cadences - UT School of Music
... • Either or both of the above two rules are broken. • The progression could involve an inversion of the V chord, and inversion of the I chord, or both chords in inversion. • The progression could also be a leading tone chord to tonic (viio-I); this progression will always be an imperfect authentic s ...
... • Either or both of the above two rules are broken. • The progression could involve an inversion of the V chord, and inversion of the I chord, or both chords in inversion. • The progression could also be a leading tone chord to tonic (viio-I); this progression will always be an imperfect authentic s ...
Theory Intro
... Ê Tonic triad (I) is made of scale degrees 1-3-5 Ê Subdominant triad (IV) is made of scale degrees 4-6-1 ...
... Ê Tonic triad (I) is made of scale degrees 1-3-5 Ê Subdominant triad (IV) is made of scale degrees 4-6-1 ...
The Augmented Sixth Chord
... The augmented sixth chord was born in the Baroque period but occurs with greater frequency in the Romantic period. The aug. sixth chord may be understood as being derived from chromatic alterations of the iiº7 or iv7 chords. They do not function as subdominants, however, but function as predominants ...
... The augmented sixth chord was born in the Baroque period but occurs with greater frequency in the Romantic period. The aug. sixth chord may be understood as being derived from chromatic alterations of the iiº7 or iv7 chords. They do not function as subdominants, however, but function as predominants ...
Study Sheet for Keyboards Resource on the wiki
... in a measure (can be any #) and what types of notes get one beat (can only be half notes (2), quarter notes (4), eighths (8), sixteenths (16) and higher multiples of 16. The most common time signature is 4/4, or common time. Know symbols for eighth, quarter, and half rests. Scales and Key Signatures ...
... in a measure (can be any #) and what types of notes get one beat (can only be half notes (2), quarter notes (4), eighths (8), sixteenths (16) and higher multiples of 16. The most common time signature is 4/4, or common time. Know symbols for eighth, quarter, and half rests. Scales and Key Signatures ...
You Can Get It If You Really Want (p
... Song is in Db major throughout (but see Instrumental below) Relies almost exclusively on primary chords I IV & V(7) except for:o 9th bar of the Verses, e.g. b.22 – chord iii (Fm) o E major chord in the Instrumental (bs.37 and 41) o Chord sequence in bars 39 and 43 which end each 4-bar phrase with ha ...
... Song is in Db major throughout (but see Instrumental below) Relies almost exclusively on primary chords I IV & V(7) except for:o 9th bar of the Verses, e.g. b.22 – chord iii (Fm) o E major chord in the Instrumental (bs.37 and 41) o Chord sequence in bars 39 and 43 which end each 4-bar phrase with ha ...
Music Appreciation Class Fall 2014 Chapter 1
... Provides the basic harmonic and melodic material for a given piece of music. A selection of pitches within the interval of an octave. Major scales (diatonic) pattern: WWhWWWh in steps. Tonic- the home key, original note. Semitone- a half-step (ex. Bb to B, one note to the next on a piano) Also calle ...
... Provides the basic harmonic and melodic material for a given piece of music. A selection of pitches within the interval of an octave. Major scales (diatonic) pattern: WWhWWWh in steps. Tonic- the home key, original note. Semitone- a half-step (ex. Bb to B, one note to the next on a piano) Also calle ...
Chromaticism I
... on a chord by chord basis) reinforce, or are reducible to, the structural norms of a single diatonic system. However, it is possible to create harmonic units that are built out of scale-degree representatives from multiple modes. Just as the harmonic minor scale is called artificial because it is no ...
... on a chord by chord basis) reinforce, or are reducible to, the structural norms of a single diatonic system. However, it is possible to create harmonic units that are built out of scale-degree representatives from multiple modes. Just as the harmonic minor scale is called artificial because it is no ...
level 11 - Hlubek Piano Studio
... a cappella: unaccompanied trill: alternation of two notes a second apart supertonic: second degree of the scale submediant: sixth degree of the scale deceptive cadence: a cadence consisting of V-vi chordal progression half cadence: a cadence consisting of the chord progression ii-V or I-V ...
... a cappella: unaccompanied trill: alternation of two notes a second apart supertonic: second degree of the scale submediant: sixth degree of the scale deceptive cadence: a cadence consisting of V-vi chordal progression half cadence: a cadence consisting of the chord progression ii-V or I-V ...
Block Class Revision 2015 Set A
... Perfect V-I – found at end or middle Plagal IV-I – found at end or middle Imperfect I – V - found in the middle – never at end. ii – V- found in the middle – never at end. IV-V- found in the middle – never at end. Interrupted V-vi- found in the middle – never at end. Never repeat the same chord twic ...
... Perfect V-I – found at end or middle Plagal IV-I – found at end or middle Imperfect I – V - found in the middle – never at end. ii – V- found in the middle – never at end. IV-V- found in the middle – never at end. Interrupted V-vi- found in the middle – never at end. Never repeat the same chord twic ...
Required Graduate Music Theory Examinations
... examinations in aural skills and written theory BEFORE classes begin. The date and time for these examinations is listed in the “Orientation Schedule” published by the Division of Music each year and em ...
... examinations in aural skills and written theory BEFORE classes begin. The date and time for these examinations is listed in the “Orientation Schedule” published by the Division of Music each year and em ...
What is the harmony?
... The ways in which pitches relate are not random. There are consistent patterns used over and over in music regardless of style. The more pleasing a pattern sounds, the more often it gets used. Likewise, less pleasing patterns tend to be avoided. The more you learn about harmony, the less random cho ...
... The ways in which pitches relate are not random. There are consistent patterns used over and over in music regardless of style. The more pleasing a pattern sounds, the more often it gets used. Likewise, less pleasing patterns tend to be avoided. The more you learn about harmony, the less random cho ...
Don Gray - Arranging Barbershop
... 4. Basses: roots and fifths only; not below low-F, not above middle-C. ...
... 4. Basses: roots and fifths only; not below low-F, not above middle-C. ...
AP-Music-Theory-Study-Guide
... • Consonance- pleasing to the ear, major and more 3rds and 6ths and perfect 5ths and 8ves • Dissonant- unpleasant to the ear, all other intervals, except P4, which is only dissonant in bass • Diatonic- chords that contain only notes found in the scale • Chromatic- chords that contain notes not found ...
... • Consonance- pleasing to the ear, major and more 3rds and 6ths and perfect 5ths and 8ves • Dissonant- unpleasant to the ear, all other intervals, except P4, which is only dissonant in bass • Diatonic- chords that contain only notes found in the scale • Chromatic- chords that contain notes not found ...
Harmonic Progression - LearnMusicTheory.net
... A harmonic progression is a goal-directed succession of chords. Composers from the 1600s through the 1800s favored certain strong harmonic progressions. The strongest of all progressions involves the root of the chord moving down a fifth (or up a fourth), especially dominant (V) to tonic (I or i). ...
... A harmonic progression is a goal-directed succession of chords. Composers from the 1600s through the 1800s favored certain strong harmonic progressions. The strongest of all progressions involves the root of the chord moving down a fifth (or up a fourth), especially dominant (V) to tonic (I or i). ...
Scales, Modes, and Chord/Cluster Concepts for 20th
... All whole steps (only 7 notes in an octave) Whole-Tone Scale Octatonic Scale (in C D Eb F Gb Ab A B C The most common ones alternate whole-step/half-step or halfjazz, this is called a C Db Eb E F# G A Bb C step/whole-step to create 9 notes in an octave "Diminished" Scale) (in jazz, these are the two ...
... All whole steps (only 7 notes in an octave) Whole-Tone Scale Octatonic Scale (in C D Eb F Gb Ab A B C The most common ones alternate whole-step/half-step or halfjazz, this is called a C Db Eb E F# G A Bb C step/whole-step to create 9 notes in an octave "Diminished" Scale) (in jazz, these are the two ...
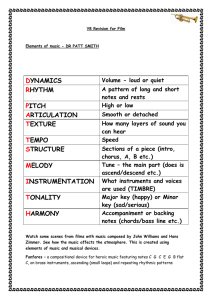
dynamics rhythm pitch articulation texture tempo
... Fanfares – a compositional device for heroic music featuring notes C G C E G B flat C, on brass instruments, ascending (small leaps) and repeating rhythmic patterns ...
... Fanfares – a compositional device for heroic music featuring notes C G C E G B flat C, on brass instruments, ascending (small leaps) and repeating rhythmic patterns ...
Concepts for the Music Theory Sections of the Graduate Preliminary
... tonic (diatonic triad built on scale step 1) supertonic (diatonic triad built on scale step 2) mediant (diatonic triad built on scale step 3) subdominant (diatonic triad built on scale step 4) dominant (diatonic triad built on scale step 5) submediant (diatonic triad built on scale step 6) leading t ...
... tonic (diatonic triad built on scale step 1) supertonic (diatonic triad built on scale step 2) mediant (diatonic triad built on scale step 3) subdominant (diatonic triad built on scale step 4) dominant (diatonic triad built on scale step 5) submediant (diatonic triad built on scale step 6) leading t ...
Power Point presentation: basics of music
... • Contains main musical ideas of piece – Motive = short, distinct figure – Riff = motive with a distinct rhythm that repeats throughout piece ...
... • Contains main musical ideas of piece – Motive = short, distinct figure – Riff = motive with a distinct rhythm that repeats throughout piece ...
Milhaud Describes Polytonality
... us to study the possibility of superimposing several keys sounded simultaneously. Contrapuntal writing also contributes to this study. The day when canons were admitted at intervals other than the octave marked the birth of the principle of polytonality. This type of counterpoint consists in combini ...
... us to study the possibility of superimposing several keys sounded simultaneously. Contrapuntal writing also contributes to this study. The day when canons were admitted at intervals other than the octave marked the birth of the principle of polytonality. This type of counterpoint consists in combini ...
Elements of Music - Harmony
... HARMONY Harmony is created when two or more notes (pitches) sound at the same time. Another way to think of it is the combination of a melody and its accompaniment. Harmony is often thought of as the art of combining pitches into chords (several notes played simultaneously as a “block”). In this way ...
... HARMONY Harmony is created when two or more notes (pitches) sound at the same time. Another way to think of it is the combination of a melody and its accompaniment. Harmony is often thought of as the art of combining pitches into chords (several notes played simultaneously as a “block”). In this way ...
Blues Chords and Scales in E Minor (G Major)
... Blues Chords and Scales in E Minor (G Major) The blues is a very influential style of music. It is the principal inspiration for what eventually became rock music. The basic blues chord progression is based on a repeated 12 bar pattern. This is called the 12-Bar Blues. The diagram below illustrating ...
... Blues Chords and Scales in E Minor (G Major) The blues is a very influential style of music. It is the principal inspiration for what eventually became rock music. The basic blues chord progression is based on a repeated 12 bar pattern. This is called the 12-Bar Blues. The diagram below illustrating ...
Chords, Keys, and Scales - What are they, and
... semitones are found between the 2nd and 3rd notes (B and C) and the 5th and 6th notes (E and F). This pattern gives a different sound/flavour, which we call minor. When we build a snowman chord on A with no black keys we have the A minor triad (A C E). It has a very different sound from a major tria ...
... semitones are found between the 2nd and 3rd notes (B and C) and the 5th and 6th notes (E and F). This pattern gives a different sound/flavour, which we call minor. When we build a snowman chord on A with no black keys we have the A minor triad (A C E). It has a very different sound from a major tria ...
11ths and 13ths - Scored Changes
... Note that this same chord can be found written differently. C11 automatically implies that the major 3rd is omitted. The third symbol (in the second bar) shows that the same chord can be thought of as being a minor 7th on a pedal note a perfect fifth below. This is often easier for a piano player to ...
... Note that this same chord can be found written differently. C11 automatically implies that the major 3rd is omitted. The third symbol (in the second bar) shows that the same chord can be thought of as being a minor 7th on a pedal note a perfect fifth below. This is often easier for a piano player to ...
Summary of Tonal Harmony - Leon Couch`s Course Listings
... 1. All the rest of the non-chord tones are pt, nt, susp, with either the approach or the resolution disrupted. The only absolutely forbidden NCT is one with leaps on both sides of a dissonance; i.e., arpeggios must outline a chord. 2. The pedal point is considered dissonant by K&P while harmonies pr ...
... 1. All the rest of the non-chord tones are pt, nt, susp, with either the approach or the resolution disrupted. The only absolutely forbidden NCT is one with leaps on both sides of a dissonance; i.e., arpeggios must outline a chord. 2. The pedal point is considered dissonant by K&P while harmonies pr ...
Chord (music)

A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of three or more notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. These need not actually be played together: arpeggios and broken chords may, for many practical and theoretical purposes, constitute chords. Chords and sequences of chords are frequently used in modern Western, West African and Oceanian music, whereas they are absent from the music of many other parts of the world.In tonal Western classical music, the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: further notes may be added to give tetrads such as seventh chords and added tone chords, as well as extended chords and tone clusters. Triads commonly found in the Western classical tradition are major, minor, augmented and diminished chords. The descriptions major, minor, augmented, and diminished are referred to collectively as chordal quality. Chords are also commonly classified by their root note—for instance, a C major triad consists of the pitch classes C, E, and G. Chords may also be classified by inversion, the way in which their pitches are vertically arranged.An ordered series of chords is called a chord progression. Although any chord may in principle be followed by any other chord, certain patterns of chords have been accepted as establishing key in common-practice harmony. To describe this, Western music theory has developed the practicing of numbering chords using Roman numerals which represent the number of diatonic steps up from the tonic note of the scale. Common ways of notating or representing chords in Western music other than conventional staff notation include Roman numerals, figured bass, macro symbols (sometimes used in modern musicology), and chord charts. Each of these systems is more likely to appear in certain contexts: figured bass notation was used prominently in notation of Baroque music, macro symbols are used in modern musicology, and chord charts are typically found in the lead sheets used in popular music.