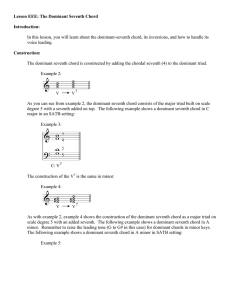
Lesson EEE: The Dominant Seventh Chord
... one of the voices.] Conclusion: In this lesson we have discussed the various formations of one of the most important harmonic progressions and cadential idioms in tonal music: V7 to I. The voice leading of these various configurations is determined primarily by the presence of tendency tones 7 and 4 ...
... one of the voices.] Conclusion: In this lesson we have discussed the various formations of one of the most important harmonic progressions and cadential idioms in tonal music: V7 to I. The voice leading of these various configurations is determined primarily by the presence of tendency tones 7 and 4 ...
playing giant steps with one scale
... As Mark Levine has pointed out (in The Jazz Piano Book and The Jazz Theory Book), this means that it’s possible to play the tune using just three pentatonic scales – F#, Bb and D major pentatonics, which fit all the chords from the II-V-Is in B, Eb and G respectively. To use this approach, all you h ...
... As Mark Levine has pointed out (in The Jazz Piano Book and The Jazz Theory Book), this means that it’s possible to play the tune using just three pentatonic scales – F#, Bb and D major pentatonics, which fit all the chords from the II-V-Is in B, Eb and G respectively. To use this approach, all you h ...
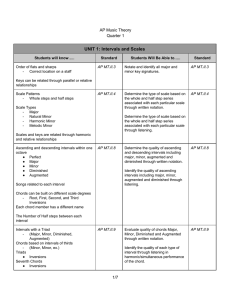
UNIT 1: Intervals and Scales
... dominant quality because this chord shares 2 notes with the V chord (double third/bass note and move all voices stepwise as much as possible) Second inversionOnly Primary chords are found in second inversion and they must only be used for the function of either: passing, cadential, or aux ...
... dominant quality because this chord shares 2 notes with the V chord (double third/bass note and move all voices stepwise as much as possible) Second inversionOnly Primary chords are found in second inversion and they must only be used for the function of either: passing, cadential, or aux ...
Handel: Chorus: `And the Glory of the Lord` from the oratorio
... Use of ornamented melodic parts Major/minor keys rather than modes. Diatonic (meaning notes/chords belonging to the key) chords (e.g. I, IV, V, II and VI) Basso continuo usually played by cello and supported by chords on the harpsichords/organ. Monophonic (a single melodic line with no accompaniment ...
... Use of ornamented melodic parts Major/minor keys rather than modes. Diatonic (meaning notes/chords belonging to the key) chords (e.g. I, IV, V, II and VI) Basso continuo usually played by cello and supported by chords on the harpsichords/organ. Monophonic (a single melodic line with no accompaniment ...
scottish - Gryffe Music
... melodic figures which are constantly repeated with very slight changes each time ...
... melodic figures which are constantly repeated with very slight changes each time ...
AoS2 – Harmony and Tonality
... ! The strongest not in any scale is the tonic (the note the scale starts and ends on) ! This has an effect on the other notes in the scale; in tonal music there is always the feeling tha ...
... ! The strongest not in any scale is the tonic (the note the scale starts and ends on) ! This has an effect on the other notes in the scale; in tonal music there is always the feeling tha ...
Quick Guide To Chord Charts The term harmonic rhythm refers to
... Quick Guide To Chord Charts The term harmonic rhythm refers to the sequence of chords (harmonies) that governs a song or other musical work, and to the timing (rhythm) of the changes from each chord to the next. It is relatively easy to devise a rhythm guitar accompaniment once the harmonic rhythm o ...
... Quick Guide To Chord Charts The term harmonic rhythm refers to the sequence of chords (harmonies) that governs a song or other musical work, and to the timing (rhythm) of the changes from each chord to the next. It is relatively easy to devise a rhythm guitar accompaniment once the harmonic rhythm o ...
Diatonic Harmony Primer - John Ely`s Steel Guitar Web
... that scale degree and carrying the name associated with that degree. So the tonic triad is built on degree 1, 3, and 5; the supertonic triad is build on degree 2, 4, and 6; and so on. The seven diatonic triads for the key of C are shown in the diagram (right) and are commonly labeled using the Roman ...
... that scale degree and carrying the name associated with that degree. So the tonic triad is built on degree 1, 3, and 5; the supertonic triad is build on degree 2, 4, and 6; and so on. The seven diatonic triads for the key of C are shown in the diagram (right) and are commonly labeled using the Roman ...
Music Vocabulary Terms
... minor scales: 3 for each note: Natural Minor Scale, Melodic Minor Scale, and Harmonic Minor Scale. Although Major and Minor scales are most common, there are many other types of scales. Intervals: The distance between two notes. Intervals can be determined up or down. Intervals of unison (same note) ...
... minor scales: 3 for each note: Natural Minor Scale, Melodic Minor Scale, and Harmonic Minor Scale. Although Major and Minor scales are most common, there are many other types of scales. Intervals: The distance between two notes. Intervals can be determined up or down. Intervals of unison (same note) ...
Tristan, Isolde
... chord from Wagner’s opera. In the pedalling indications, which are marked with a gradually upward-slanting line, it is intended that each player depress the pedal before playing a new chord, and then gradually release it over about 3 seconds whilst sustaining the written pitches with fingers, thus c ...
... chord from Wagner’s opera. In the pedalling indications, which are marked with a gradually upward-slanting line, it is intended that each player depress the pedal before playing a new chord, and then gradually release it over about 3 seconds whilst sustaining the written pitches with fingers, thus c ...
HIGH FREQUENCY VOCABULARY AND DEFINITIONS 5TH
... Interval of eight notes, either up or down A short repeated rhythmic or melodic pattern Music based on a five tone scale Very soft Soft The highest pitched instrument in the woodwind family , ; in 4/4 time, receives one beat Single-reed instrument in the woodwind family The notation of the entire ...
... Interval of eight notes, either up or down A short repeated rhythmic or melodic pattern Music based on a five tone scale Very soft Soft The highest pitched instrument in the woodwind family , ; in 4/4 time, receives one beat Single-reed instrument in the woodwind family The notation of the entire ...
music
... I can play an altered 12-bar chord sequence. I can improvise a 12 bar melody using the C blues scale. EXTENSION: I can improvise and play the chord sequence using both hands. I can locate and name the blue notes in the blues scale on C. I can accurately play the blues scale on C. I can compose a 12- ...
... I can play an altered 12-bar chord sequence. I can improvise a 12 bar melody using the C blues scale. EXTENSION: I can improvise and play the chord sequence using both hands. I can locate and name the blue notes in the blues scale on C. I can accurately play the blues scale on C. I can compose a 12- ...
Jazz Piano Quartal Voicing Workshop
... Ever since Bill Evans, Herbie Hancock, Chick Corea, and McCoy Tyner began to usher in the era of modern jazz piano, the left hand voicing underwent a remarkable transformation. Not only did the content (the actual chord voicings) change, but the context (the way that the voicings were used and the f ...
... Ever since Bill Evans, Herbie Hancock, Chick Corea, and McCoy Tyner began to usher in the era of modern jazz piano, the left hand voicing underwent a remarkable transformation. Not only did the content (the actual chord voicings) change, but the context (the way that the voicings were used and the f ...
Melody - Cengage Learning
... share of the time in, and return to their key center or tonic. The key center often changes. A change of key is called a modulation ...
... share of the time in, and return to their key center or tonic. The key center often changes. A change of key is called a modulation ...
Tonal Harmony Chapter 23 Enharmonic Spellings and Enharmonic
... Noticed that the analysis of the first chord in m41 is not a common chord (G:I = BbVI). This is because it is the cadential six-four chord in m.42 not the V7/IV = Ger+6, that tells us that a modulation is taking place. REMEMBER to always look for the common chord by backing up one chord from the cho ...
... Noticed that the analysis of the first chord in m41 is not a common chord (G:I = BbVI). This is because it is the cadential six-four chord in m.42 not the V7/IV = Ger+6, that tells us that a modulation is taking place. REMEMBER to always look for the common chord by backing up one chord from the cho ...
Chapter 10 Harmonic Progression
... tonality • The intervals formed by the roots of adjacent chords ...
... tonality • The intervals formed by the roots of adjacent chords ...
The Elements of Music
... – Musical = sounds that supply support and enrichment to the melody – Harmony in the sense of chord changes, ...
... – Musical = sounds that supply support and enrichment to the melody – Harmony in the sense of chord changes, ...
S3 Theory Matters Workbook
... Using the example, this would be C, D and E. So, C and E are a 3rd apart. Another example… What is the distance between G and C? Count G, A, B and C. There are 4 notes named so the distance between G and C is a 4th. The easiest way to do this is counting on your fingers, or using a diagram like the ...
... Using the example, this would be C, D and E. So, C and E are a 3rd apart. Another example… What is the distance between G and C? Count G, A, B and C. There are 4 notes named so the distance between G and C is a 4th. The easiest way to do this is counting on your fingers, or using a diagram like the ...
Music Theory IV Dr. Feezell Midterm Review Sheet
... 1. Name the three important characteristics of tonal harmony in the late nineteenth century discussed in class. (Answer: Increasing chromaticism, evaded cadences, and weakening of dominant harmony) 2. Define chromatic mediant (p. 313) and doubly chromatic mediant (p. 436). Hint: “doubly” is the one ...
... 1. Name the three important characteristics of tonal harmony in the late nineteenth century discussed in class. (Answer: Increasing chromaticism, evaded cadences, and weakening of dominant harmony) 2. Define chromatic mediant (p. 313) and doubly chromatic mediant (p. 436). Hint: “doubly” is the one ...
Introducing Musical STYLE newx
... • HOMOPHONIC (chordal) – one melody with accompaniment. The accompaniment is usually in chords, either block chords or broken chords. In ”block” chords, the notes are all played at the same time, then either held or repeated. Organs can hold repeated notes for an indefinite time, although on stringe ...
... • HOMOPHONIC (chordal) – one melody with accompaniment. The accompaniment is usually in chords, either block chords or broken chords. In ”block” chords, the notes are all played at the same time, then either held or repeated. Organs can hold repeated notes for an indefinite time, although on stringe ...
STRATFORD PUBLIC SCHOOLS Music Department – Music Theory
... Demonstrate a knowledge of all cadences aurally and through analysis of music. Write cadences in 3 and 4 part harmony. Analyze music in terms of phrases and periods aurally and in written form. Create diagrams of musical form based on phrases, periods, and cadences. Recognize a motive and how it is ...
... Demonstrate a knowledge of all cadences aurally and through analysis of music. Write cadences in 3 and 4 part harmony. Analyze music in terms of phrases and periods aurally and in written form. Create diagrams of musical form based on phrases, periods, and cadences. Recognize a motive and how it is ...
A GUIDE TO THE TERMINOLOGY OF GERMAN HARMONY
... The overtly dualistic elements of Riemannian harmony were among the first to fall out of favor, though earlier in this century their presence can still be strongly felt. For example, prewar German writers routinely used the term “dominant harmony” to refer not to a type of chord, V, but to a type of ...
... The overtly dualistic elements of Riemannian harmony were among the first to fall out of favor, though earlier in this century their presence can still be strongly felt. For example, prewar German writers routinely used the term “dominant harmony” to refer not to a type of chord, V, but to a type of ...
2 – First Species Counterpoint
... will also notice that octaves occur most often at the first and last notes. When an octave occurs in the interior of a phrase it should be approached and left in contrary motion by step as it is in both solutions in example 2-1. It will be no surprise to any music theory student that parallel fifths ...
... will also notice that octaves occur most often at the first and last notes. When an octave occurs in the interior of a phrase it should be approached and left in contrary motion by step as it is in both solutions in example 2-1. It will be no surprise to any music theory student that parallel fifths ...
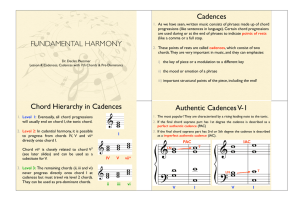
Cadences Chord Hierarchy in Cadences Authentic Cadences V
... chords. They are very important in music, and they can emphasise:! ...
... chords. They are very important in music, and they can emphasise:! ...
Chord (music)

A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of three or more notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. These need not actually be played together: arpeggios and broken chords may, for many practical and theoretical purposes, constitute chords. Chords and sequences of chords are frequently used in modern Western, West African and Oceanian music, whereas they are absent from the music of many other parts of the world.In tonal Western classical music, the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: further notes may be added to give tetrads such as seventh chords and added tone chords, as well as extended chords and tone clusters. Triads commonly found in the Western classical tradition are major, minor, augmented and diminished chords. The descriptions major, minor, augmented, and diminished are referred to collectively as chordal quality. Chords are also commonly classified by their root note—for instance, a C major triad consists of the pitch classes C, E, and G. Chords may also be classified by inversion, the way in which their pitches are vertically arranged.An ordered series of chords is called a chord progression. Although any chord may in principle be followed by any other chord, certain patterns of chords have been accepted as establishing key in common-practice harmony. To describe this, Western music theory has developed the practicing of numbering chords using Roman numerals which represent the number of diatonic steps up from the tonic note of the scale. Common ways of notating or representing chords in Western music other than conventional staff notation include Roman numerals, figured bass, macro symbols (sometimes used in modern musicology), and chord charts. Each of these systems is more likely to appear in certain contexts: figured bass notation was used prominently in notation of Baroque music, macro symbols are used in modern musicology, and chord charts are typically found in the lead sheets used in popular music.