ap® music theory 2013 scoring guidelines
... II. Chord Symbols (8 points) A. Award 1 point for each chord symbol correct in both Roman and Arabic numerals. B. Award ½ point for each correct Roman numeral that has incorrect or missing Arabic numerals. C. Accept the correct Roman numeral regardless of its case. D. Accept “ii” (or “II”) as a corr ...
... II. Chord Symbols (8 points) A. Award 1 point for each chord symbol correct in both Roman and Arabic numerals. B. Award ½ point for each correct Roman numeral that has incorrect or missing Arabic numerals. C. Accept the correct Roman numeral regardless of its case. D. Accept “ii” (or “II”) as a corr ...
Night in Tunisia thoughts,
... 3) almost all the alterations the dim scale contains the chord tones of the dominant seventh chord, plus these alterations: b9, +9, +11, 13 So it makes sense to use over any dominant seventh with extensions, the notable exceptions being natural 9, and b13, which we have other scales to handle (maybe ...
... 3) almost all the alterations the dim scale contains the chord tones of the dominant seventh chord, plus these alterations: b9, +9, +11, 13 So it makes sense to use over any dominant seventh with extensions, the notable exceptions being natural 9, and b13, which we have other scales to handle (maybe ...
DCVLE - AP Central - The College Board
... • In a three- or four-part texture, a rising d5→P5 is acceptable ONLY in the progressions I V$ I6 and I vii°6 I6 (no deduction). • A rising d5→P5 in other progressions is unacceptable (1 point error). • The reverse, a rising P5→d5, is acceptable voice leading (no deduction). • Unequal fifths in eith ...
... • In a three- or four-part texture, a rising d5→P5 is acceptable ONLY in the progressions I V$ I6 and I vii°6 I6 (no deduction). • A rising d5→P5 in other progressions is unacceptable (1 point error). • The reverse, a rising P5→d5, is acceptable voice leading (no deduction). • Unequal fifths in eith ...
Music Theory in a Minute BILL CARLSON MUSIC INFORMATICS AND COMPUTING DR. CHUAN
... Relative Minor Scale Every Major Scale has a Relative Minor Scale It is the based on the Major 6th The Relative Minor will have the exact same notes/key as the Major Scale The Major Scale can be turned into the Parallel Minor flatting the 3rd, 6th & 7th pitches The Major and Relative Minor ...
... Relative Minor Scale Every Major Scale has a Relative Minor Scale It is the based on the Major 6th The Relative Minor will have the exact same notes/key as the Major Scale The Major Scale can be turned into the Parallel Minor flatting the 3rd, 6th & 7th pitches The Major and Relative Minor ...
Revision Pack for: MUSIC AS
... bass musical notation in which numerals and symbols (often accidentals) indicate called the antecedent, comes to a point of partial completeness; it is balanced by the intervals, chords, and non-chord tones that a musician playing harpsichord, organ, lute (or consequent, a phrase of the same length ...
... bass musical notation in which numerals and symbols (often accidentals) indicate called the antecedent, comes to a point of partial completeness; it is balanced by the intervals, chords, and non-chord tones that a musician playing harpsichord, organ, lute (or consequent, a phrase of the same length ...
01_front - Massey Research Online
... topics of scales, melody, voicings, harmony and rhythm are examined in separate chapters with over two hundred notated musical examples used to demonstrate the materials in their context. This thesis also seeks to explain the relationships between these elements and presents the material in a fonn a ...
... topics of scales, melody, voicings, harmony and rhythm are examined in separate chapters with over two hundred notated musical examples used to demonstrate the materials in their context. This thesis also seeks to explain the relationships between these elements and presents the material in a fonn a ...
chap3 hw Compute the Frequencies of the Notes of the C
... PROBLEM: We have seen that musical tones can be modeled mathematically by sinusoidal signals. If you read music or play the piano you are aware of the fact that the piano keyboard is divided into octaves, with the tones in each octave being twice the frequency of the corresponding tones in the next ...
... PROBLEM: We have seen that musical tones can be modeled mathematically by sinusoidal signals. If you read music or play the piano you are aware of the fact that the piano keyboard is divided into octaves, with the tones in each octave being twice the frequency of the corresponding tones in the next ...
Romantic and impressionist harmony
... mix chord of I with chord of VI . A special case is I withaltered I, also a mixed third chord or split−third chord with both major and minor third, usually separated by an octave or more. It can be seen as a form of bitonality, which combines chords from different keys. After some basic examples, tw ...
... mix chord of I with chord of VI . A special case is I withaltered I, also a mixed third chord or split−third chord with both major and minor third, usually separated by an octave or more. It can be seen as a form of bitonality, which combines chords from different keys. After some basic examples, tw ...
Stage 1: Desired Results Stage 2 : Assessment Evidence Stage 3
... A. Sight-‐singing (major and minor modes, treble and bass clefs, diatonic and chromatic melodies, simple and compound meters) B. Melodic dictation (major and minor modes, treble and bass clefs, diatonic and ...
... A. Sight-‐singing (major and minor modes, treble and bass clefs, diatonic and chromatic melodies, simple and compound meters) B. Melodic dictation (major and minor modes, treble and bass clefs, diatonic and ...
your name - Julianne Baird
... b. The resting place at the end of a phrase c . the melody that serves as the starting point for a more extended piece of music d. the repetition of a melodic pattern at a higher or lower pitch 14. Harmony refers to a. the way chords are constructed and how they follow each other b. living in peace ...
... b. The resting place at the end of a phrase c . the melody that serves as the starting point for a more extended piece of music d. the repetition of a melodic pattern at a higher or lower pitch 14. Harmony refers to a. the way chords are constructed and how they follow each other b. living in peace ...
1 - Julianne Baird
... b. The resting place at the end of a phrase c . the melody that serves as the starting point for a more extended piece of music d. the repetition of a melodic pattern at a higher or lower pitch 14. Harmony refers to a. the way chords are constructed and how they follow each other b. living in peace ...
... b. The resting place at the end of a phrase c . the melody that serves as the starting point for a more extended piece of music d. the repetition of a melodic pattern at a higher or lower pitch 14. Harmony refers to a. the way chords are constructed and how they follow each other b. living in peace ...
1 - Julianne Baird
... b. The resting place at the end of a phrase c . the melody that serves as the starting point for a more extended piece of music d. the repetition of a melodic pattern at a higher or lower pitch 14. Harmony refers to a. the way chords are constructed and how they follow each other b. living in peace ...
... b. The resting place at the end of a phrase c . the melody that serves as the starting point for a more extended piece of music d. the repetition of a melodic pattern at a higher or lower pitch 14. Harmony refers to a. the way chords are constructed and how they follow each other b. living in peace ...
Music Music Functions: Physical
... Underlining expected reaction of the audience- confirms viewer understanding of the scene. Deceiving audience as to what has actually happened- a conscious decision on the part of the director to “trick” the audience into perceiving the scene in an alternate way also known as “a red herring” ...
... Underlining expected reaction of the audience- confirms viewer understanding of the scene. Deceiving audience as to what has actually happened- a conscious decision on the part of the director to “trick” the audience into perceiving the scene in an alternate way also known as “a red herring” ...
Sample Responses Q6 - AP Central
... A. Award 2 points for acceptable voice leading between two correctly realized chords. NB: This includes the voice leading from the given chord to the second chord. B. Award only 1 point for voice leading between two correctly realized chords (as defined in I.A.) that features exactly one of the foll ...
... A. Award 2 points for acceptable voice leading between two correctly realized chords. NB: This includes the voice leading from the given chord to the second chord. B. Award only 1 point for voice leading between two correctly realized chords (as defined in I.A.) that features exactly one of the foll ...
Matt Pike Music 122 Final Paper Ravel – String Quartet in F Major
... use of diatonic methods. One of the ways this is accomplished is through a practice called “polytonality”. This refers to the use of more than one diatonic key simultaneously. At first glance, the harmony seems to be chromatic, or simply atonal, but upon inspection, two distinct keys are audible, an ...
... use of diatonic methods. One of the ways this is accomplished is through a practice called “polytonality”. This refers to the use of more than one diatonic key simultaneously. At first glance, the harmony seems to be chromatic, or simply atonal, but upon inspection, two distinct keys are audible, an ...
prelude
... same number of half and whole steps. a. true b. false [a] 20. The arrangement of half and whole steps is the same in both the major and minor scales. a. true b. false [b] 21. The tonic is the __________ note of a diatonic scale. a. first b. second c. fifth d. last [a] ...
... same number of half and whole steps. a. true b. false [a] 20. The arrangement of half and whole steps is the same in both the major and minor scales. a. true b. false [b] 21. The tonic is the __________ note of a diatonic scale. a. first b. second c. fifth d. last [a] ...
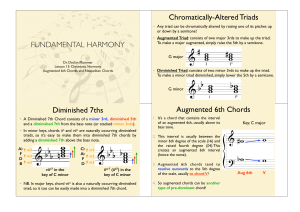
FUNDAMENTAL HARMONY Chromatically
... • In minor keys, chords iio and viio are naturally occurring diminished triads, so it’s easy to make them into diminished 7th chords by adding a diminished 7th above the bass note. ...
... • In minor keys, chords iio and viio are naturally occurring diminished triads, so it’s easy to make them into diminished 7th chords by adding a diminished 7th above the bass note. ...
HARMONIC ANALYSIS for Scale Selection and Chord Substitution BY CURT SHELLER
... The first chord, a Dm7 is in both the major and minor charts. In a major tonality it’s a II chord in the key of C, a III chord in the key of Bb and a VI chord in the key of F. In a minor tonality it’s a I chord in the key of D minor and a IV chord in the key of A minor. The second chord, G7 is found ...
... The first chord, a Dm7 is in both the major and minor charts. In a major tonality it’s a II chord in the key of C, a III chord in the key of Bb and a VI chord in the key of F. In a minor tonality it’s a I chord in the key of D minor and a IV chord in the key of A minor. The second chord, G7 is found ...
Chromaticism II: Tonicization/Modulation
... A possible terminological confusion arises with the use of Roman numerals, which can refer to specific, individual chords, or to regions within a key. Furthermore, the terms "tonal region" and "key area" are used interchangeably, and can be referred to by letter name (e.g., G), or Roman numeral (e.g ...
... A possible terminological confusion arises with the use of Roman numerals, which can refer to specific, individual chords, or to regions within a key. Furthermore, the terms "tonal region" and "key area" are used interchangeably, and can be referred to by letter name (e.g., G), or Roman numeral (e.g ...
lhs music theory homework 5b.389-446
... Write the alto and tenor voices and supply the Roman numeral analysis. The last soprano note of measure one should be E not F# as written and the C in the bass should have its stem down. (Be sure the type of Roman numeral reflects the quality of each triad.) ...
... Write the alto and tenor voices and supply the Roman numeral analysis. The last soprano note of measure one should be E not F# as written and the C in the bass should have its stem down. (Be sure the type of Roman numeral reflects the quality of each triad.) ...
Generating Guitar Scores from a MIDI Source
... Therefore, we do not describe this process in details. For more information on this topic, see [1]0. 3.2. Chord matching: The goal in this step is to select appropriate chords for the simple score using an appropriate sampling frequency. The main principle for the selection is to match the melody of ...
... Therefore, we do not describe this process in details. For more information on this topic, see [1]0. 3.2. Chord matching: The goal in this step is to select appropriate chords for the simple score using an appropriate sampling frequency. The main principle for the selection is to match the melody of ...
Review for Exam No.
... A texture in which a single voice takes over the melodic interest while the accompanying voices are subordinate is called: A. B. C. D. ...
... A texture in which a single voice takes over the melodic interest while the accompanying voices are subordinate is called: A. B. C. D. ...
20th Cent Definitions
... (chord) The simultaneous sounding of different notes Imitation One voice or instrument imitates another Improvisation Creation of music at the same time it is performed Interval The distance between two pitches Key A collection of tones that make up a scale such that they refer to a tonic, or keynot ...
... (chord) The simultaneous sounding of different notes Imitation One voice or instrument imitates another Improvisation Creation of music at the same time it is performed Interval The distance between two pitches Key A collection of tones that make up a scale such that they refer to a tonic, or keynot ...
Automatic Chord Detection - People Pages
... fundamentals. Double arrow in the center points to harmonics corresponding to pitches B5 and C6 . Double arrow on the right points to harmonics corresponding to pitches G6 and G]6 . ...
... fundamentals. Double arrow in the center points to harmonics corresponding to pitches B5 and C6 . Double arrow on the right points to harmonics corresponding to pitches G6 and G]6 . ...
Chapter 3 Melody and Harmony
... Most music centers around a home pitch ─ the key center or tonic Most pieces usually begin, spend a good share of the time in, and return to their key center or tonic. ...
... Most music centers around a home pitch ─ the key center or tonic Most pieces usually begin, spend a good share of the time in, and return to their key center or tonic. ...
Chord (music)

A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of three or more notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. These need not actually be played together: arpeggios and broken chords may, for many practical and theoretical purposes, constitute chords. Chords and sequences of chords are frequently used in modern Western, West African and Oceanian music, whereas they are absent from the music of many other parts of the world.In tonal Western classical music, the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: further notes may be added to give tetrads such as seventh chords and added tone chords, as well as extended chords and tone clusters. Triads commonly found in the Western classical tradition are major, minor, augmented and diminished chords. The descriptions major, minor, augmented, and diminished are referred to collectively as chordal quality. Chords are also commonly classified by their root note—for instance, a C major triad consists of the pitch classes C, E, and G. Chords may also be classified by inversion, the way in which their pitches are vertically arranged.An ordered series of chords is called a chord progression. Although any chord may in principle be followed by any other chord, certain patterns of chords have been accepted as establishing key in common-practice harmony. To describe this, Western music theory has developed the practicing of numbering chords using Roman numerals which represent the number of diatonic steps up from the tonic note of the scale. Common ways of notating or representing chords in Western music other than conventional staff notation include Roman numerals, figured bass, macro symbols (sometimes used in modern musicology), and chord charts. Each of these systems is more likely to appear in certain contexts: figured bass notation was used prominently in notation of Baroque music, macro symbols are used in modern musicology, and chord charts are typically found in the lead sheets used in popular music.