of neuronal cell types are generated during the development of the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS)—a ...
Presence of vesicular glutamate transporter-2 in
... stimulatory effects have also been observed in other species (Estienne et al., 1989; Shahab et al., 1993). Some of the actions of glutamate on the somatotropic axis may also be exerted at the hypophysial level. Ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors are expressed by anterior pituitary cells ...
... stimulatory effects have also been observed in other species (Estienne et al., 1989; Shahab et al., 1993). Some of the actions of glutamate on the somatotropic axis may also be exerted at the hypophysial level. Ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors are expressed by anterior pituitary cells ...
Adaptation of Firing Rate and Spike
... The time courses of the rate increase and the rate decrease were calculated by fitting the initial 200 s of the firing rate histogram with a sum of rising and falling exponentials, obtaining time constants of 11 ⫾ 3 s (N ⫽ 8) and 105 ⫾ 20 s (N ⫽ 6; in the other two cells, the rate decrease was not o ...
... The time courses of the rate increase and the rate decrease were calculated by fitting the initial 200 s of the firing rate histogram with a sum of rising and falling exponentials, obtaining time constants of 11 ⫾ 3 s (N ⫽ 8) and 105 ⫾ 20 s (N ⫽ 6; in the other two cells, the rate decrease was not o ...
PDF
... In this Section we consider our simple mathematical model of axon growth (Li et al., 2007; Borisyuk et al., 2008). This model has been studied in detail and has been used here for generation of the connectome model of the whole spinal cord. For the convenience of the reader we include here a brief r ...
... In this Section we consider our simple mathematical model of axon growth (Li et al., 2007; Borisyuk et al., 2008). This model has been studied in detail and has been used here for generation of the connectome model of the whole spinal cord. For the convenience of the reader we include here a brief r ...
Fine-scale specificity of cortical networks depends on inhibitory cell
... receive input from different cortical layers. Neighboring neurons of the same type, however, tend to receive local input from the same cortical layers. Most recently, it has been found that even neighboring neurons of the same anatomical type can, nevertheless, receive input from different sources22 ...
... receive input from different cortical layers. Neighboring neurons of the same type, however, tend to receive local input from the same cortical layers. Most recently, it has been found that even neighboring neurons of the same anatomical type can, nevertheless, receive input from different sources22 ...
Auditory Cortical Neurons are Sensitive to Static and Continuously
... described a few years earlier by Rose and his colleagues ( 1966) for neurons in the inferior colliculus. The discharges of certain cortical cells responding to low-stimulus frequencies were shown to be a periodic function of ITD, and when this property was studied at several different frequencies an ...
... described a few years earlier by Rose and his colleagues ( 1966) for neurons in the inferior colliculus. The discharges of certain cortical cells responding to low-stimulus frequencies were shown to be a periodic function of ITD, and when this property was studied at several different frequencies an ...
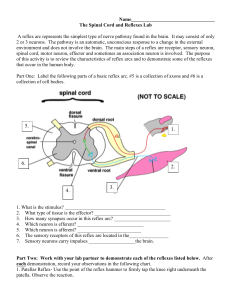
Name__________________________________ The Spinal Cord
... Name__________________________________ The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve ...
... Name__________________________________ The Spinal Cord and Reflexes Lab A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve ...