Music - Edutopia
... Chance Music Music in which composers deliberately leave parts of the composition and performance undetermined. (Aspects such as melody, rhythm, dynamics, timbre, and form are left wholly or partly to the discretion and creativity of the performer. It is also known as aleatory music.) Classroom Inst ...
... Chance Music Music in which composers deliberately leave parts of the composition and performance undetermined. (Aspects such as melody, rhythm, dynamics, timbre, and form are left wholly or partly to the discretion and creativity of the performer. It is also known as aleatory music.) Classroom Inst ...
Paul Ayick
... other have also become blurred. No doubt this world Music phenomena can be attributed to a globe made increasingly smaller by improved modes of both communication and travel. Regardless, in this fine article Mr. Nketia illustrates specific ways that these cultural musical idioms might best be employ ...
... other have also become blurred. No doubt this world Music phenomena can be attributed to a globe made increasingly smaller by improved modes of both communication and travel. Regardless, in this fine article Mr. Nketia illustrates specific ways that these cultural musical idioms might best be employ ...
music terminology
... Double flat ( bb ): Lower the tone one full step Double sharp: ( ø ): Raise the tone one full step Dynamics: The level (amplitude) or loudness of sound Pianissimo (pp) - very soft Piano (p) - soft Mezzo piano (mp) - medium soft Mezzo forte (f) - medium loud Forte (f) - loud Fortissimo (ff) - very l ...
... Double flat ( bb ): Lower the tone one full step Double sharp: ( ø ): Raise the tone one full step Dynamics: The level (amplitude) or loudness of sound Pianissimo (pp) - very soft Piano (p) - soft Mezzo piano (mp) - medium soft Mezzo forte (f) - medium loud Forte (f) - loud Fortissimo (ff) - very l ...
Chapter 4 Weekly Questions: Total Points = 4 Last summer, an
... [0.25] 1. Using our number system in the context of this problem, what is the place value for the stem? [0.25] 2. Using our number system in the context of this problem, what is the place value for the leaves? [0.5] 3. In context, write an interpretation of row containing 7 (5 7). [1] 4a. State the ...
... [0.25] 1. Using our number system in the context of this problem, what is the place value for the stem? [0.25] 2. Using our number system in the context of this problem, what is the place value for the leaves? [0.5] 3. In context, write an interpretation of row containing 7 (5 7). [1] 4a. State the ...
Lesson one –basic parallege (Or sign
... Gregorios Protopsaltes, Chrysanthos, Metropolitan of Mardytos, and Chourmouzios the Archivist of the Great Church, who reformed the notation and devised this system of teaching say that the notes and their names should be memorized both forward and backward, and should flow from the lips like the ru ...
... Gregorios Protopsaltes, Chrysanthos, Metropolitan of Mardytos, and Chourmouzios the Archivist of the Great Church, who reformed the notation and devised this system of teaching say that the notes and their names should be memorized both forward and backward, and should flow from the lips like the ru ...
Neo-classicism - DMU
... Neo-classicism. A movement of style in the works of certain 20th-century composers, who, particularly during the period between the two world wars, revived the balanced forms and clearly perceptible thematic processes of earlier styles to replace what were, to them, the increasingly exaggerated gest ...
... Neo-classicism. A movement of style in the works of certain 20th-century composers, who, particularly during the period between the two world wars, revived the balanced forms and clearly perceptible thematic processes of earlier styles to replace what were, to them, the increasingly exaggerated gest ...
Name: Motina Barracks Course: Music 101 Report Summary A scale
... A scale is a group of eight note which is arrange in a particular order. Every Major scale has eight tones which is called an octave. The numbers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 are called degrees. While the musical alphabet is A B C D E FG and the first and eighth note have the same name for example (C D E F G A B ...
... A scale is a group of eight note which is arrange in a particular order. Every Major scale has eight tones which is called an octave. The numbers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 are called degrees. While the musical alphabet is A B C D E FG and the first and eighth note have the same name for example (C D E F G A B ...
Musical Terms - Rogers State University
... • System of organizing pitches • Give cohesion to a piece of music • Just a few are the major, minor, modal, and pentatonic scales. • In non-Western cultures, scales, patterns or even certain notes may associated with extra musical ideas from nature or religion. ...
... • System of organizing pitches • Give cohesion to a piece of music • Just a few are the major, minor, modal, and pentatonic scales. • In non-Western cultures, scales, patterns or even certain notes may associated with extra musical ideas from nature or religion. ...
expressionist - davenantperformingarts
... I can explain the context of Peripetie and the Expressionist movement? (Understanding – Grade C) I can analyse the music and give examples of where specific compositional techniques are used (Analysis – Grade A/B) ...
... I can explain the context of Peripetie and the Expressionist movement? (Understanding – Grade C) I can analyse the music and give examples of where specific compositional techniques are used (Analysis – Grade A/B) ...
Vocabulary Guide - Heath Vocal Music
... Pitch - the highness of lowness of a tone Timbre - tone quality Interval - the distance between two notes in regards to pitch 2nd - step; neighbor notes 3rd - skip; from line to line or space to space Unison - all voice parts singing the same pitches ...
... Pitch - the highness of lowness of a tone Timbre - tone quality Interval - the distance between two notes in regards to pitch 2nd - step; neighbor notes 3rd - skip; from line to line or space to space Unison - all voice parts singing the same pitches ...
Harmony, Key, and Texture from 11/13/14 and
... • The interweaving of melody and harmony • Monophonic - one unaccompanied melody • Homophonic - one melody with some type of accompaniment (most common texture) • Polyphonic - two or more melodies at the same time.May be with or without accompaniment. This is "the crowning achievement of Western Mus ...
... • The interweaving of melody and harmony • Monophonic - one unaccompanied melody • Homophonic - one melody with some type of accompaniment (most common texture) • Polyphonic - two or more melodies at the same time.May be with or without accompaniment. This is "the crowning achievement of Western Mus ...
10:5 class notes
... 1 write out notes as a scale (start on any note) 2 find largest interval btw 2 adjacent notes 3 put the top note of this pair on the bottom of the set in case of a tie 4 compare all possible normal-ordered sets 5 from lowest to 2nd highest, 3rd highest, etc 6 the set that has the smallest interval b ...
... 1 write out notes as a scale (start on any note) 2 find largest interval btw 2 adjacent notes 3 put the top note of this pair on the bottom of the set in case of a tie 4 compare all possible normal-ordered sets 5 from lowest to 2nd highest, 3rd highest, etc 6 the set that has the smallest interval b ...
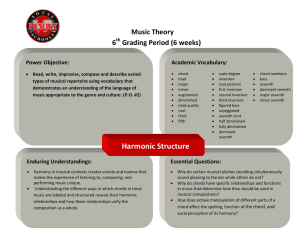
Harmonic Structure
... Harmony in musical contexts creates variety and nuance that makes the experience of listening to, composing, and performing music unique. Understanding the different ways in which chords in tonal music are labeled and structured reveals their harmonic relationships and how these relationships unify ...
... Harmony in musical contexts creates variety and nuance that makes the experience of listening to, composing, and performing music unique. Understanding the different ways in which chords in tonal music are labeled and structured reveals their harmonic relationships and how these relationships unify ...
The Elements of Music
... Fast vibrations produce high pitches, and slow vibrations produce low pitches. Musicians use a staff with various clefs to notate pitch. ...
... Fast vibrations produce high pitches, and slow vibrations produce low pitches. Musicians use a staff with various clefs to notate pitch. ...
non-serial criteria in the pitch organization of webern`s twelve
... Paradoxically, though logically, pantonality was a language that constantly overflowed its own boundaries. But, in spite of this contradiction, we can distinguish certain clear tendencies that are characteristic of this exceptional musical language: —Tension and concentration were created by constan ...
... Paradoxically, though logically, pantonality was a language that constantly overflowed its own boundaries. But, in spite of this contradiction, we can distinguish certain clear tendencies that are characteristic of this exceptional musical language: —Tension and concentration were created by constan ...
Score Reading Vocabulary Key signature: The sharps or flats that
... Key signature: The sharps or flats that are placed at the beginning of a staff to indicate the key of the music Time Signature: A symbol with 2 numbers, one on top of the other (like a fraction), that indicates how many beats are in a measure; the bottom number indicates the type of notes that recei ...
... Key signature: The sharps or flats that are placed at the beginning of a staff to indicate the key of the music Time Signature: A symbol with 2 numbers, one on top of the other (like a fraction), that indicates how many beats are in a measure; the bottom number indicates the type of notes that recei ...
Freshman Band Scale Checkoff/Final Exam Freshman Band Final
... Flat—lowers the pitch of a note ½ step Natural—cancels a flat or sharp Phrase-- a musical thought or sentence Ritardando (ritard, rit)—gradually slow the tempo Sharp—raises the pitch of a note ½ step Slur—curved line that connects two or more notes of different pitches Tie—curved line that connects ...
... Flat—lowers the pitch of a note ½ step Natural—cancels a flat or sharp Phrase-- a musical thought or sentence Ritardando (ritard, rit)—gradually slow the tempo Sharp—raises the pitch of a note ½ step Slur—curved line that connects two or more notes of different pitches Tie—curved line that connects ...
AS Music Technology - NW 14-19
... • Loud Sounds vs. Quiet Sounds – how does it affect the music…? • Italian terms are also used to describe dynamics: – Quiet ...
... • Loud Sounds vs. Quiet Sounds – how does it affect the music…? • Italian terms are also used to describe dynamics: – Quiet ...
lesson 2: musical alphabet, scale degrees and solfeggio
... DO (1) - RE (2) - MI (3) - FA (4) - SO (5) - LA (6) - TI (7) - DO (1) ...
... DO (1) - RE (2) - MI (3) - FA (4) - SO (5) - LA (6) - TI (7) - DO (1) ...
my summary of the major scale
... C, D, E, F, G, A, B, C A major scale begins with the letter C (lower), and also ends with the letter C (upper). Similarly, if the major scale begins with a F it also ends with a F. The major scales have numbers that represents each letter, these numbers are called degrees. The first scale is lower C ...
... C, D, E, F, G, A, B, C A major scale begins with the letter C (lower), and also ends with the letter C (upper). Similarly, if the major scale begins with a F it also ends with a F. The major scales have numbers that represents each letter, these numbers are called degrees. The first scale is lower C ...
What is Tonality - California State University, Los Angeles
... which is symmetrical in two respects: it divides the octave by equal intervals. and it is self-invertible.+ The symmetry inherent in the semitonal scale implies a new kind of musicd equivalence. whereas in the diatonic context thers is only intervallic equir alence, in the twelve-tone context there ...
... which is symmetrical in two respects: it divides the octave by equal intervals. and it is self-invertible.+ The symmetry inherent in the semitonal scale implies a new kind of musicd equivalence. whereas in the diatonic context thers is only intervallic equir alence, in the twelve-tone context there ...
Variation
... Add notes Add a harmony – drone, bass, chord 6. Retrograde – start at the end and play backwards 7. Add a counter-melody. ...
... Add notes Add a harmony – drone, bass, chord 6. Retrograde – start at the end and play backwards 7. Add a counter-melody. ...
most of the music is cast in sonata form or closely related forms
... During the Renaissance, the relaxation of the Church’s political control over society meant that composers were allowed greater freedom to be influenced by art, classical mythology and even astronomy and mathematics. Music could be published and distributed for the first time. Most music written dur ...
... During the Renaissance, the relaxation of the Church’s political control over society meant that composers were allowed greater freedom to be influenced by art, classical mythology and even astronomy and mathematics. Music could be published and distributed for the first time. Most music written dur ...