ROOTS LEVEL - Youth Music Project
... Finger Numbers on both hands Identify all of the line and space note names on the Treble Clef Play treble clef notes in c position (C, D, E, F, G) Demonstrate understanding of measure, bar lines, double bar lines, repeat, staff, treble clef Understand and demonstrate ability to follow ...
... Finger Numbers on both hands Identify all of the line and space note names on the Treble Clef Play treble clef notes in c position (C, D, E, F, G) Demonstrate understanding of measure, bar lines, double bar lines, repeat, staff, treble clef Understand and demonstrate ability to follow ...
SEVENTH CHORDS Every triad can be extended by adding another
... Seventh chords will be of various qualities. The quality of the seventh chord is designated by the quality of the triad and the quality of the seventh: SEVENTH CHORD major (M) minor (m) dominant (Mm) [fully] diminished (o) half-diminished (o| ) augmented (A) minor - major (mM) ...
... Seventh chords will be of various qualities. The quality of the seventh chord is designated by the quality of the triad and the quality of the seventh: SEVENTH CHORD major (M) minor (m) dominant (Mm) [fully] diminished (o) half-diminished (o| ) augmented (A) minor - major (mM) ...
Slide 1
... Building a minor Dominant 7th Chord When you see a chord chart with symbols like Am7 or Dm7, these symbols are for a “dominant” 7th (= b7th). Any minor dominant chord is built with a b3 and b7 (relative to the root of the chord). An Am7 chord “fits” the key of C because every note in Am7 (the vi7 i ...
... Building a minor Dominant 7th Chord When you see a chord chart with symbols like Am7 or Dm7, these symbols are for a “dominant” 7th (= b7th). Any minor dominant chord is built with a b3 and b7 (relative to the root of the chord). An Am7 chord “fits” the key of C because every note in Am7 (the vi7 i ...
Siyahamba is in the key of F major. Notice that the key signature at
... either adding single finger chords or full chords. ...
... either adding single finger chords or full chords. ...
musical texture
... The word “mono” means one or single.Therefore we hear monophonic texture when a person sings alone without accompaniment or background music. So we can say that monophonic texture is heard when a single melodic line is performed without accompaniment. That single melody could be played or sung by on ...
... The word “mono” means one or single.Therefore we hear monophonic texture when a person sings alone without accompaniment or background music. So we can say that monophonic texture is heard when a single melodic line is performed without accompaniment. That single melody could be played or sung by on ...
Lecture 5
... When two or more melodies are played, sung, or sounding simultaneously. Another term associated with this is called polyphonic. This style of music makes for a more interesting listening experience, with greater depth of chord structures and plays more into dissonance listening. Yet we have gr ...
... When two or more melodies are played, sung, or sounding simultaneously. Another term associated with this is called polyphonic. This style of music makes for a more interesting listening experience, with greater depth of chord structures and plays more into dissonance listening. Yet we have gr ...
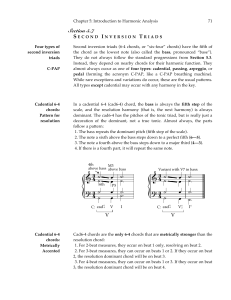
Second Inversion Triads
... Second inversion triads (6-4 chords, or “six-four” chords) have the fifth of the chord as the lowest note (also called the bass, pronounced “base”). They do not always follow the standard progressions from Section 5.3. Instead, they depend on nearby chords for their harmonic function. They almost al ...
... Second inversion triads (6-4 chords, or “six-four” chords) have the fifth of the chord as the lowest note (also called the bass, pronounced “base”). They do not always follow the standard progressions from Section 5.3. Instead, they depend on nearby chords for their harmonic function. They almost al ...
TERMS AND CONCEPTS OF 20TH C. MUSIC GENERAL: ostinato
... methods of establishing a tonal center -accent dynamics ostinato pedal point register reiteration / repetition return mixed-interval chords -- a chord that combines 2 or more interval types (with their inversions / compounds) to form a complex sonority neotonality -- music that is tonal but in which ...
... methods of establishing a tonal center -accent dynamics ostinato pedal point register reiteration / repetition return mixed-interval chords -- a chord that combines 2 or more interval types (with their inversions / compounds) to form a complex sonority neotonality -- music that is tonal but in which ...
Symbolic Music Representations
... The most common naming convention for intervals uses two attributes to describe them: quality and number. Quality Quality: perfect, major, minor, augmented, diminished. Number Number: unison, second, third, fifth, sixth, seventh, octave and is based on counting staff positions ...
... The most common naming convention for intervals uses two attributes to describe them: quality and number. Quality Quality: perfect, major, minor, augmented, diminished. Number Number: unison, second, third, fifth, sixth, seventh, octave and is based on counting staff positions ...
study guide - Junior High Band
... playing the notes that change from scale to scale. Example: When playing in F7 (F G A Bb C D Eb) and moving to Bb7 (Bb C D Eb F G Ab) emphasize the A in the F scale and the Ab in the Bb scale. All the other notes are the same in both scales. ...
... playing the notes that change from scale to scale. Example: When playing in F7 (F G A Bb C D Eb) and moving to Bb7 (Bb C D Eb F G Ab) emphasize the A in the F scale and the Ab in the Bb scale. All the other notes are the same in both scales. ...
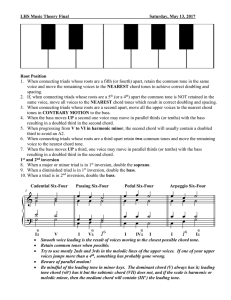
lhs music theory final exam review sheet
... 2. If, when connecting triads whose roots are a 5th (or a 4th) apart the common tone is NOT retained in the same voice, move all voices to the NEAREST chord tones which result in correct doubling and spacing. 3. When connecting triads whose roots are a second apart, move all the upper voices to the ...
... 2. If, when connecting triads whose roots are a 5th (or a 4th) apart the common tone is NOT retained in the same voice, move all voices to the NEAREST chord tones which result in correct doubling and spacing. 3. When connecting triads whose roots are a second apart, move all the upper voices to the ...
Document
... Time Signature – two numbers that appear at the beginning of a piece of music which indicate how many beats there are in a bar. Dorian Mode – a scale running from D to D on the keyboard using only white notes Jig – an Irish Dance ...
... Time Signature – two numbers that appear at the beginning of a piece of music which indicate how many beats there are in a bar. Dorian Mode – a scale running from D to D on the keyboard using only white notes Jig – an Irish Dance ...
non–chord tones - KIMBERLY CHOIRS
... • Non–chord tones (NCTs) (or non–harmonic tones) are notes that do not belong in a certain chord. • A step (ST) is equal to an interval of a generic second. • A skip (SK) is equal to an interval of a generic third or more. • A passing tone (PT) is approached by step and then continues by step in the ...
... • Non–chord tones (NCTs) (or non–harmonic tones) are notes that do not belong in a certain chord. • A step (ST) is equal to an interval of a generic second. • A skip (SK) is equal to an interval of a generic third or more. • A passing tone (PT) is approached by step and then continues by step in the ...
Tonal Harmony Chapter 3 Introduction to Triads and Seventh
... Interval between the root and the added note is some kind of 7th (major, minor, diminished) o Major seventh (M7) : major triad + major 7th o Major-minor seventh (Mn7) : major triad + minor 7th o Minor seventh (mm7) : minor triad + minor 7th o Half-diminished 7th (ᶲ7): diminished triad + minor 7th ...
... Interval between the root and the added note is some kind of 7th (major, minor, diminished) o Major seventh (M7) : major triad + major 7th o Major-minor seventh (Mn7) : major triad + minor 7th o Minor seventh (mm7) : minor triad + minor 7th o Half-diminished 7th (ᶲ7): diminished triad + minor 7th ...
Harmony Rules - Jeanie`s Online Music Studio
... A Plagal cadence is chords IV – I and has a finished sound bring the music to a close. Write down the available notes. • We work these exactly as for the perfect cadence except there is no leading note. * Write in the bass notes (the root of each chord). * Keep the note in common to both chords in t ...
... A Plagal cadence is chords IV – I and has a finished sound bring the music to a close. Write down the available notes. • We work these exactly as for the perfect cadence except there is no leading note. * Write in the bass notes (the root of each chord). * Keep the note in common to both chords in t ...
Music Fundamentals Primer Lesson 4
... B, and D. There are three possible arrangements of these three notes within a single octave (shown in step 2). The one arrangement in which all of the adjacent intervals are thirds is the most compact form, which is called “root position” (marked with the asterisk). Once root position is found, we ...
... B, and D. There are three possible arrangements of these three notes within a single octave (shown in step 2). The one arrangement in which all of the adjacent intervals are thirds is the most compact form, which is called “root position” (marked with the asterisk). Once root position is found, we ...
The Common-Tone Diminished Seventh Chord 7
... which is the same as one of the notes of the 7 chord. Although the ct 7 chord may embellish any triad or dominant seventh˜ chord, it most often progresses to I or V7 in major (minor examples are rare). The ct 7 chord may be spelled˜ in any manner as long as one of the notes be the same as the root o ...
... which is the same as one of the notes of the 7 chord. Although the ct 7 chord may embellish any triad or dominant seventh˜ chord, it most often progresses to I or V7 in major (minor examples are rare). The ct 7 chord may be spelled˜ in any manner as long as one of the notes be the same as the root o ...
Tonal Harmony Chapter 22 Augmented Sixth Chord
... Like N6, the +6 originated in the minor mode, but it was soon found to be equally useful in major keys When used in major keys, it is often preceded by mode mixture ...
... Like N6, the +6 originated in the minor mode, but it was soon found to be equally useful in major keys When used in major keys, it is often preceded by mode mixture ...
Musical Terms - Rogers State University
... even certain notes may associated with extra musical ideas from nature or religion. ...
... even certain notes may associated with extra musical ideas from nature or religion. ...
Popular Music Theory - The Academy Of Popular Music
... For example, in twelve-tone equal temperament* the notes C♯ and D♭ are enharmonic (or enharmonically equivalent) notes. Namely, they are the same key on a keyboard (see below), and thus they are identical in pitch, although they have different names and different roles in harmony and chord progressi ...
... For example, in twelve-tone equal temperament* the notes C♯ and D♭ are enharmonic (or enharmonically equivalent) notes. Namely, they are the same key on a keyboard (see below), and thus they are identical in pitch, although they have different names and different roles in harmony and chord progressi ...
Music 11, 7/24/06 Fundamental of harmony Melodies are often built
... melody as an “outline” that fills in the space of the triad. For example, a melody C-D-EF-G might imply a C-major triad by the way it visits all its members. Some notes, though, do not fit into the triad this example highlights. These are “non-chord tones,” but so long as they are not accentuated, t ...
... melody as an “outline” that fills in the space of the triad. For example, a melody C-D-EF-G might imply a C-major triad by the way it visits all its members. Some notes, though, do not fit into the triad this example highlights. These are “non-chord tones,” but so long as they are not accentuated, t ...
• Melody = a succession of pitches at specific durations that begins
... a 'piece' = a musical composition which is played on instruments. ...
... a 'piece' = a musical composition which is played on instruments. ...
Tonal Harmony Chapter 15 Other Diatonic Seventh Chords
... o In minor, when the root of the submediant seventh moves up by step to rasied 7th, the 6th must be raised to avoid an interval of +2. The chord that results when 6th is raised is a half diminished seventh: #viø7 ø7 #vi usually serves as a passing chord between two chords of dominant function (V o ...
... o In minor, when the root of the submediant seventh moves up by step to rasied 7th, the 6th must be raised to avoid an interval of +2. The chord that results when 6th is raised is a half diminished seventh: #viø7 ø7 #vi usually serves as a passing chord between two chords of dominant function (V o ...
Other diatonic 7th chords
... The IV7 can be a major seventh chord (in major) and minor seventh chord (in minor) and rarely a majorminor seventh chord in the melodic minor mode. Like its triad version, the IV7 usually goes to V or viio6, and may first pass through ii(7) or I/i6/4 VI7 The VI7 can be a minor seventh chord (in majo ...
... The IV7 can be a major seventh chord (in major) and minor seventh chord (in minor) and rarely a majorminor seventh chord in the melodic minor mode. Like its triad version, the IV7 usually goes to V or viio6, and may first pass through ii(7) or I/i6/4 VI7 The VI7 can be a minor seventh chord (in majo ...
Chord (music)

A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of three or more notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. These need not actually be played together: arpeggios and broken chords may, for many practical and theoretical purposes, constitute chords. Chords and sequences of chords are frequently used in modern Western, West African and Oceanian music, whereas they are absent from the music of many other parts of the world.In tonal Western classical music, the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: further notes may be added to give tetrads such as seventh chords and added tone chords, as well as extended chords and tone clusters. Triads commonly found in the Western classical tradition are major, minor, augmented and diminished chords. The descriptions major, minor, augmented, and diminished are referred to collectively as chordal quality. Chords are also commonly classified by their root note—for instance, a C major triad consists of the pitch classes C, E, and G. Chords may also be classified by inversion, the way in which their pitches are vertically arranged.An ordered series of chords is called a chord progression. Although any chord may in principle be followed by any other chord, certain patterns of chords have been accepted as establishing key in common-practice harmony. To describe this, Western music theory has developed the practicing of numbering chords using Roman numerals which represent the number of diatonic steps up from the tonic note of the scale. Common ways of notating or representing chords in Western music other than conventional staff notation include Roman numerals, figured bass, macro symbols (sometimes used in modern musicology), and chord charts. Each of these systems is more likely to appear in certain contexts: figured bass notation was used prominently in notation of Baroque music, macro symbols are used in modern musicology, and chord charts are typically found in the lead sheets used in popular music.