A Non-Pythagorean Musical Scale Based on Logarithms
... positions corresponding to logarithmic pitches marked on the fingerboards. Specially-constructed flutes, xylophones and marimbas, specially-tuned harps, and other acoustic instruments might also be utilized in performances. Certainly the natural harmonics of each instrument will interfere to some de ...
... positions corresponding to logarithmic pitches marked on the fingerboards. Specially-constructed flutes, xylophones and marimbas, specially-tuned harps, and other acoustic instruments might also be utilized in performances. Certainly the natural harmonics of each instrument will interfere to some de ...
The Renaissance Period
... cultural activity as Europe began to rediscover and identify with its Greco-Roman heritage. The natural sciences (in particular astronomy) began advancing at a rapid pace, and some philosophers began to discuss secular humanism as a valid system. The discovery of the American continents by European ...
... cultural activity as Europe began to rediscover and identify with its Greco-Roman heritage. The natural sciences (in particular astronomy) began advancing at a rapid pace, and some philosophers began to discuss secular humanism as a valid system. The discovery of the American continents by European ...
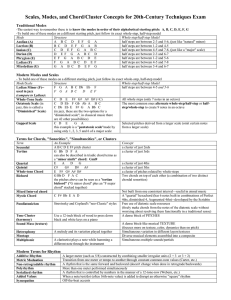
Instrumental Music Interm 2nd 9 weeks
... I can independently implement teacher provided practice strategies to improve my performance. ...
... I can independently implement teacher provided practice strategies to improve my performance. ...
About Diapason
... While celebrating the profound influence on my own work of both Harry Partch and John Cage, I should also mention some aspects of much of my music—and ...
... While celebrating the profound influence on my own work of both Harry Partch and John Cage, I should also mention some aspects of much of my music—and ...
The Music Alphabet
... Music’s Alphabet and the Diatonic Major Scale If music is a language then it should have an alphabet like all other languages. The musical alphabet is called the Chromatic Scale. All by itself the chromatic scale is difficult to do much with. This is because all the pitches are the same distance apa ...
... Music’s Alphabet and the Diatonic Major Scale If music is a language then it should have an alphabet like all other languages. The musical alphabet is called the Chromatic Scale. All by itself the chromatic scale is difficult to do much with. This is because all the pitches are the same distance apa ...
Chapter 1: The Basics Microtonal Notation
... An octave division of theoretically equal steps which, in performance on acoustic instruments, will undergo many small inflections from the theoretical pitch depending on context. ...
... An octave division of theoretically equal steps which, in performance on acoustic instruments, will undergo many small inflections from the theoretical pitch depending on context. ...
Document
... • Contain seven pitches • The eighth note of the scale (octave) repeats the starting pitch • Examples: major scales, minor scales, church modes ...
... • Contain seven pitches • The eighth note of the scale (octave) repeats the starting pitch • Examples: major scales, minor scales, church modes ...
Mr Allen`s Final Review
... -------------------------------Chromatic Scale – Moving by ½ steps. Please know your chromatic fingers, two octaves extra credit! ...
... -------------------------------Chromatic Scale – Moving by ½ steps. Please know your chromatic fingers, two octaves extra credit! ...
Grade 9 Music Exam Review
... 2. variety and excitement added by repeating the melody up the octave which is the only thing that gives the piece a wide range. 1. Dramatic intro with long notes with ...
... 2. variety and excitement added by repeating the melody up the octave which is the only thing that gives the piece a wide range. 1. Dramatic intro with long notes with ...
(Answers and Exam Piece).
... 2. variety and excitement added by repeating the melody up the octave which is the only thing that gives the piece a wide range. 1. Dramatic intro with long notes with ...
... 2. variety and excitement added by repeating the melody up the octave which is the only thing that gives the piece a wide range. 1. Dramatic intro with long notes with ...
Elements of Music - Harmony
... **If a melody centers around the note C, it is said to be in the Key of C. Keys can also be major or minor. Each key has a family of chords associated with it. Modulation is the process of changing from one key center (tonic) to another. Sometimes a piece of music will have several different key cen ...
... **If a melody centers around the note C, it is said to be in the Key of C. Keys can also be major or minor. Each key has a family of chords associated with it. Modulation is the process of changing from one key center (tonic) to another. Sometimes a piece of music will have several different key cen ...
Scales, Modes, and Chord/Cluster Concepts for 20th
... Free use of diatonic scale resources (freely make chords from the notes of the diatonic scale without worrying about resolving them functionally in a traditional sense) A dense block of PITCHES A dense block-like musical TEXTURE (focuses more on texture, color, dynamics than on pitch) Simultaneous v ...
... Free use of diatonic scale resources (freely make chords from the notes of the diatonic scale without worrying about resolving them functionally in a traditional sense) A dense block of PITCHES A dense block-like musical TEXTURE (focuses more on texture, color, dynamics than on pitch) Simultaneous v ...
WORLD OF THE STRING QUARTET Glossary
... also been used to indicate a comic or ironically comic composition, usually fast-moving and often one movement within a larger work.^ Franz Schubert (1797-1828) – Austrian composer who made seminal contributions in the areas of orchestral, chamber, and piano music, and most especially the German lie ...
... also been used to indicate a comic or ironically comic composition, usually fast-moving and often one movement within a larger work.^ Franz Schubert (1797-1828) – Austrian composer who made seminal contributions in the areas of orchestral, chamber, and piano music, and most especially the German lie ...
Week 3 Pitch Class
... Scales: differ from pitch class in that they are ordered Chromatic Scale: made up entirely of half steps Start on given pitch If no key signature, use sharps ascending and flats descending ...
... Scales: differ from pitch class in that they are ordered Chromatic Scale: made up entirely of half steps Start on given pitch If no key signature, use sharps ascending and flats descending ...
Document
... Burns, E. M., & Ward, W. D. (1978). Categorical perception - phenomenon or epiphenomenon: evidence from experiments in the perception of melodic musical intervals. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 63, 456-468. ...
... Burns, E. M., & Ward, W. D. (1978). Categorical perception - phenomenon or epiphenomenon: evidence from experiments in the perception of melodic musical intervals. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 63, 456-468. ...
Mathematics and Music (Mathematical World, Vol. 28)
... generate a 12-tone row in 12-tone music. Algebraic investigations are also central to Chapter 8; they culminate in the proof of the fact that Z is a principal ideal domain. It is noted in passing what prime numbers are and how one can find them with the sieve of Eratosthenes. It is then easy to desc ...
... generate a 12-tone row in 12-tone music. Algebraic investigations are also central to Chapter 8; they culminate in the proof of the fact that Z is a principal ideal domain. It is noted in passing what prime numbers are and how one can find them with the sieve of Eratosthenes. It is then easy to desc ...
Music Fundamentals – Quiz 1 Review Pitch and Intervals Identify the
... Identify the following pitches on the staff with their correct pitch class. Use the top space for those in the treble clef and the bottom space for those in the bass clef; the first example is completed for you. ...
... Identify the following pitches on the staff with their correct pitch class. Use the top space for those in the treble clef and the bottom space for those in the bass clef; the first example is completed for you. ...
Music Performance Assessments - IgniteArt
... are parallel to or partner with what they are/have experienced; pieces are “stories” i.e. about something Young composer uses their own emotional response to music to help predict how others will experience music; compositions are both about something but also express something ...
... are parallel to or partner with what they are/have experienced; pieces are “stories” i.e. about something Young composer uses their own emotional response to music to help predict how others will experience music; compositions are both about something but also express something ...
Der Kranke Mond - Pierrot Lunaire Schoenberg
... Background Information and Performance Circumstances The Romantic style of the 19th Century had always been about the heightened expression of emotions. In the early 20th Century, Austrian composers like Arnold Schoenberg and his follower Anton Berg sought to take this a stage further by describing ...
... Background Information and Performance Circumstances The Romantic style of the 19th Century had always been about the heightened expression of emotions. In the early 20th Century, Austrian composers like Arnold Schoenberg and his follower Anton Berg sought to take this a stage further by describing ...
Here are some important points about pitch: • Pitch is the “highness
... and F, and B and C are half-steps. In order to recreate the distinct sound of a major scale beginning and ending on any other note, we will need to introduce new pitches. This is because the location of the halfsteps (between the third and fourth notes, and between the seventh and eighth notes) is t ...
... and F, and B and C are half-steps. In order to recreate the distinct sound of a major scale beginning and ending on any other note, we will need to introduce new pitches. This is because the location of the halfsteps (between the third and fourth notes, and between the seventh and eighth notes) is t ...
Postmodern Concepts of Musical Time Jonathan D. Kramer
... counterpoint with one another, creating-at least for this particular postmodern listener-a richly multiple time sense. ...
... counterpoint with one another, creating-at least for this particular postmodern listener-a richly multiple time sense. ...
Music Glossary - Trenton Public Schools
... The retuning of a stringed instrument in order to play notes below the ordinary range of the instrument or to produce an ...
... The retuning of a stringed instrument in order to play notes below the ordinary range of the instrument or to produce an ...
essay - Dartmouth Math Home
... kind of static sound. Furthermore, fractal relationships in intensity are also manifested in rhythmic structures; the strongest 1/f relationships that have been found in music are found in frequencies of less than 1 Hz, that is, rhythmic frequencies (Loy). This suggests that musical downbeats have ...
... kind of static sound. Furthermore, fractal relationships in intensity are also manifested in rhythmic structures; the strongest 1/f relationships that have been found in music are found in frequencies of less than 1 Hz, that is, rhythmic frequencies (Loy). This suggests that musical downbeats have ...
melody and syncopation
... There is also another structure when we take into account the notes and pitches of every melody. It depends on the scale. A scale is a sequence of notes from which melodies and harmony can be derived. Scales are named according to the first note or degree. For example, in the C (do) major scale the ...
... There is also another structure when we take into account the notes and pitches of every melody. It depends on the scale. A scale is a sequence of notes from which melodies and harmony can be derived. Scales are named according to the first note or degree. For example, in the C (do) major scale the ...